Abstract
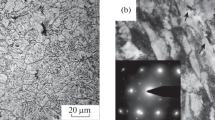
In this study, we consider the mechanism and kinetics of structure formation in the hardened zone during thermal deformation treatment of reinforced steel. Depending on the cooling rate and temperature conditions of austenite decomposition, pearlite and martensitic transformations are shown to occur with the formation of a gradient-layered structure, leading to structure modification of the surface layer of steel at a constant chemical composition, structure, and properties of the central layers of the workpiece. A high cooling rate due to a large temperature gradient near the surface is the reason for the formation of a finely dispersed layered structure. A diffusion-free martensitic transformation develops in the surface zone, leading to the formation of acicular martensite. In the underlying layers, the decomposition of austenite proceeds by diffusion and is accompanied by the formation of a lamellar ferrite–carbide mixture of varying dispersion degrees. An increase in the cooling rate leads to a strong refinement of the structure (grain point according to GOST 5639–82 is 11 in the surface layer and 8 in the core) characterized by an increase in the dispersion degree of the ferrite–carbide mixture, which causes an increase in strength and reduction of the plastic characteristics of steel. It is noted that the formation of a gradient-layered structure in the surface layer of strain-hardened reinforced steel allows excluding a sharp transition from the martensite structure to troosto-martensitic and mixed pearlite structures. This increases the contact-fatigue strength of reinforced steel and its crack resistance.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Tushinskii, L.I., Problems of modern material science in 21st century, Fundam. Prikl. Probl. Chern. Metall., 2004, no. 7, pp. 23–49.
Dolzhenkov, I.E., Thermal and combined deformation-heat treatment of rolled metal, Fundam. Prikl. Probl. Chern. Metall., 2004, no. 7, pp. 61–71.
Sidorenko, O.G., Fedorova, I.P., Sukhoi, A.P., et al., Structure formation in rebar strengthened by discontinuous quenching, Steel Transl., 2012, vol. 42, no. 1, pp. 81–83.
Akimbekova, Zh.M., Kanaev, A.T., and Omarov, A.K., Quality improvement of reinforced bar steel from rolling heating by deformation-thermal hardening, Vestn. Evraz. Nats. Univ., 2005, no. 4, pp. 91–96.
Bogomolov, A.V., Kanaev, A.T., Serzhanov, R.I., et al., KZ Patent 20116, 2008.
Kanaev, A.T., Bogomolov, A.V., and Reshotkina, E.N., Defects and thermal hardening of reinforcement rolled from continuous-cast billet, Steel Transl., 2010, vol. 40, no. 6, pp. 586–589.
Kovalenko, V.V. and Kozlova, E.V., Fizicheskaya priroda formirovaniya i evolyutsii gradientnykh strukturno-fazovykh sostoyanii v stalyakh i splavakh (Physical Nature of Formation and Evolution of Gradient Structural-Phase States in Steels and Alloys), Novokuznetsk: Sib. Gos. Ind. Univ., 2009.
Ivanov, Yu.F., Kolubaeva, Yu.A., Kornet, E.V., et al., Formation of fine structure and phase composition of construction steel during quenching, Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Chern. Metall., 2009, no. 4, pp. 23–28.
Habraken, L. and de Brouwer J.L., De Ferri Metallographia: Metallographic Atlas of Iron, Steels and Cast Irons, Vol 1: Fundamentals of Metallography, Brussels: Academiques Europeennes, 1966.
Kostyrev, V.B., Efimov, O.Yu., and Ivanov, Yu.F., Formation of gradient structural-phase states during thermomechanical hardening, Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Chern. Metall., 2011, no. 4, pp. 24–27.
Kanaev, A.T., Klaubaev, E.B., and Auel’bekova, A.E., Effictive modernization of the surface layer structure of rolled steels by interrupted quenching, Proc. XI Int. Sci.-Pract. Conf. “Zprávy Vědecké Ideje-2015,”, Prague, 2015, pp. 67–71.
Bogomolov, A.V., Kanaev, A.T., and Reshotkina, E.N., Influence of intermittent quenching and self-tempering on the mechanical properties of rebar steel, Steel Transl., 2018, vol. 48, no. 2, pp. 130–134.
Uzlov, I.G., Razdobreev, V.G., and Sidorenko, O.G., New technological solutions for thermomechanical hardening of reinforced bars of various strength classes, Metall. Gornorudn. Prom-st., 2004, no. 5, pp. 61–64.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by A. Ivanov
About this article
Cite this article
Kanaev, A.T., Bogomolov, A.V. Formation of a Gradient-Layered Structure during Thermal Deformation Treatment of Reinforced Steel. Steel Transl. 50, 509–513 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0967091220070074
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0967091220070074