Abstract
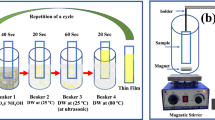
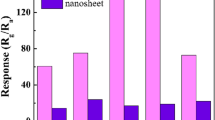
In this study, Zn(OH)F nanorods were synthesized via a microwave-assisted hydrothermal process and employed for NO2 gas sensor, for the first time. Without adding NH4F in the synthesis process, caltrop-like ZnO structure was formed. The characteristics of Zn(OH)F nanorods were characterized by using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and compared to those of caltrop-like ZnO. Additionally, the Zn(OH)F nanorods were further systematically studied by annealing them at 250, 350, and 450 °C to examine thermal stability. The Zn(OH)F nanorods start to transform after annealing at 350 °C. The sensor based on the Zn(OH)F nanorods showed very high response of 63.4 toward 1.3 ppm of NO2 gas at 100 °C, which is 8.6 times higher than the response of the sensor based on the caltrop-like ZnO. In addition, the sensor based on Zn(OH)F nanorods showed an excellent selectivity toward H2 (5 ppm), C2H5OH (10.6 ppm), NH3 (10.6 ppm), C6H5CH3 (36.2 ppm), and CH3COCH3 (2.8 ppm).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Chen et al., ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 3, 6440 (2020).
R. Souissi et al., Sens. Actuators B 319, 128280 (2020).
T-J. Hsueh, C-H. Peng and W-S. Chen, Sens. Actuators B 304, 127319 (2020).
W. Du et al., J. Alloys Compd. 834, 155209 (2020).
Z. Liu et al., Sens. Actuators B 308, 127650 (2020).
P. S. Shewale and K-S. Yun, J. Alloys Compd. 837, 155527 (2020).
S. Agarwal et al., Sens. Actuators B 292, 24 (2019).
H-Y. Lee, Y-C. Heish and C-T. Lee, J. Alloys Compd. 773, 950 (2019).
J. Wang et al., J. Hazard. Mater. 381, 120919 (2020).
S. Wan et al., Adv. Mater. 29, 1700286 (2017).
H. Yang et al., J. Hazard. Mater. 333, 250 (2017).
Q. Wang et al., J. Mater. Chem. A 7, 14180 (2019).
Q-L. Huang et al., Cryst. Growth Des. 8, 1412 (2008).
S. Nundy et al., Ceram. Int. 46, 5706 (2020).
J-K. Song et al., Nanoscale Res. Lett. 4, 1512 (2009).
L. Wu et al., Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 2897 (2009).
J. Jiang, Y. Li, S. Tan and Z. Huang, Mater. Lett. 64, 2191 (2010).
D. I. Son et al., Nat. Nanotechnol. 7, 465 (2012).
F. Xu, L Sun, M. Dai and Y. Lu, J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 15377 (2010).
S. Lepoutre et al., J. Mater. Chem. 20, 537 (2010).
P. Sharma et al., Nat. Mater. 2, 673 (2003).
S. Sepulveda-Guzman et al., Mater. Chem. Phys. 115, 172 (2009).
M. Wang, L. Jiang, E. J. Kim and S. H. Hahn, RSC Adv. 5, 87496 (2015).
J-H. Park and K-H. Kin, Sens. Actuators B 56, 50 (1999).
F-H. Zhang et al., J. Alloys Compd. 805, 180 (2019).
C. Zou, F. Liang and S. Xue, Appl. Surf. Sci. 353, 1061 (2015).
D. Barreca et al., Sens. Actuators B 160, 79 (2011).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Korea Basic Science Institute (KBSI) National Research Facilities & Equipment Center (NFEC) grant funded by the Korea government (Ministry of Education) (No. 2019R1A6C1030010). Also, J.-S. Park was partially supported by Project No. P0006858 of International Collaboration Program by KIAT and MOTIE in Rep. Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eom, Ty., Park, JS. & Lee, HJ. Zn(OH)F Nanorods for Highly Sensitive NO2 Gas Sensor Applications. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 77, 1055–1060 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.77.1055
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.77.1055