Abstract
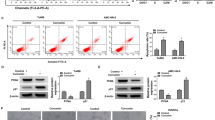
This study aimed to investigate the effect of Catharanthus roseus L. (C. roseus) leaf extract on the migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cell line and elucidate the molecular mechanisms of action. Effect of the extract on cell viability was evaluated by MTT (3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl2H-tetrazoliumbromide) assay. Anti-migratory and anti-invasive effects were evaluated using scratch and Transwell assays. Effect on the levels and activities of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 was determined using ELISA and gelatin zymography. Furthermore, changes in the expression of 84 genes commonly involved in cell motility were assessed by Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) and cell motility RT2 profiler PCR array. Gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analyses were performed using DAVID. Using STRING and Cytoscape software, hub genes were determined. The extract significantly (p < 0.001) inhibited the migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells at non-cytotoxic concentrations. The activities and levels of MMP-2 and MMP-9 were decreased in a dose-dependent manner following C. roseus exposure. At 4 µg/mL, the extract significantly downregulated the expression of 52 genes involved in extracellular matrix degradation, cytoskeleton reorganisation, focal adhesions and invadopodia formation. GO and KEGG pathway analysis revealed that the downregulated genes were significantly enriched in biological processes and pathways closely related to cell motility. Our findings showed that C. roseus inhibited the migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells through altering the expression of various motility-related genes. This study provided data about the potential of C. roseus phytochemicals as promising therapeutic agents against breast cancer metastasis, especially at gene level.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C. roseus :
-
Catharanthus roseus L.
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl2H-tetrazoliumbromide
- MMP-2:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-2
- MMP-9:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-9
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction
- GO:
-
Gene ontology
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- DAVID:
-
Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery
- STRING:
-
Search Tool for Retrieval of Interacting Genes / Proteins
- PPI:
-
Protein-protein interaction
- TNBC:
-
Triple-negative breast cancer
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- MIAs:
-
Monoterpenoid indole alkaloids
- HER-2:
-
Human epidermal growth factor receptor-2
References
Acevedo-Díaz A, Ortiz-Soto G, Suárez-Arroyo IJ, Zayas-Santiago A, Martínez Montemayor MM (2019) Ganoderma lucidum extract reduces the Motility of breast cancer cells mediated by the RAC–Lamellipodin axis. Nutrients 11:1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11051116
Ajuru MG, Ajuru G, Nmom FW, Worlu CW, Igoma PG (2019) Acute toxicity study and determination of median lethal dose of Catharanthus roseus in Wistar Albino rats. J Appl Sci 19:217–222. https://doi.org/10.3923/jas.2019.217.222
Al Dhaheri Y, Attoub S, Arafat K, AbuQamar S, Viallet J, Saleh A, Al Agha H, Eid A, Iratni R (2013) Anti-metastatic and anti-tumor growth effects of Origanum majorana on highly metastatic human breast cancer cells: inhibition of NFκB signaling and reduction of nitric oxide production. PLoS One 8:e68808. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0068808
Bates D, Eastman A (2017) Microtubule destabilising agents: far more than just antimitotic anticancer drugs. Br J Clin Pharmacol 83:255–268. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.13126
Bijman MN, van Nieuw Amerongen GP, Laurens N, van Hinsbergh VW, Boven E (2006) Microtubule-targeting agents inhibit angiogenesis at subtoxic concentrations, a process associated with inhibition of Rac1 and Cdc42 activity and changes in the endothelial cytoskeleton. Mol Cancer Ther 5:2348–2357. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0242
Chagas CM, Alisaraie L (2019) Metabolites of vinca alkaloid vinblastine: tubulin binding and activation of nausea-associated receptors. ACS Omega 4:9784–9799. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b00652
Chen L, Bi S, Hou J, Zhao Z, Wang C, Xie S (2019) Targeting p21-activated kinase 1 inhibits growth and metastasis via Raf1/MEK1/ERK signaling in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cell Commun Signal 17:31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-019-0343-5
Choudhari AS, Mandave PC, Deshpande M, Ranjekar P, Prakash O (2020) Phytochemicals in cancer treatment: from preclinical studies to clinical practice. Front Pharmacol 10:1614. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.01614
Denkert C, Liedtke C, Tutt A, von Minckwitz G (2017) Molecular alterations in triple-negative breast cancer—the road to new treatment strategies. Lancet 389:2430–2442. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32454-0
Di D, Chen L, Guo Y, Wang L, Wang H, Ju J (2018) Association of BCSC-1 and MMP-14 with human breast cancer. Oncol Lett 15:5020–5026. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.7972
Eckert MA, Yang J (2011) Targeting invadopodia to block breast cancer metastasis. Oncotarget 2:562–568. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.301
Eltayeb NM, Ng SY, Ismail Z, Salhimi SM (2016) Anti-invasive effect of Catharanthus roseus extract on highly metastatic human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells. J Teknol 78:35–40. https://doi.org/10.11113/jt.v78.9870
Fajardo AM, Browne T, Graff H, Kleier K, Neltner K, McCall C, Meyer B, Douglass L, Carter J (2015) Targeting PAK1 activity in breast cancer: Inhibition of cell growth, survival, motility, and signaling. Cancer Res 75:1024. https://doi.org/10.1158/15387445.AM20151024
Fields GB (2019) The rebirth of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors: moving beyond the dogma. Cells 8:984. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8090984
Fife CM, McCarroll JA, Kavallaris M (2014) Movers and shakers: cell cytoskeleton in cancer metastasis. Br J Pharmacol 171:5507–5523. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.12704
Fernández-Pérez F, Almagro L, Pedreño MA, Gomez Ros LV (2013) Synergistic and cytotoxic action of indole alkaloids produced from elicited cell cultures of Catharanthus roseus. Pharm Biol 51:304–310. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880209.2012.722646
Fu H, Wu R, Li Y, Zhang L, Tang X, Tu J, Zhou W, Wang J, Shou Q (2016) Safflower yellow prevents pulmonary metastasis of breast cancer by inhibiting tumor cell invadopodia. Am J Chin Med 44:1491–1506. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0192415X1650083X
Haga RB, Ridley AJ (2016) Rho GTPases: Regulation and roles in cancer cell biology. Small GTPases 7:207–221. https://doi.org/10.1080/21541248.2016.1232583
Harun S, Israf D, Tham C, Lam KW, Cheema MS, Md Hashim NF (2018) The molecular targets and anti-invasive effects of 2, 6-bis-(4-hydroxyl-3methoxybenzylidine) cyclohexanone or BHMC in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Molecules 23:865. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23040865
Hirokawa Y, Arnold M, Nakajima H, Zalcberg J, Maruta H (2005) Signal therapy of breast cancers by the HDAC inhibitor FK228 that blocks the activation of PAK1 and abrogates the tamoxifen-resistance. Cancer Biol Ther 4:956–960. https://doi.org/10.4161/cbt.4.9.1911
Hoshino D, Branch KM, Weaver AM (2013) Signaling inputs to invadopodia and podosomes. J Cell Sci 126:2979–2989. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.079475
Jabłońska-Trypuć A, Matejczyk M, Rosochacki S (2016) Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), the main extracellular matrix (ECM) enzymes in collagen degradation, as a target for anticancer drugs. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 31:177–183. https://doi.org/10.3109/14756366.2016.1161620
Jacob A, Prekeris R (2015) The regulation of MMP targeting to invadopodia during cancer metastasis. Fron Cell Dev Biol 3:4. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2015.00004
Kapinova A, Kubatka P, Golubnitschaja O, Kello M, Zubor P, Solar P, Pec M (2018) Dietary phytochemicals in breast cancer research: anticancer effects and potential utility for effective chemoprevention. Environ Health Prev Med 23:36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12199-018-0724-1
Kasorn A, Loison F, Kangsamaksin T, Jongrungruangchok S, Ponglikitmongkol M (2018) Terrein inhibits migration of human breast cancer cells via inhibition of the Rho and Rac signaling pathways. Oncol Rep 39:1378–1386. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2018.6189
Korobeynikov V, Borakove M, Feng Y, Wuest WM, Koval AB, Nikonova AS, Serebriiskii I, Chernoff J, Borges VF, Golemis EA, Shagisultanova E (2019) Combined inhibition of Aurora A and p21-activated kinase 1 as a new treatment strategy in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Tr 177:369–382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-019-05329-2
Kumar R, Gururaj AE, Barnes CJ (2006) p21-activated kinases in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6:459. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc1892
Li C, Zhao Y, Yang D, Yu Y, Guo H, Zhao Z, Zhang B, Yin X (2014) Inhibitory effects of kaempferol on the invasion of human breast carcinoma cells by downregulating the expression and activity of matrix metalloproteinase-9. Biochem Cell Biol 93:16–27. https://doi.org/10.1139/bcb-2014-0067
Li H, Qiu Z, Li F, Wang C (2017) The relationship between MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression levels with breast cancer incidence and prognosis. Oncol Lett 14:5865–5870. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.6924
Liang Y, Chen H, Ji L, Du J, Xie X, Li X, Lou Y (2018) Talin2 regulates breast cancer cell migration and invasion by apoptosis. Oncol Lett 16:285–293. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.8641
Ling B, Watt K, Banerjee S, Newsted D, Truesdell P, Adams J, Sidhu SS, Craig AW (2017) A novel immunotherapy targeting MMP-14 limits hypoxia, immune suppression and metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer models. Oncotarget 8:58372–58385. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.17702
Mali AV, Wagh UV, Hegde MV, Chandorkar SS, Surve SV, Patole MV (2012) In vitro anti-metastatic activity of enterolactone, a mammalian lignan derived from flax lignan, and down-regulation of matrix metalloproteinases in MCF-7 and MDA MB 231 cell lines. Indian J Cancer 49:181–187. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-509X.98948
Manser E, Leung T, Salihuddin H, Zhao ZS, Lim L (1994) A brain serine/threonine protein kinase activated by Cdc42 and Rac1. Nature 367:40–46. https://doi.org/10.1038/367040a0
McSherry EA, Donatello S, Hopkins AM, McDonnell S (2007) Molecular basis of invasion in breast cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:3201–3218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-7388-0
Montalto FI, Giordano F, Chiodo C, Marsico S, Mauro L, Sisci D, Aquila S, Lanzino M, Panno ML, Andò S, De Amicis F (2019) Progesterone receptor B signaling reduces breast cancer cell aggressiveness: role of cyclin-D1/Cdk4 mediating paxillin phosphorylation. Cancers 11:1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11081201
Murphy DA, Courtneidge SA (2011) The ‘ins’ and ‘outs’ of podosomes and invadopodia: characteristics, formation and function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12:413–426. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3141
National Institutes of Health (NIH) (2020) Image J, Image J download for windows. http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij/download.html. Accessed 5 Jan 2020
Nho KJ, Chun JM, Kim DS, Kim HK (2015) Ampelopsis japonica ethanol extract suppresses migration and invasion in human MDAMB231 breast cancer cells. Mol Med Rep 11:3722–3728. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.3179
Ong CC, Gierke S, Pitt C, Sagolla M, Cheng CK, Zhou W, Jubb AM, Strickland L, Schmidt M, Duron SG, Campbell DA (2015) Small molecule inhibition of group I p21-activated kinases in breast cancer induces apoptosis and potentiates the activity of microtubule stabilizing agents. Breast Cancer Res 17:59. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-015-0564-5
Pezzani R, Salehi B, Vitalini S, Iriti M, Zuñiga FA, Sharifi-Rad J, Martorell M, Martins N (2019) Synergistic effects of plant derivatives and conventional chemotherapeutic agents: an update on the cancer perspective. Medicina 55:110. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55040110
Rachmi E, Purnomo BB, Endharti AT, Fitri LE (2020) Afzelin inhibits migration of MDA-MB-231 cells by suppressing FAK expression and Rac1 activation. J Appl Pharm Sci 10:077–082. https://doi.org/10.7324/JAPS.2020.101010
Radu M, Semenova G, Kosoff R, Chernoff J (2014) PAK signalling during the development and progression of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 14:13–25. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3645
Redig AJ, McAllister SS (2013) Breast cancer as a systemic disease: a view of metastasis. J Intern Med 27:113–126. https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.12084
Rider L, Oladimeji P, Diakonova M (2013) PAK1 regulates breast cancer cell invasion through secretion of matrix metalloproteinases in response to prolactin and three-dimensional collagen IV. Mol Endocrinol 27:1048–1064. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2012-1322
Schlienger S, Ramirez RA, Claing A (2015) ARF1 regulates adhesion of MDA-MB-231 invasive breast cancer cells through formation of focal adhesions. Cell Signal 27:403–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.11.032
Shah P, Djisam R, Damulira H, Aganze A, Danquah M (2016) Embelin inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis and alters gene expression profiles in breast cancer cells. Pharmacol Rep 68:638–644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2016.01.004
Sharma A, Amin D, Sankaranarayanan A, Arora R, Mathur AK (2019) Present status of Catharanthus roseus monoterpenoid indole alkaloids engineering in homo-and hetero-logous systems. Biotechnol Lett 42:11–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-019-02757-4
Shen J, Cao B, Wang Y, Ma C, Zeng Z, Liu L, Li X, Tao D, Gong J, Xie D (2018) Hippo component YAP promotes focal adhesion and tumour aggressiveness via transcriptionally activating THBS1/FAK signalling in breast cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37:175. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0850-z
Shih YW (2017) Apigenin regulates matrix metalloproteinase-2/9 and Rho Gtpase family through FAk signal to reduce breast cancer MCF-7 cells metastasis. Int J Biotech Bioeng 3:258–267. https://doi.org/10.25141/2475-3432-2017-7.0249
Shin SA, Moon S, Kim WY, Paek SM, Park HH, Lee CS (2018) Structure-based classification and anti-cancer effects of plant metabolites. Int J Mol Sci 19:2651. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092651
Siddiqui MJ, Ismail Z, Saidan NH (2011) Simultaneous determination of secondary metabolites from Vinca rosea plant extractives by reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography. Pharmacogn Mag 7:92–96. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-1296.80662
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S, Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos A, Tsafou KP, Kuhn M (2015) STRING v10: protein–protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D447–D452. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1003
Tauro M, Lynch C (2018) Cutting to the chase: how matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity controls breast-cancer-to-bone metastasis. Cancers 10:185. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10060185
Tian Y, Xu L, He Y, Xu X, Li K, Ma Y, Gao Y, Wei D, Wei L (2018) Knockdown of RAC1 and VASP gene expression inhibits breast cancer cell migration. Oncol Lett 16:2151–2160. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.8930
Tieng FYF, Latifah SY, Md Hashim NF, Khaza’ai H, Ahmat N, Gopalsamy B, Wibowo A (2019) Ampelopsin E reduces the invasiveness of the triple negative breast cancer cell line, MDA-MB-231. Molecules 24:2619. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24142619
Vutukuri VR, Das MC, Reddy M, Prabodh S, Sunethri P (2017) Evaluation of acute oral toxicity of ethanol leaves extract of Catharanthus roseus in Wistar albino rats. J Clin Diag Res 11:FF01–FF04. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2017/24937.9325
Wang N, Wang Q, Tang H, Zhang F, Zheng Y, Wang S, Zhang J, Wang Z, Xie X (2017) Direct inhibition of ACTN4 by ellagic acid limits breast cancer metastasis via regulation of β-catenin stabilization in cancer stem cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 36:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-017-0635-9
Wang T, Jiang R, Bai J, Zhang K (2020) Integrative bioinformatic analyses of genome-wide association studies for understanding the genetic bases of human height. Biologia 1–8. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-020-00550-7
Wang X, Decker CC, Zechner L, Krstin S, Wink M (2019) In vitro wound healing of tumor cells: inhibition of cell migration by selected cytotoxic alkaloids. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol 20:4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40360-018-0284-4
Yamaguchi H, Condeelis J (2007) Regulation of the actin cytoskeleton in cancer cell migration and invasion. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1773:642–652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.07.001
Yao Y, Chu Y, Xu B, Hu Q, Song Q (2019) Risk factors for distant metastasis of patients with primary triple-negative breast cancer. Biosci Rep 39:BSR20190288. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20190288
Yin M, Ma W, An L (2017) Cortactin in cancer cell migration and invasion. Oncotarget 8:88232. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.21088
Zhou X, Seto SW, Chang D, Kiat H, Razmovski-Naumovski V, Chan K, Bensoussan A (2016) Synergistic effects of Chinese herbal medicine: a comprehensive review of methodology and current research. Front Pharmacol 7:201. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2016.00201
Acknowledgements
We wish to acknowledge Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM) and The World Academy of Sciences (TWAS) for USM-TWAS Postgraduate Fellowship (FR number 3240275091) and financial support to Nagla.
Funding
This study was funded by RUI grant (1001/PFARMASI/8011003), Universiti Sains Malaysia and FRGS grant (203.PFarmasi.6711764) Ministry of Higher Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 99.2 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eltayeb, N.M., Al-Amin, M., Yousif, A.M. et al. Catharanthus roseus L. extract downregulates the expression profile of motility-related genes in highly invasive human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231. Biologia 76, 1017–1032 (2021). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-020-00641-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-020-00641-5