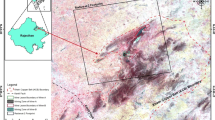
Abstract
Satellite data are making revolutionary changes in the field of archaeology, and nowadays they have been widely used by the scientific community for regular mapping and monitoring of cultural heritage sites. The development of synthetic aperture radar (SAR) sensors helps in monitoring the heritage site with higher accuracy. This study uses the Persistent Scatter Interferometric SAR (PSInSAR), which is an advanced technique of differential SAR interferometry to find the surface deformation of the Angkor Wat temple and its premises. Seven interferometric data from the Phased Array type L-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (PALSAR) of Advanced Land Observing Satellite-1 (ALOS-1) for the period 2006–2009 and ten interferometric data from the ALOS-2 PALSAR-2 for the period 2014–2018 have been used in this study to identify the deformation pattern. It is found from this study that the Angkor Wat temple and its outer walls are stable.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, M. Z., Chu, H.-J., & Burbey, T. J. (2020). Mapping and predicting subsidence from spatio-temporal regression models of groundwater-drawdown and subsidence observations. Hydrogeology Journal. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-020-02211-0.
APSARA. (2012). Angkor Charter. Siem Reap, Cambodia. https://www.unesco.org/new/fileadmin/MULTIMEDIA/FIELD/Phnom_Penh/pdf/angkor_charter_rev_jul_2014-en.pdf
Babu, A., & Kumar, S. (2019a). PSInSAR processing for volcanic ground deformation monitoring over fogo Island. In J. Martínez-Frías (Ed.s), Proceedings. Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute (MDPI AG). (Vol. 24, pp. 3:1–8).
Babu, A., & Kumar, S. (2019). SBAS interferometric analysis for volcanic eruption of Hawaii island. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 370, 31–50.
Baillie, B. (2006). Conservation of the sacred at Angkor Wat: Further reflections on living heritage. Conservation and Management of Archaeological Sites, 8(3), 123–131. https://doi.org/10.1179/175355206x265788.
Bartolino, J.R., & Cunningham W.L. (2003). Ground-Water Depletion Across the Nation. U.S Geological Survey Fact Sheet 103–03. https://pubs.usgs.gov/fs/fs-103-03/#pdf
Bell, J. W., Amelung, F., Ferretti, A., Bianchi, M., & Novali, F. (2008). Permanent scatterer InSAR reveals seasonal and long-term aquifer-system response to groundwater pumping and artificial recharge. Water Resources Research. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007WR006152.
Besoya, M., Govil, H., & Bhaumik, P. (2020). A review on surface deformation evaluation using multitemporal SAR interferometry techniques. Spatial Information Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41324-020-00344-8.
Bonforte, A., Guglielmino, F., Coltelli, M., Ferretti, A., & Puglisi, G. (2011). Structural assessment of mount Etna volcano from permanent scatterers analysis. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010GC003213.
Bürgmann, R., Rosen, P. A., & Fielding, E. J. (2000). Synthetic aperture radar interferometry to measure earth’s surface topography and its deformation. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 28(1), 169–209. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.169.
Carò, F., Basso, E., & Leona, M. (2016). The Earth sciences from the perspective of an art museum. Elements, 12(1), 33–38. https://doi.org/10.2113/gselements.12.1.33.
Carter, A., Heng, P., Stark, M., Chhay, R., & Evans, D. (2018). Urbanism and residential patterning in Angkor. Journal of Field Archaeology, 43(6), 492–506. https://doi.org/10.1080/00934690.2018.1503034.
Castagnetti, C., Cosentini, R. M., Lancellotta, R., & Capra, A. (2017). Geodetic monitoring and geotechnical analyses of subsidence induced settlements of historic structures. Structural Control and Health Monitoring. https://doi.org/10.1002/stc.2030.
Castillo, C. C., Carter, A., Kingwell-Banham, E., Zhuang, Y., Weisskopf, A., Chhay, R., et al. (2020). The Khmer did not live by rice alone: Archaeobotanical investigations at Angkor Wat and Ta Prohm. Archaeological Research in Asia. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ara.2020.100213.
Chapman, B., & Blom, R. G. (2013). Synthetic aperture radar, technology, past and future applications to archaeology. In D. C. Comer & M. J. Harrower (Eds.), Mapping archaeological landscapes from space (pp. 113–131). New York, NY: Springer.
Chase, A. F., Chase, D. Z., Weishampel, J. F., Drake, J. B., Shrestha, R. L., Slatton, K. C., et al. (2011). Airborne LiDAR, archaeology, and the ancient Maya landscape at Caracol. Belize. Journal of Archaeological Science, 38(2), 387–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jas.2010.09.018.
Chen, F., Guo, H., Ishwaran, N., Liu, J., Wang, X., Zhou, W., & Tang, P. (2019). Understanding the relationship between the water crisis and sustainability of the Angkor world heritage site. Remote Sensing of Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.111293.
Chen, F., Guo, H., Ma, P., Lin, H., Wang, C., Ishwaran, N., & Hang, P. (2017). Radar interferometry offers new insights into threats to the Angkor site. Science Advances, 3(3), e1601284. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1601284.
Chen, F, Jiang, A., & Ishwaran, N. (2014). Angkor site monitoring and evaluation by radar remote sensing. In Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering (Vol. 9260, pp. 1–9).
Chen, F., Lasaponara, R., & Masini, N. (2017). An overview of satellite synthetic aperture radar remote sensing in archaeology: From site detection to monitoring. Journal of Cultural Heritage, 23, 5–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.culher.2015.05.003.
Chen, G., Zhang, Y., Zeng, R., Yang, Z., Chen, X., Zhao, F., & Meng, X. (2018). Detection of land subsidence associated with land creation and rapid urbanization in the Chinese loess plateau using time series InSAR: A case study of Lanzhou new district. Remote Sensing. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020270.
Cœdès, G. (1906). La stèle de Ta-Prohm. Bulletin de l’Ecole française d’Extrême-Orient. Tome, 6(1), 44–86.
Comerci, V., Vittori, E., Cipolloni, C., Di Manna, P., Guerrieri, L., Nisio, S., et al. (2015). Geohazards monitoring in Roma from InSAR and in situ data: Outcomes of the PanGeo project. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 172(11), 2997–3028. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-015-1066-1.
Crosetto, M., Crippa, B., & Biescas, E. (2005). Early detection and in-depth analysis of deformation phenomena by radar interferometry. Engineering Geology, 79(1–2), 81–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2004.10.016.
Crosetto, M., Monserrat, O., Cuevas-González, M., Devanthéry, N., & Crippa, B. (2016). Persistent scatterer interferometry: A review. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 115, 78–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2015.10.011.
Cuenca-García, C., Risbøl, O., Bates, C. R., Stamnes, A. A., Skoglund, F., Ødegård, O., et al. (2020). Sensing archaeology in the north: The use of non-destructive geophysical and remote sensing methods in archaeology in Scandinavian and North Atlantic territories. Remote Sensing. https://doi.org/10.3390/RS12183102.
Erban, L. E., Gorelick, S. M., Zebker, H. A., & Fendorf, S. (2013). Release of arsenic to deep groundwater in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam, linked to pumping-induced land subsidence. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(34), 13751–13756. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1300503110.
Evans, D., & Fletcher, R. (2015). The landscape of Angkor Wat redefined. Antiquity, 89(348), 1402–1419.
Evans, D. H., Fletcher, R. J., Pottier, C., Chevance, J.-B., Soutif, D., Tan, B. S., et al. (2013). Uncovering archaeological landscapes at Angkor using lidar. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 110(31), 12595–12600. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1306539110.
Evans, D., Pottier, C., Fletcher, R., Hensley, S., Tapley, I., Milne, A., & Barbetti, M. (2007). A comprehensive archaeological map of the world’s largest preindustrial settlement complex at Angkor, Cambodia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104(36), 14277–14282. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0702525104.
Evans, D., & Traviglia, A. (2012). Uncovering Angkor: Integrated remote sensing applications in the archaeology of early Cambodia. Remote Sensing and Digital Image Processing, 16, 197–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-8801-7_9.
Ezquerro, P., Tomas, R., Bejar-Pizarro, M., Fernandez-Merodo, J. A., Guardiola-Albert, C., Staller, A., et al. (2020). Improving multi-technique monitoring using Sentinel-1 and Cosmo-SkyMed data and upgrading groundwater model capabilities. Science of the Total Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134757.
Falser, M. S. (2014). From a colonial reinvention to postcolonial heritage and a global commodity: performing and re-enacting Angkor Wat and the Royal Khmer Ballet. International Journal of Heritage Studies, 20(7–8), 702–723. https://doi.org/10.1080/13527258.2013.794746.
Fárová, K., Jelének, J., Kopačková-Strnadová, V., & Kycl, P. (2019). Comparing DInSAR and PSI techniques employed to Sentinel-1 data to monitor highway stability: A case study of a massive dobkovičky landslide, Czech Republic. Remote Sensing. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11222670.
Ferretti, A., Prati, C., & Rocca, F. (2001). Permanent Scatters in SAR Interferometry. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 39(1), 8–20. https://doi.org/10.1109/36.898661.
Filliozat, J. (1947). Henri Parmentier. L’art khmèr classique. Monuments du quadrant Nord-Est. Revue de l’histoire des religions, 227–228. https://www.persee.fr/doc/rhr_0035-1423_1947_num_134_1_5617
Fletcher, R., Evans, D., Pottier, C., & Rachna, C. (2015). Angkor Wat: an introduction. Antiquity, 89(348), 1388–1401.
Foroughnia, F., Nemati, S., Maghsoudi, Y., & Perissin, D. (2019). An iterative PS-InSAR method for the analysis of large spatio-temporal baseline data stacks for land subsidence estimation. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 74, 248–258.
Freeman, A., Hensley, S., & Moore, E. (1999). Analysis of radar images of Angkor, Cambodia. In IEEE 1999 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. IGARSS’99 (Cat. No.99CH36293) (Vol. 5, pp. 2572–2574). Hamburg: IEEE.
French, L. (1999). Hierarchies of value at Angkor Wat. Ethnos, 64(2), 170–191. https://doi.org/10.1080/00141844.1999.9981597.
Galloway, D. L., & Burbey, T. J. (2011). Review: Regional land subsidence accompanying groundwater extraction. Hydrogeology Journal, 19(8), 1459–1486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-011-0775-5.
Gonnuru, P., & Kumar, S. (2017). PsInSAR based land subsidence estimation of Burgan oil field using TerraSAR-X data. Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment, 9(2017), 17–25.
González, P. J., & Fernández, J. (2011). Error estimation in multitemporalInSAR deformation time series, with application to Lanzarote, Canary Islands. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JB008412.
Gumerman, G. J., & Lyons, T. R. (1971). Archeological methodology and remote sensing. Science, 172(3979), 126–132. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.172.3979.126.
Hall, C. M., Baird, T., James, M., & Ram, Y. (2016). Climate change and cultural heritage: Conservation and heritage tourism in the Anthropocene. Journal of Heritage Tourism, 11(1,SI), 10–24.
Hayhoe, R. (2019). The gift of Indian higher learning traditions to the global research university. Asia Pacific Journal of Education, 39(2,SI), 177–189.
Hooper, A., Zebker, H., Segall, P., & Kampes, B. (2004). A new method for measuring deformation on volcanoes and other natural terrains using InSAR persistent scatterers. Geophysical Research Letters, 31(23), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GL021737.
Hopewell, E. F. (1938). Correspondence. Journal of The Royal Central Asian Society, 25(4), 674–675. https://doi.org/10.1080/03068373808730883.
Jarus, O. (2018). Angkor Wat: History of Ancient Temple. Future US Inc. Retrieved 9 September, 2020, from https://www.livescience.com/23841-angkor-wat.html.
Joshi, V. (2018). Bas reliefs at Angkor Wat siem reap. Retrieved 23 October 2018, from, https://coloursonmypalette.blogspot.com/2018/08/bas-reliefs-at-angkor-wat-siem-reap.html.
Kak, S. (1999). The solar equation in Angkor Wat. Indian Journal of History of Science, 34(179), 117–126.
Lagios, E., Papadimitriou, P., Novali, F., Sakkas, V., Fumagalli, A., Vlachou, K., & Del Conte, S. (2012). Combined seismicity pattern analysis, DGPS and PSInSAR studies in the broader area of Cephalonia (Greece). Tectonophysics, 524–525, 43–58.
Lasaponara, R., & Masini, N. (2011). Satellite remote sensing in archaeology: Past, present and future perspectives. Journal of Archaeological Science, 38(9), 1995–2002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jas.2011.02.002.
Levin, N., Ali, S., Crandall, D., & Kark, S. (2019). World heritage in danger: Big data and remote sensing can help protect sites in conflict zones. Global Environmental Change, 55, 97–104.
Liu, X., Wang, Y., & Yan, S. (2018). Interferometric SAR time series analysis for ground subsidence of the abandoned mining area in North Peixian using sentinel-1A TOPS data. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 46(3), 451–461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-017-0708-4.
Locard, H. (2015). The myth of Angkor as an essential component of the khmer rouge utopia. In M. Falser (Ed.), Cultural heritage as civilizing mission: From decay to recovery (pp. 201–222). Cham: Springer.
Majumdar, S., Smith, R., Butler, J. J., Jr., & Lakshmi, V. (2020). Groundwater withdrawal prediction using integrated multi-temporal remote sensing datasets and machine learning. Water Resources Research. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020WR028059.
Mangiameli, M., Candiano, A., Fargione, G., Gennaro, A., & Mussumeci, G. (2020). Multispectral satellite imagery processing to recognize the archaeological features: The NW part of Mount Etna (Sicily, Italy). Mathematical Methods in the Applied Sciences, 43(13), 7640–7646. https://doi.org/10.1002/mma.5990.
Meisina, C., Zucca, F., Notti, D., Colombo, A., Cucchi, A., Savio, G., et al. (2008). Geological interpretation of PSInSAR data at regional scale. Sensors, 8(11), 7469–7492. https://doi.org/10.3390/s8117469.
Meskell, L. (2002). Negative heritage and past mastering in archaeology. Anthropological Quarterly, 75(3), 557–574. https://doi.org/10.1353/anq.2002.0050.
Milillo, P., Giardina, G., Perissin, D., Milillo, G., Coletta, A., & Terranova, C. (2019). Pre-collapse space geodetic observations of critical infrastructure: The Morandi bridge. Genoa: Remote Sensing. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121403.
Ministry of Tourism. (2018). Tourism statistics report year 2018. Phnom Penh, Cambodia. https://amchamcambodia.net/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/Year_2018.pdf
Monroe, J. W. (1995). Angkor Wat: A case study in the legal problems of international cultural resource management. The Journal of Arts Management, Law, and Society, 24(4), 277–286. https://doi.org/10.1080/10632921.1995.9941775.
Moore, E., Freeman, T., & Hensley, S. (2007). Spaceborne and airborne radar at Angkor: Introducing new technology to the ancient site. In J. Wiseman & F. El-Baz (Eds.), Remote sensing in archaeology (pp. 185–216). New York, NY: Springer.
Nicu, I. C. (2017). Natural hazards—a threat for immovable cultural heritage. A review. International Journal of Conservation Science, 8(3), 375–388.
Nishigaki, M., Takahashi, S., Takahashi, M., & Maruo, Y. (2013). Groundwater development and management in Siem Reap, Cambodia: Impacts of groundwater pumping on Angkor Wat. In Geotechnical Engineering for the Preservation of Monuments and Historic Sites - Proc. of the 2nd International Symp. on Geotechnical Engineering for the Preservation of Monuments and Historic Sites (pp. 595–601). Napoli, Italy.
Parcak, S. H. (2009). Satellite remote sensing for archaeology. Satellite Remote Sensing for Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203881460.
Peou, H., Natarajan, I., Tianhua, H., & Philippe, D. (2016). From conservation to sustainable development—a case study of Angkor world heritage site, Cambodia. Journal of Environmental Science and Engineering A, 5(3), 141–155.
Perissin, D. (2019a). Coregistration Parameters. SARPROZ Manual. Co-registration process in,one is using only orbits. Retrieved 24 October, 2020, from, https://sarproz.com/manual/coreg_param.html#:~:text=The
Perissin, D. (2019b). SARPROZ Software Manual. Retrieved 25 October, 2020, from, https://www.sarproz.com/software-manual/.
Priest, A. (1939). Indian Sculpture. The Metropolitan Museum of Art Bulletin, 34(6), 152–158. https://doi.org/10.2307/3256606.
Qin, Y., & Perissin, D. (2015). Monitoring ground subsidence in Hong Kong via spaceborne radar: Experiments and validation. Remote Sensing, 7(8), 10715–10736. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70810715.
Qiu, Z., Ma, Y., & Guo, X. (2016). Atmospheric phase screen correction in ground-based SAR with PS technique. SpringerPlus. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-3262-6.
Rasmussen, W. C., & Bradford, G. M. (1977). Ground-water resources of Cambodia. Washington DC: U.S. Government Printing Office.
Reeder-Myers, L. A. (2015). Cultural heritage at risk in the twenty-first century: A vulnerability assessment of coastal archaeological sites in the United States. The Journal of Island and Coastal Archaeology, 10(3), 436–445. https://doi.org/10.1080/15564894.2015.1008074.
Roberts, T. R. (2002). Fish scenes, symbolism, and kingship in the bas-reliefs of Angkor Wat and the Bayon. Natural History Bulletin of The Siam Society (NHBSS), 50(2), 135–193.
Rowland, B. (1964). The world’s image in indian architecture. Journal of the Royal Society of Arts, 112(5099), 795–809.
Si, Y., Chen, B., Gong, H., & Gao, M. (2018). Temporal and spatial evolution of land subsidence induced by groundwater exploitation and construction in the Eastern Chaoyang District, Beijing, China. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 46(10), 1657–1665. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-018-0821-z.
Siedel, H., Pfefferkorn, S., von Plehwe-Leisen, E., & Leisen, H. (2010). Sandstone weathering in tropical climate: Results of low-destructive investigations at the temple of Angkor Wat, Cambodia. Engineering Geology, 115(3), 182–192.
Smith, R., Knight, R., & Fendorf, S. (2018). Overpumping leads to California groundwater arsenic threat. Nature Communications, 9(1), 2089. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04475-3.
Smith, R. G., & Majumdar, S. (2020). Groundwater storage loss associated with land subsidence in Western United States mapped using machine learning. Water Resources Research. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019WR026621.
Sok, C. (2017). Angkor water crisis. The UNESCO Courier, 19–22. https://en.unesco.org/courier/2017-april-june/angkor-water-crisis
Solari, L., Ciampalini, A., Raspini, F., Bianchini, S., & Moretti, S. (2016). PSInSAR analysis in the pisa urban area (Italy): A case study of subsidence related to stratigraphical factors and urbanization. Remote Sensing, 8(2), 120.
Sonnemann, T. F., O’Reilly, D., Rachna, C., Fletcher, R., & Pottier, C. (2015). The buried ‘towers’ of Angkor Wat. Antiquity, 89(348), 1420–1438.
Sonnemann, T. F. (2011). Angkor Underground—Applying GPR to analyse the diachronic structure of a great urban complex. University of Sydney.; Department of Archaeology. Retrieved from https://hdl.handle.net/2123/8069
Sophearith, S. (2005). The life of the Rāmāyana in ancient Cambodia: A study of the political, religious and ethical roles of an epic tale in real time (I). Udaya, 6, 93–150.
Sophearith, S. (2006). The life of the Rāmāyana in ancient Cambodia: A study of the political, religious and ethical roles of an epic tale in real time (II). Udaya, 7, 45–72.
Sousa, J. J., Hooper, A. J., Hanssen, R. F., Bastos, L. C., & Ruiz, A. M. (2011). Persistent scattererInSAR: A comparison of methodologies based on a model of temporal deformation vs. spatial correlation selection criteria. Remote Sensing of Environment, 115(10), 2652–2663.
Stark, M. T., Evans, D., Rachna, C., Piphal, H., & Carter, A. (2015). Residential patterning at Angkor Wat. Antiquity, 89(348), 1439–1455.
Stencel, R., Gifford, F., & Morón, E. (1976). Astronomy and cosmology at Angkor Wat. Science, 193(4250), 281–287. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.193.4250.281.
Tapete, D., Cigna, F., & Donoghue, D. N. M. (2016). “Looting marks” in space-borne SAR imagery: Measuring rates of archaeological looting in Apamea (Syria) with TerraSAR-X Staring Spotlight. Remote Sensing of Environment, 178, 42–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2016.02.055.
Tu, J., Gu, D., Wu, Y., & Yi, D. (2012). Error modeling and analysis for InSAR spatial baseline determination of satellite formation flying. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2012, 140301. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/140301.
UNESCO World Heritage Centre. (2020). World Heritage List. UNESCO. Retrieved 12 October, 2020, from, https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/?&type=cultural.https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/?&type=cultural.
Vicari, A., Famiglietti, N. A., Colangelo, G., & Cecere, G. (2019). A comparison of multi temporal interferometry techniques for landslide susceptibility assessment in urban area: an example on stigliano (MT), a town of Southern of Italy. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, 10(1), 836–852. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2018.1549113.
Vilardo, G., Isaia, R., Ventura, G., De Martino, P., & Terranova, C. (2010). InSAR permanent scatterer analysis reveals fault re-activation during inflation and deflation episodes at CampiFlegrei caldera. Remote Sensing of Environment, 114(10), 2373–2383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2010.05.014.
Wager, J. (1995). Environmental planning for a world heritage site: Case study of Angkor, Cambodia. Journal of Environmental Planning and Management, 38(3), 419–434. https://doi.org/10.1080/09640569512959.
Waterton, E., & Smith, L. (2008). Heritage protection for the 21st century. Cultural Trends, 17(3), 197–203. https://doi.org/10.1080/09548960802362157.
World Heritage Committee. (1992). Convention concerning the protection of the world cultural and natural heritage. Santa Fe. https://whc.unesco.org/archive/1992/whc-92-conf002-12e.pdf
Yang, C.-H., & Soergel, U. (2018). Adaptive 4d Psi-based change detection. ISPRS Annals of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, IV–3, 245–250.
Yogesh, K. (2017). Historic Tamil Nadu temples fallinginto decay: Unesco report Chennai News–Times of India. The Times of India.
Zakšek, K., Oštir, K., & Kokalj, Z. (2011). Sky-view factor as a relief visualization technique. Remote Sensing, 3(2), 398–415. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs3020398.
Zhang, Y., Ling, F., Foody, G. M., Ge, Y., Boyd, D. S., Li, X., et al. (2019). Mapping annual forest cover by fusing PALSAR/PALSAR-2 and MODIS NDVI during 2007–2016. Remote Sensing of Environment, 224, 74–91.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their sincere gratitude to the SARPROZ software team for providing the license. The authors are thankful to the German Aerospace Center (DLR) Oberpfaffenhofen for providing TerraSAR-X/TanDEM-X data under the Project Id -NTI_POLI6635 on PolInSAR Tomography for above ground biomass estimation and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) for providing the L-band ALOS-2 PALSAR-2 datasets under the proposal number 1408 of RA4 with the title Hydrological parameter retrieval and glacier dynamics study with L-band SAR data. The authors are also grateful to the Alaska Satellite Facility (ASF) for providing ALOS-1 PALSAR-1 data through ASF Vertex Data Search.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SK contributed to conceptualization, data processing, formal analysis, manuscript preparation, supervision, methodology, satellite data selection, software, validation, writing—reviewing and editing. VKS contributed to data processing, formal analysis, manuscript preparation. AB was involved in data processing, visualization, investigation, reviewing and editing. PKT was involved in data curation. SA was involved in project administration.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Vignesh, S.K., Babu, A. et al. PSInSAR-Based Surface Deformation Mapping of Angkor Wat Cultural Heritage Site. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 49, 827–842 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-020-01257-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-020-01257-7