Abstract
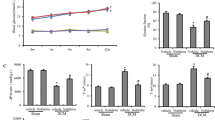
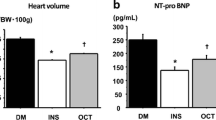
Cardiovascular complications are among the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in diabetes mellitus (DM). Despite the anti-hyperglycemic effects of various anti-diabetic therapeutic agents like insulin, some of these drugs are implicated in precipitating cardiovascular dysfunction. There is therefore an imperative need to seek alternative drugs that may ameliorate these complications. Accordingly, the aim of the study was to investigate the effects of a dioxidovanadium (V) complex, cis-[VO2(obz)py]) on selected cardiovascular function markers in STZ-induced diabetic rats. The vanadium complex (40 mg kg) was administered orally twice every 3rd day 5 weeks, non-diabetic and diabetic control groups received distilled water whereas the insulin group received subcutaneous insulin injections twice daily for 5 weeks. Blood glucose concentrations, mean arterial pressure (MAP), heart rate, triglycerides (TG) and total cholesterol concentrations were monitored weekly for 5 weeks. Rats were then euthanised and blood and hearts were collected for biochemical analysis. There was a significant decrease in blood glucose, triglycerides, cholesterol concentrations as well as blood pressure of vanadium treated rats compared to the untreated diabetic animals. Vanadium treatment also attenuated cardiac oxidative stress and decreased the expression of transforming growth factor β1 (TGFβ1) and Smad7. Lastly, the administration of the vanadium complex significantly decreased C reactive protein (CRP) and cardiotropin 1(CT-1) concentrations in the plasma and heart tissues. The administration of the dioxidovanadium(V) complex to diabetic rats culminated into cardio-protective effects. Taken together, these observations suggest that this metal complex exhibit a significant potential as an alternative therapeutic drug for DM management.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Additional/raw data can be made available upon request.
References
Alique M, Luna C, Carracedo J, Ramı´Rez R (2015) LDL biochemical modifications: a link between atherosclerosis and aging. Food Nutr Res 59:29240
Aragno M, Mastrocola R, Alloatti G, Vercellinatto I, Bardini P, Geuna S, Catalano MG, Danni O, Boccuzzi G (2008) Oxidative stress triggers cardiac fibrosis in the heart of diabetic rats. Endocrinology 149:380–388
Arayne S, Sultana N, Haroon U, Mesaik MA (2009) Synthesis, characterization, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory activities of enoxacin metal complexes. Bioinorg Chem Appl. https://doi.org/10.1155/2009/914105
Ashik U, Ara R, Mahroof-Tahir M, Maqsood ZT, Khan KM, Khan SN, Siddiqui H, Choudhary MI (2008) Synthesis, spectroscopy, and biological properties of vanadium(IV)—hydrazide complexes. Chem Biodivers 5:82–92
Bhanot S, Michoulas A, Mcneill JH (1995) Antihypertensive effects of vanadium compounds in hyperinsulinemic, hypertensive rats. Mol Cell Biochem 153:205–209
Bhuiyan S, Fukunaga K (2009) Cardioprotection by vanadium compounds targeting Akt-mediated signalling. J Pharmacol Sci 110:1–13
Bon H, Hales P, Lumb S, Holdsworth G, Johnson T, Qureshi O, Twomey BM (2019) Spontaneous extracellular matrix accumulation in a human in vitro model of renal fibrosis is mediated by αV integrins. Nephron 142:328–350
Booysen IN, Hlela T, Ackerman MP, Xulu B (2015) Mono- and polynuclear vanadium(IV) and -(V) compounds with 2-substituted phenyl/pyridyl heterocyclic chelates. Polyhedron 85:144–150
Ceretta LB, Reus GZ, Abelaira HM, Ribeiro KF, Zappellini G, Felisbino FF, Steckert AV, Dal-Pizzol F, Quevedo J (2011) Increased oxidative stress and imbalance in antioxidant enzymes in the brains of alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Exp Diabetes Res. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/302682
Chait A, Eckel RH (2016) Lipids, lipoproteins, and cardiovascular disease: clinical pharmacology now and in the future. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 101:804–814
Coderre L, Srivastava AK (2004) Vanadium and the cardiovascular functions. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 82:833–839
Crowley SD, Gurley SB, Herrera MJ, Ruiz P, Griffiths R, Kumar AP, Kim H, Smithies O, Le TH, Coffman TM (2006) Angiotensin II causes hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy through its receptors in the kidney. PNAS. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0605545103
Domingo L (2002) Vanadium and tungsten derivatives as antidiabetic agents. Biol Trace Elem Res 88:1–16
Eguchi K, Boden-Albala B, Jin Z, Rundek T, Sacco RL, Homma S, Di Tullio MR (2008) Association between diabetes mellitus and left ventricular hypertrophy in a multi-ethnic population. Am J Cardiol 101:1787–1791
Goldberg IJ (2001) Diabetic dyslipidemia: causes and consequences. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:965–971
Grisanti LA (2018) Diabetes and arrhythmias: pathophysiology, mechanisms and therapeutic outcomes. Front Physiol 9:1669
Herrera J, Henke CA, Bitterman PB (2018) Extracellular matrix as a driver of progressive fibrosis. J Clin Investig 128:45–53
Heyliger CE, Tahilliani AG, Mcneill JH (1985) Effect of vanadate on elevated blood glucose and depressed cardiac performance of diabetic rats. Science 277:1474–1477
Hussain T, Tan B, Yin Y, Blachier F, Tossou MCB, Rahu N (2016) Oxidative stress and inflammation: what polyphenols can do for us? Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016:9
Imura H, Shimada A, Naota M, Morita T, Togawa M, Hasegawa T, Seko Y (2012) Vanadium toxicity in mice: possible impairment of lipid metabolism and mucosal epithelial cell necrosis in the small intestine. Toxicol Pathol 41:842–856
Kamiya Y, Miyazono K, Miyazawa K (2010) Smad7 inhibits transforming growth factor-β family type I receptors through two distinct modes of interaction. J Biol Chem 258:30804–30813
Kim ME, Han K, Joung HN, Baek K, Song K, Kwon H (2019) Cholesterol levels and development of cardiovascular disease in Koreans with type 2 diabetes mellitus and without pre-existing cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Diabetol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-019-0943-9
Komolafe O, Adeyemi O, Adewole S, Obuotor E (2001) Streptozotocin-induced diabetes alters the serum lipid profiles of adult wistar rats. Internet J Cardiovasc Res 7:1066–1084
Lenzen S (2007) The mechanisms of alloxan- and streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Diabetologia 51:216–226
Leon BM, Maddox TM (2015) Diabetes and cardiovascular disease: epidemiology, biological mechanisms, treatment recommendations and future research. World J Diabetes 6:1246–1258
Li JH, Huang XR, Zhu HJ, Johnson R, Lan Y (2003) Role of TGF-β signaling in extracellular matrix production under high glucose conditions. Kidney Int 43:2010–2019
Lindschau C, Quass P, Menne J, Güler F, Fiebeler A, Leitges M, Luft FC, Haller H (2003) Glucose-induced TGF-β1 and TGF-β receptor-1 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells is mediated by protein kinase C-α. Hypertension 42:335–341
Lopez-Andresa N, Fortunob MA, Diezb J, Zannada F, Lacolleya P, Rossignola P (2010) Vascular effects of cardiotrophin-1: a role in hypertension? J Hypertens 10:1261–1272
Madlala HP, Van Heerden FR, Mubagwa K, Musabayane CT (2015) Changes in renal function and oxidative status associated with the hypotensive effects of oleanolic acid and related synthetic derivatives in experimental animals. PLoS ONE 10:e0128192
Manhiani MM, Sheppard TA, Brands MW (2012) Mechanism for sodium retention by insulin + glucose in diabetes may involve renal epithelial sodium channels (ENaC). FASEB J 26:867
Mannucci E, Dicembrin I, Lauria A, Pozzilli E (2013) Is glucose control important for prevention of cardiovascular disease in diabetes? Am Diabetes Assoc 36:259–263
Matsunami T, Sato Y, Sato T, Yukawa M (2010) Antioxidant status and lipid peroxidation in diabetic rats under hyperbaric oxygen exposure. Physiol Res 59:97–104
Mkhwanazi BN, Serumula MR, Myburg RB, Van Heerden FR, Musabayane CT (2014) Antioxidant effects of maslinic acid in livers, hearts and kidneys of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: effects on kidney function. Ren Fail 36:419–431
Moodahadu LS, Dhall R, Zargar AH, Bangera S, Ramani L, Katipally R (2014) Tight glycemic control and cardiovascular effects in type 2 diabetic patients. Heart Views 15:111–120
Musabayane CT, Munjeri O, Bwititi P, Osim EE (2000) Orally administered, insulin-loaded amidated pectin hydrogel beads sustain plasma concentrations of insulin in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. J Endocrinol 164:1–6
Muthaian R, Pakirisamy RM, Parasuraman S, Raveendran R (2016) Hypertension influences the exponential progression of inflammation and oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic kidney. J Pharmacol Pharmacother 7:159–164
Ozaki K, Terayama Y, Matsuura T, Narama I (2018) Effect of combined dyslipidemia and hyperglycemia on diabetic peripheral neuropathy in alloxan-induced diabetic WBN/Kob rats. J Toxicol Pathol 31:125–133
Quezada M, Wang J, Hoang V, Mcgee EA (2012) Smad7 is a transforming growth factor-beta–inducible mediator of apoptosis in granulosa cells. Fertil Steril 97:1452–1459
Renfrew AK (2014) Transition metal complexes with bioactive ligands: mechanisms for selective ligand release and applications for drug delivery. Mettalomics 6:1324–1335
Reul BA, Amin SS, Buchet J, Ongemba LN, Crans DC, Brichard SM (1999) Effects of vanadium complexes with organic ligands on glucose metabolism: a comparison study in diabetic rats. Br J Pharmacol 126:467–477
Roy S, Mallick S, Chakraborty T, Ghosh N, Singh AK, Manna S, Majumdar S (2015) Synthesis, characterisation and antioxidant activity of luteolin–vanadium(II) complex. Food Chem 173:1172–1178
Russo I, Frangogiannis NG (2016) Diabetes-associated cardiac fibrosis: cellular effectors, molecular mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. J Mol Cell Cardiol 90:84–93
Sakellarios AI, Siogkas P, Exarchos T, Stefanou K, Bourantas CV, Athanasio L, Fotiou E, Papafaklis M, Naka KK, Michalis LK, Fotiadis DI (2011) Modelling LDL accumulation in the case of endothelial dysfunction. J Serb Soc Comput Mech 5:90–100
Savithri K, Revanasiddappa HD (2018) Synthesis and characterization of oxidovanadium(IV) complexes of 2-((E)-(6-fluorobenzo[d]thiazol-2-ylimino) methyl)-6-methoxyphenol and their antimicrobial, antioxidant, and DNA-binding studies. Bioinorg Chem Appl. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2452869
Sen S, Chakraborty R, Sridhar C, Reddy YSR, De B (2010) Free radicals, antioxidants, diseases and phytomedicines: current status and future prospect. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res 3:91–100
Shechter Y, Karlish S (1980) Insulin-like stimulation of glucose oxidation in rat adipocytes by vanadyl (IV) ions. Nature 284:556–558
Shinde UA, Sharma G, Goyal RK (2004) In vitro insulin mimicking action of bis(maltolato)oxovanadium (IV). Indian J Pharm Sci 66:392–395
Sibiya NH (2014a) The effects of oxidovanadium complexes on glucose metabolism in liver and skeletal muscle cell lines. Master of Medical Science, Univesity of Kwazulu Natal
Sibiya NH (2014b) The effects of oxidovanadium complexes on glucose metabolism in liver and skeletal muscle cell lines. University of KwaZulu Natal
Silva BR, Pernomian L, Bendhack LM (2012) Contribution of oxidative stress to endothelial dysfunction in hypertension. Front Physiol 3:1–5
Srivastava AK (2000) Anti-diabetic and toxic effects of vanadium compounds. Mol Cell Biochem 206:177–182
Srivastava AK, Mehdi MZ (2004) Insulino-mimetic and anti-diabetic effects of vanadium compounds. Diabetes Med 22:2–13
Strout HV, Vicario PP, Biswas C, Saperstein R, Brady EJ, Pilch PF, Berger J (1990) Vanadate treatment of streptozotocin diabetic rats restores expression of the insulin-responsive glucose transporter in skeletal muscle. Endocrinology 126:2728–2732
Subramanyam G (2015) Effect of vanadium supplementation on high fat diet induced hyperlipidemia. Heart Rythm 67:125
Sun RW, Ma D, Wong EL, Che C (2007a) Some uses of transition metal complexes as anti-cancer and anti-HIV agents. Dalton Trans 2007:4884–4892
Sun RW, Ma DL, Wong EL, Che CM (2007b) Some uses of transition metal complexes as anti-cancer and anti-HIV agents. Dalton Trans 43:4884–4892
Takeuchi K, Mcgowan FXJ, Glynn P, Moran AM, Rader CM, Cao-Danh H, Del Nido PJ (1998) Glucose transporter upregulation improves ischemic tolerance in hypertrophied failing heart. Circulation 98:11234–11241
Treviño S, Díaz A, Sánchez-Lara E, Sanchez-Gaytan BL, Manuel Perez-Aguilar J, González-Vergara E (2019) Vanadium in biological action: chemical, pharmacological aspects, and metabolic implications in diabetes mellitus. Biol Trace Elem Res 188:68–98
Wang S, Lapage J, Hirschberg R (1999) Glomerular ultrafiltration of IGF-I may contribute to increased renal sodium retention in diabetic nephropathy. Transl Res 134:154–160
WHO (1999) Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Biomedical Research Unity (BRU), University of KwaZulu Natal for the supply and housing of the animals, as well as the Chemistry department for synthesising the vanadium compound used in this study.
Funding
This study was partly funded by NRF South Africa, Incentive Funding for Rated Researchers NRF and the University of KwaZulu-Natal, College of Health Sciences research division. The views expressed are those of the authors and should not be attributed to the DST, NRF or the University of KwaZulu-Natal.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Ethics approval
All animal experimentation was reviewed and approved by the Animal Research Ethics Committee of the University of KwaZulu-Natal (AREC/054/017D).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mbatha, B., Khathi, A., Sibiya, N. et al. Cardio-protective effects of a dioxidovanadium(V) complex in male sprague–dawley rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Biometals 34, 161–173 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-020-00270-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-020-00270-0