Abstract
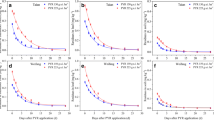
In this study, a practical and excellent method was used to determine the famoxadone and cymoxanil via high-performance liquid chromatography equipped utilizing ultraviolet detector lamp (HPLC-UV) for investigating the dissipation behavior and residue distribution of famoxadone and cymoxanil in cucumber and soil ecosystem. The limit of quantification (LOQS) of famoxadone and cymoxanil in cucumber were 0.50, 1.00, 2.00 and 0.05, 0.50, 1.00 mg kg−1 in soil, respectively. The limit of detection (LODS) of both famoxadone and cymoxanil were 8.0 ng. The average recoveries (n = 5) of the fungicide ranged from 84.10 to 108.02% with the relative standard deviations (RSDs) typically < 9.23%. The fungicide was applied to cucumber and soil at the range of doses (275.6–413.4 g a.i.ha−1) three or four times. The half-lives of famoxadone and cymoxanil in cucumber and soil were 1.34–16.12 days, which followed the first-order chemical reaction kinetics equation Ct = C0 × e-kt. The residues of famoxadone and cymoxanil in cucumber at the pre-harvest interval (PHI, 3 days) were below 8.0 × 10−8 g and 8.0 × 10−9 g, respectively. Overall, this study evaluated the food safety and the environmental fate of famoxadone and cymoxanil in cucumber and soil ecosystem. In addition, this study would promote the series of work on the pesticide exposure assessment of these fungicides as well.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahammed, S. T. P., et al. (2015). Residue dissipation and processing factor for dimethomorph, famoxadone and cymoxanil during raisin preparation. Food Chemistry, 170, 180–185.
Álvarez-Martín, A., et al. (2016). Effect of different rates of spent mushroom substrate on the dissipation and bioavailability of cymoxanil and tebuconazole in an agricultural soil. Science of the Total Environment., 550, 495–503.
Baderna, D., et al. (2015). Acute phytotoxicity of seven metals alone and in mixture: are Italian soil threshold concentrations suitable for plant protection? Environmental Research., 140, 102–111.
Balayiannis, G., et al. (2014). Rapid determination of famoxadone and cymoxanil in commercial pesticide formulation by high performance liquid chromatography using a c18 monolithic rod column. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology., 93, 775–780.
Brophy, T. F., & Laing, M. D. (1992). Screening of fungicides for the control of downy mildew on container-grown cabbage seedlings. Crop Protection., 11, 160–164.
Céspedes, M. C., et al. (2013). Physiological and molecular characterization of Phytophthora infestans isolates from the Central Colombian Andean Region. Revista Iberoamericana De Micología., 30, 81–87.
Chang, K. F., et al. (2013). Yield loss and management of downy mildew on field pea in Alberta. Canada. Crop Protection., 46, 23–28.
Chang, C. H., et al. (2017). The interactions among organophosphate pesticide exposure, oxidative stress, and genetic polymorphisms of dopamine receptor D4 increase the risk of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children. Environmental Research., 160, 339–346.
Cortivo, C. D., et al. (2017). Biostimulant effects of seed-applied sedaxane fungicide: morphological and physiological changes in maize seedlings. Frontiers in Plant Science., 8, 2072.
De, M. A. S., et al. (2006). A comparison of a gas chromatographic with electron-capture detection and a gas chromatographic with mass spectrometric detection screening methods for the analysis of famoxadone in grapes and wines. Journal of Chromatography A., 1103, 362–367.
Díaz-Álvarez, M., & Martín-Esteban, A. (2018). Hollow fiber membrane-protected molecularly imprinted microspheres for micro solid-phase extraction and clean-up of thiabendazole in citrus samples. Journal of Chromatography A, 1531, 39–45
Diop, A., et al. (2016). Monitoring survey of the use patterns and pesticide residues on vegetables in the Niayes zone. Senegal. Chemosphere., 144, 1715–1721.
Fayette, J., et al. (2012). The role of cymoxanil and famoxadone in the management of bacterial spot on tomato and pepper and bacterial leaf spot on lettuce. Crop Protection., 31, 107–112.
Fayette, J., et al. (2016). Organic compounds increase the efficacy of famoxadone+cymoxanil in the control of bacterial leaf spot of lettuce. Crop Protection., 89, 47–50.
Ge, J., et al. (2010). Dissipation and residue of famoxadone in grape and soil. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment., 162, 219–224.
Gisi, U., Sierotzki, H. (2008). Fungicide modes of action and resistance in downy mildews. The downy mildews-genetics. Molecular Biology and Control. Springer, Dordrecht, 157–167.
Guan, A., et al. (2017). Discovery of a new fungicide candidate through lead optimization of pyrimidinamine derivatives and its activity against cucumber downy mildew. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 65(49), 10829–10835.
Halo, B. A., et al. (2018). Aspergillus terreus inhibits growth and induces morphological abnormalities in Pythium aphanidermatum and suppresses Pythium-induced damping-off of cucumber. Frontiers in Microbiology., 9, 95.
Jesús, F., et al. (2018). Miniaturized QuEChERS based methodology for multiresidue determination of pesticides in odonate nymphs as ecosystem biomonitors. Talanta., 178, 410.
Jiang, L., et al. (2018). Effects of earthworm casts on sorption-desorption, degradation, and bioavailability of nonylphenol in soil. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(8), 7968–7977.
Lehmann, E., et al. (2018). Development of a modified QuEChERS method for multi-class pesticide analysis in human hair by GC-MS and UPLC-MS/MS. Analytica Chimica Acta, 999, 87.
Lerro, C. C., et al. (2018). A nested case-control study of polychlorinated biphenyls, organochlorine pesticides, and thyroid cancer in the Janus Serum Bank cohort. Environmental Research., 165, 125.
Likas, D. T., et al. (2007). Rapid gas chromatographic method for the determination of famoxadone, trifloxystrobin and fenhexamid residues in tomato, grape and wine samples. Journal of Chromatography A., 1150, 208–214.
Lin, H., et al. (2018). Consumption of fruit and vegetables might mitigate the adverse effects of ambient PM2.5 on lung function among adults. Environmental Research., 160, 77–82.
Liu, C., et al. (2010). Famoxadone residue and dissipation in watermelon and soil. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 73, 183–188.
Liu, X., et al. (2014). Dissipation and residue of metalaxyl and cymoxanil in pepper and soil. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment., 186, 5307–5313.
Mariod, A. A., Mohamed, E. S. M., & Hussein, I. H. (2017). Unconventional oilseeds and oil sources. Academic Press.
Martínez-Piernas, A. B., et al. (2018). Validation and application of a multiresidue method based on liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for evaluating the plant uptake of 74 microcontaminants in crops irrigated with treated municipal wastewater. Journal of Chromatography A., 1534, 10.
Mateljan, G. (2007). The world's healthiest foods: essential guide for the healthiest way of eating. GMF publishing.
Mukherjee, P. K., et al. (2013). Phytochemical and therapeutic potential of cucumber. Fitoterapia., 84, 227–236.
Mulero, J., et al. (2015). Phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of red wine made from grapes treated with different fungicides. Food Chemistry., 180, 25–31.
Neik, T. X., et al. (2017). Current status and challenges in identifying disease resistance genes in Brassica napus. Frontiers in Plant Science., 8, 1788.
Pearson, B. L., et al. (2016). Identification of chemicals that mimic transcriptional changes associated with autism, brain aging and neurodegeneration. Nature Communications, 7, 11173.
Pember, S. O., et al. (2005). Mechanistic differences in inhibition of ubiquinol cytochrome c reductase by the proximal Qo-site inhibitors famoxadone and methoxyacrylate stilbene. Archives of Biochemistry & Biophysics., 435, 280–290.
Qian, M., et al. (2011). Stereoselective determination of famoxadone enantiomers with HPLC-MS/MS and evaluation of their dissipation process in spinach. Journal of Separation Science., 34, 1236–1243.
Ribeiro, I. C., et al. (2000). Yeasts as a model for assessing the toxicity of the fungicides Penconazol, Cymoxanil and Dichlofluanid. Chemosphere., 41, 1637–1642.
Samsidar, A., Shafiquzzaman S., & Sharifudin Md, S. (2018). A review of extraction, analytical and advanced methods for determination of pesticides in environment and foodstuffs. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 71, 188–201.
Serres, J. M., & Carraro, G. A. (1976). DPX-3217, a new fungicide for the control of grape downy mildew, potato late blight and other Peronosporales. Gent: Rijksuniversiteit Faculteit Landbouwwetenschappen.
Shaw, G. M., et al. (2018). Residential agricultural pesticide exposures and risks of preeclampsia. Environmental Research., 164, 546–555.
Sternberg, J. A., et al. (2001). Famoxadone: the discovery and optimisation of a new agricultural fungicide. Pest Management Science., 57, 143.
Tang, W., et al. (2017). Pyrethroid pesticide residues in the global environment: an overview. Chemosphere., 191, 990.
Tellier, F., et al. (2009). Metabolism of fungicidal cyanooximes, cymoxanil and analogues in various strains of Botrytis cinerea. Pest Management Science., 65, 129.
Toffolatti, S. L., et al. (2015). Sensitivity to cymoxanil in Italian populations of Plasmopara viticola oospores. Pest Management Science., 71, 1182–1188.
Walorczyk, S., et al. (2015). Determination of pesticide residues in samples of green minor crops by gas chromatography and ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry. Talanta., 132, 197–204.
Wang, L., et al. (2016). New approach for the simultaneous determination fungicide residues in food samples by using carbon nanofiber packed microcolumn coupled with HPLC. Food Control, 60, 1–6.
Yang, S., et al. (2018). A CsMYB6-CsTRY module regulates fruit trichome initiation in cucumber. Journal of Experimental Botany, 69(8), 1887–1902.
Zhang, M., et al. (2015). Agricultural pesticide use and food safety: California’s model. Journal of Integrative Agriculture., 14, 2340–2357.
Zhang, S., et al. (2017a). Melatonin attenuates potato late blight by disrupting cell growth, stress tolerance, fungicide susceptibility and homeostasis of gene expression in Phytophthora infestans. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8, 1993.
Zhang, W., et al. (2017b). Multiple gene genealogy reveals high genetic diversity and evidence for multiple origins of Chinese Plasmopara viticola population. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 1–11.
Zhang, M., et al. (2018). Application of pseudo-template molecularly imprinted polymers by atom transfer radical polymerization to the solid-phase extraction of pyrethroids. Talanta., 178, 1011–1016.
Funding
The study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51709103).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• A method for detecting famoxadone and cymoxanil in cucumber/soil was developed.
• Famoxadone/cymoxanil residue dissipation followed the first-order reaction kinetic.
• The half-lives of famoxadone and cymoxanil in cucumber were 1.34–2.52 days.
• The half-lives of famoxadone and cymoxanil in soil ecosystem were 3.08–16.12 days.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, J., Chen, L., Xiang, Y. et al. Dissipation Behavior and Residue Distribution of Famoxadone and Cymoxanil in Cucumber and Soil Ecosystem Under Open-Field Conditions. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 558 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04907-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04907-1