Abstract
For simultaneous analysis of four fat-soluble tocopherols (α-, β-, γ-, and δ-) in edible oils, an efficient and green method using deep eutectic solvent-based liquid-phase microextraction (DES-LPME) coupled with reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) was developed. The DESs formed by different quaternary ammonium salts and ethanol were used as the extractants. Tetrabutylammonium chloride (TBAC)-ethanol DES at a molar ratio of 1:2 achieved the best extraction efficiency. Under the optimized conditions, the detection limits were in the range of 2.1–3.0 ng mL−1. The intra-day and inter-day repeatability were in the ranges of 3.9–5.3% and 4.8–7.1%, respectively, and the recoveries for the real samples varied from 80.7% to 105.4%. The developed method was successfully employed for the determination of all four tocopherol homologues with an RP-HPLC system containing a COSMOSIL π-NAP column in five edible oils collected locally.

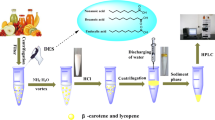
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Theriault A, Chao J, Wang Q, Gapor A, Adeli K. Tocotrienol: a review of its therapeutic potential. Clin Biochem. 1999;32:309–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-9120(99)00027-2.
Górnaś P. Unique variability of tocopherol composition in various seed oils recovered from by-products of apple industry: rapid and simple determination of all four homologues (α, β, γ and δ) by RP-HPLC/FLD. Food Chem. 2015;172:129–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.09.051.
Lechner M, Reiter B, Lorbeer E. Determination of tocopherols and sterols in vegetable oils by solid-phase extraction and subsequent capillary gas chromatographic analysis. J Chromatogr A. 1999;857:231–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(99)00751-7.
Gliszczynska-Swiglo A, Sikorska E. Simple reversed-phase liquid chromatography method for determination of tocopherols in edible plant oils. J Chromatogr A. 2004;1048:195–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2004.07.051.
San Andrés MP, Otero J, Vera S. High performance liquid chromatography method for the simultaneous determination of α-, γ- and δ-tocopherol in vegetable oils in presence of hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide/n-propanol in mobile phase. Food Chem. 2011;126:1470–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.11.161.
Li J, Bi Y, Sun S, Peng D. Simultaneous analysis of tert-butylhydroquinone, tert-butylquinone, butylated hydroxytoluene, 2-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole, 3-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole, α-tocopherol, γ-tocopherol, and δ-tocopherol in edible oils by normal-phase high performance liquid chromatography. Food Chem. 2017;234:205–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.04.176.
Chen H, Angiuli M, Ferrari C, Tombari E, Salvetti G, Bramanti E. Tocopherol speciation as first screening for the assessment of extra virgin olive oil quality by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography/fluorescence detector. Food Chem. 2011;125:1423–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.10.026.
Schwartz H, Ollilainen V, Piironen V, Lampi A. Tocopherol, tocotrienol and plant sterol contents of vegetable oils and industrial fats. J Food Compos Anal. 2008;21:152–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2007.07.012.
Zhang L, Wang S, Yang R, Mao J, Jiang J, Wang X, et al. Simultaneous determination of tocopherols, carotenoids and phytosterols in edible vegetable oil by ultrasound-assisted saponification, LLE and LC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2019;289:313–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.03.067.
Abidi SL. Chromatographic analysis of tocol-derived lipid antioxidants. J Chromatogr A. 2000;881:197–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(00)00131-X.
Cert A, Moreda W, Perez-Camino MC. Chromatographic analysis of minor constituents in vegetable oils. J Chromatogr A. 2000;881:131–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(00)00389-7.
Grigoriadou D, Androulaki A, Psomiadou E, Tsimidou M. Solid phase extraction in the analysis of squalene and tocopherols in olive oil. Food Chem. 2007;105:675–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.12.065.
Yan Y, Chen X, Hu S, Bai X. Applications of liquid-phase microextraction techniques in natural product analysis: a review. J Chromatogr A. 2014;1368:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.09.068.
Kokosa JM. Selecting an extraction solvent for a greener liquid phase microextraction (LPME) mode-based analytical method. TrAC Trend Anal Chem. 2019;118:238–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.05.012.
Xie QL, Liu SH, Fan YY, Zhang XK. Development of a dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction method for the determination of α-tocopherol in pigmented wheat by high-performance liquid chromatography. Food Anal Methods. 2013;7:21–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-013-9592-x.
Vinas P, Bravo-Bravo M, Lopez-Garcia I, Pastor-Belda M, Hernandez-Cordoba M. Pressurized liquid extraction and dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for determination of tocopherols and tocotrienols in plant foods by liquid chromatography with fluorescence and atmospheric pressure chemical ionization-mass spectrometry detection. Talanta. 2014;119:98–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2013.10.053.
Shammugasamy B, Ramakrishnan Y, Ghazali HM, Muhammad K. Combination of saponification and dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of tocopherols and tocotrienols in cereals by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 2013;1300:31–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2013.03.036.
Zhang Q, De Oliveira Vigier K, Royer S, Jerome F. Deep eutectic solvents: syntheses, properties and applications. Chem Soc Rev. 2012;41:7108–46. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cs35178a.
Wang H, Huang X, Qian H, Lu R, Zhang S, Zhou W, et al. Vortex-assisted deep eutectic solvent reversed-phase liquid-liquid microextraction of triazine herbicides in edible vegetable oils. J Chromatogr A. 2019;1589:10–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.12.049.
Shahbaz K, Mjalli FS, Hashim MA, AlNashef IM. Using deep eutectic solvents based on. methyl triphenyl phosphunium bromide for the removal of glycerol from palm-oil-based. Biodiesel. Energ Fuel. 2011;25:2671–8. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef2004943.
Yi L, Feng J, Li W, Luo Z. High-performance separation of phenolic compounds from coal-based liquid oil by deep eutectic solvents. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2019;7:7777–83. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b06734.
Liu W, Zong B, Yu J, Bi Y. Ultrasonic-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction based on natural deep eutectic solvent for the HPLC-UV determination of tert-butylhydroquinone from soybean oils. Food Anal Methods. 2018;11:1797–803. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-018-1174-5.
Ferrone V, Genovese S, Carlucci M, Tiecco M, Germani R, Preziuso F, Epifano F, Carlucci G, Taddeo VA. A green deep eutectic solvent dispersive liquid-liquid micro-extraction (DES-DLLME) for the UHPLC-PDA determination of oxyprenylated phenylpropanoids in olive, soy, peanuts, corn, and sunflower oil. Food Chem 2018; 245: 578-585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.10.135.
Liu W, Fu XL, Li ZZ. Extraction of tocopherol from soybean oil deodorizer distillate by deep eutectic solvents. J Oleo Sci. 2019;68:951–8. https://doi.org/10.5650/jos.ess19146.
Khezeli T, Daneshfar A, Sahraei R. A green ultrasonic-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction based on deep eutectic solvent for the HPLC-UV determination of ferulic, caffeic and cinnamic acid from olive, almond, sesame and cinnamon oil. Talanta. 2016;150:577–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.12.077.
Li T, Song Y, Li J, Zhang M, Shi Y, Fan J. New low viscous hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents in vortex-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of phthalate esters from food-contacted plastics. Food Chem. 2020;309:125752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125752.
Xie QL, Xia M, Lu HQ, Shi H, Sun DK, Hou B, et al. Deep eutectic solvent-based liquid-liquid microextraction for the HPLC-DAD analysis of bisphenol a in edible oils. J Mol Liq. 2020;306:–112881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.112881.
Shishov AY, Chislov MV, Nechaeva DV, Moskvin LN, Bulatov AV. A new approach for microextraction of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from human urine samples based on in-situ deep eutectic mixture formation. J Mol Liq. 2018;272:738–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.10.006.
Guo W, Hou Y, Wu W, Ren S, Tian S, Marsh K. Separation of phenol from model oils with quaternary ammonium salts via forming deep eutectic solvents. Green Chem. 2013;15:226–9. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2GC36602A.
AOCS Official method Ce 8-89. Determination of tocopherols and tocotrienols in vegetable oils and fats by HPLC 2009.
Agricultural Standard of the People’s Republic of China, NY/T 1598-2008. Determination of tocopherol content in edible vegetable oils. 2008.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge with gratitude and appreciation financial support from the Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province (No. 201801D221090 and 201901D211582), the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21706271), the Ningxia Key Research and Development Program (Science and Technology support) Project (No. 2019BEG03071), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2019 M653488).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(PDF 152 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Q., Xia, M., Sun, D. et al. Deep eutectic solvent-based liquid-phase microextraction coupled with reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography for determination of α-, β-, γ-, and δ-tocopherol in edible oils. Anal Bioanal Chem 413, 577–584 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-03029-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-03029-1