Abstract
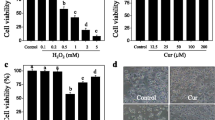
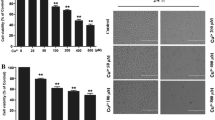
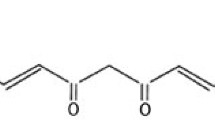
Impaired homeostasis of copper has been linked to different pathophysiological mechanisms in neurodegenerative diseases and oxidative injury has been proposed as the main mechanism. This study aims to use curcumin, a widely used antioxidative and anti-apoptotic agent, to exert the neuroprotective effect against copper in vitro and illuminate the underlying mechanism. The effect of curcumin was examined by using a cell counting kit-8 assay, flow cytometry, immunofluorescence, spectrophotometer, and western blot. Results revealed that after pretreatment with curcumin for 3 h, copper-induced toxicity and apoptosis show a significant decline. Further experiments showed that curcumin not only decreased the production of ROS and MDA but also increased the activities of the ROS scavenging enzymes SOD and CAT. Moreover, curcumin treatment alleviated the decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential and the nuclear translocation of cytochrome c induced by copper. The protein levels of pro-caspase 3, pro-caspase 9, and PARP1 were up-regulated and the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio was down-regulated in the presence of curcumin. Taken together, our study demonstrates that curcumin has neuroprotective properties against copper in SH-SY5Y cells and the potential mechanisms might be related to oxidative stress and mitochondrial apoptosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rihel J (2018) Copper on the brain. Nat Chem Biol 14(7):638–639
Hung YH, Bush AI, Cherny RA (2010) Copper in the brain and Alzheimer’s disease. J Biol Inorg Chem 15(1):61–76
Yu Y, Guerrero CR, Liu S, Amato NJ, Sharma Y, Gupta S, Wang Y (2016) Comprehensive assessment of oxidatively induced modifications of DNA in a rat model of human Wilson’s disease. Mol Cell Proteomics 15(3):810–817
Gitlin JD (2003) Wilson disease. Gastroenterology 125(6):1868–1877
Xiao G, Fan Q, Wang X, Zhou B (2013) Huntington disease arises from a combinatory toxicity of polyglutamine and copper binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(37):14995–15000
Lan AP, Chen J, Chai ZF, Hu Y (2016) The neurotoxicity of iron, copper and cobalt in Parkinson’s disease through ROS-mediated mechanisms. Biometals 29(4):665–678
Jiang D, Men L, Wang J, Zhang Y, Chickenyen S, Wang Y, Zhou F (2007) Redox reactions of copper complexes formed with different beta-amyloid peptides and their neuropathological [correction of neuropathalogical] relevance. Biochemistry 46(32):9270–9282
Menon VP, Sudheer AR (2007) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin. Adv Exp Med Biol 595:105–125
Zorofchian Moghadamtousi S, Abdul Kadir H, Hassandarvish P, Tajik H, Abubakar S, Zandi K (2014) A review on antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal activity of curcumin. Biomed Res Int 2014:186864
Arbiser JL, Klauber N, Rohan R, van Leeuwen R, Huang M-T, Fisher C, Flynn E, HR B (1998) Curcumin is an in vivo inhibitor of angiogenesis. Mol Med 4(6):376–383
Anto RJ, George J, Babu KD, Rajasekharan K, Kuttan R (1996) Antimutagenic and anticarcinogenic activity of natural and synthetic curcuminoids. Mutat Res 370(2):127–131
Kocaadam B, Sanlier N (2017) Curcumin, an active component of turmeric (Curcuma longa), and its effects on health. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 57(13):2889–2895
Bagheri H, Ghasemi F, Barreto GE, Rafiee R, Sathyapalan T, Sahebkar A (2020) Effects of curcumin on mitochondria in neurodegenerative diseases. Biofactors (Oxford, England) 46(1):5–20
Abolaji AO, Fasae KD, Iwezor CE, Aschner M, Farombi EO (2020) Curcumin attenuates copper-induced oxidative stress and neurotoxicity in Drosophila melanogaster. Toxicol Rep 7:261–268
Lan A-P, Xiong X-J, Chen J, Wang X, Chai Z-F, Hu Y (2016) AMPK inhibition enhances the neurotoxicity of cu(II) in SH-SY5Y cells. Neurotox Res 30(3):499–509
Horbay R, Bilyy R (2016) Mitochondrial dynamics during cell cycling. Apoptosis 21(12):1327–1335
Sinha K, Das J, Pal PB, Sil PC (2013) Oxidative stress: the mitochondria-dependent and mitochondria-independent pathways of apoptosis. Arch Toxicol 87(7):1157–1180
Calabrese EJ, Canada AT, Sacco C (1985) Trace elements and public health. Annu Rev Public Health 6(1):131–146
Szerdahelyi P, Kása P (1986) Histochemical demonstration of copper in normal rat brain and spinal cord. Evidence of localization in glial cells. Histochemistry 85(4):341–347
Lewińska-Preis L, Jabłońska M, Fabiańska MJ, Kita A (2011) Bioelements and mineral matter in human livers from the highly industrialized region of the Upper Silesia Coal Basin (Poland). Environ Geochem Health 33(6):595–611
Liu J, Chakraborty S, Hosseinzadeh P, Yu Y, Tian S, Petrik I, Bhagi A, Lu Y (2014) Metalloproteins containing cytochrome, iron-sulfur, or copper redox centers. Chem Rev 114(8):4366–4469
Scheiber IF, Mercer JFB, Dringen R (2014) Metabolism and functions of copper in brain. Prog Neurobiol 116:33–57
Wang J, Chen J, Tang Z, Li Y, Hu L, Pan J (2016) The effects of copper on brain microvascular endothelial cells and claudin via apoptosis and oxidative stress. Biol Trace Elem Res 174(1):132–141
Hu Z, Yu F, Gong P, Qiu Y, Zhou W, Cui Y, Li J, Chen H (2014) Subneurotoxic copper(II)-induced NF-κB-dependent microglial activation is associated with mitochondrial ROS. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 276(2):95–103
Jiang W-D, Liu Y, Hu K, Jiang J, Li S-H, Feng L, Zhou X-Q (2014) Copper exposure induces oxidative injury, disturbs the antioxidant system and changes the Nrf2/ARE (CuZnSOD) signaling in the fish brain: protective effects of myo-inositol. Aquat Toxicol 155:301–313
Corona-Rivera A, Urbina-Cano P, Bobadilla-Morales L, Vargas-Lares Jde J, Ramirez-Herrera MA, Mendoza-Magaua ML, Troyo-Sanroman R, Diaz-Esquivel P, Corona-Rivera JR (2007) Protective in vivo effect of curcumin on copper genotoxicity evaluated by comet and micronucleus assays. J Appl Genet 48(4):389–396
Hashish EA, Elgaml SA (2016) Hepatoprotective and nephroprotective effect of curcumin against copper toxicity in rats. Indian J Clin Biochem 31(3):270–277
Abbaoui A, Chatoui H, El Hiba O, Gamrani H (2017) Neuroprotective effect of curcumin-I in copper-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity in rats: a possible link with Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 660:103–108
Abbaoui A, Gamrani H (2018) Neuronal, astroglial and locomotor injuries in subchronic copper intoxicated rats are repaired by curcumin: a possible link with Parkinson’s disease. Acta Histochem 120(6):542–550
Gaggelli E, Kozlowski H, Valensin D, Valensin G (2006) Copper homeostasis and neurodegenerative disorders (Alzheimer’s, prion, and Parkinson’s diseases and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis). Chem Rev 106(6):1995–2044
Schieber M, Chandel NS (2014) ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr Biol 24(10):R453–R462
Mancuso M, Coppede F, Migliore L, Siciliano G, Murri L (2006) Mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress and neurodegeneration. J Alzheimers Dis 10(1):59–73
Tainer JA, Getzoff ED, Richardson JS, Richardson DC (1983) Structure and mechanism of copper, zinc superoxide dismutase. Nature 306(5940):284–287
Wong PC, Waggoner D, Subramaniam JR, Tessarollo L, Bartnikas TB, Culotta VC, Price DL, Rothstein J, Gitlin JD (2000) Copper chaperone for superoxide dismutase is essential to activate mammalian Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97(6):2886–2891
Hao F, Jing M, Zhao X, Liu R (2015) Spectroscopy, calorimetry and molecular simulation studies on the interaction of catalase with copper ion. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 143:100–106
Kowalczuk K, Stryjecka-Zimmer M (2002) The influence of oxidative stress on the level of malondialdehyde (MDA) in different areas of the rabbit brain. Ann Univ Mariae Curie Sklodowska Med 57(2):160–164
Mogensen M, Sahlin K, Fernström M, Glintborg D, Vind BF, Beck-Nielsen H, Højlund K (2007) Mitochondrial respiration is decreased in skeletal muscle of patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 56(6):1592–1599
Ward MW, Rego AC, Frenguelli BG, Nicholls DG (2000) Mitochondrial membrane potential and glutamate excitotoxicity in cultured cerebellar granule cells. J Neurosci 20(19):7208–7219
Wong HS, Dighe PA, Mezera V, Monternier PA, Brand MD (2017) Production of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide from specific mitochondrial sites under different bioenergetic conditions. J Biol Chem 292(41):16804–16809
Wang D, Zong C, Cheng K (2020) Chicken thalamic injury induced by copper (II) or/and arsenite exposure involves oxidative stress and inflammation-induced apoptosis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 197:110554
Liu H, Guo H, Jian Z, Cui H, Fang J, Zuo Z, Deng J, Li Y, Wang X, Zhao L (2020) Copper induces oxidative stress and apoptosis in the mouse liver. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2020:1359164
Ott M, Robertson JD, Gogvadze V, Zhivotovsky B, Orrenius S (2002) Cytochrome c release from mitochondria proceeds by a two-step process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99(3):1259–1263
Düssmann H, Rehm M, Kögel D, Prehn JH (2003) Outer mitochondrial membrane permeabilization during apoptosis triggers caspase-independent mitochondrial and caspase-dependent plasma membrane potential depolarization: a single-cell analysis. J Cell Sci 116(Pt 3):525–536
Wei MC, Zong WX, Cheng EH, Lindsten T, Panoutsakopoulou V, Ross AJ, Roth KA, MacGregor GR, Thompson CB, Korsmeyer SJ (2001) Proapoptotic BAX and BAK: a requisite gateway to mitochondrial dysfunction and death. Science 292(5517):727–730
Yu H, Zheng L, Yin L, Xu L, Qi Y, Han X, Xu Y, Liu K, Peng J (2014) Protective effects of the total saponins from Dioscorea nipponica Makino against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in mice through suppression of apoptosis and inflammation. Int Immunopharmacol 19(2):233–244
Oliver FJ, de la Rubia G, Rolli V, Ruiz-Ruiz MC, de Murcia G, Murcia JM (1998) Importance of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase and its cleavage in apoptosis. Lesson from an uncleavable mutant. J Biol Chem 273(50):33533–33539
Peña-Blanco A, García-Sáez AJ (2018) Bax, Bak and beyond—mitochondrial performance in apoptosis. FEBS J 285(3):416–431
Nur-E-Kamal A, Gross SR, Pan Z, Balklava Z, Ma J, Liu LF (2004) Nuclear translocation of cytochrome c during apoptosis. J Biol Chem 279(24):24911–24914
Shin JW, Chun KS, Kim DH, Kim SJ, Kim SH, Cho NC, Na HK, Surh YJ (2020) Curcumin induces stabilization of Nrf2 protein through Keap1 cysteine modification. Biochem Pharmacol 173:113820
Song MO, Mattie MD, Lee C-H, Freedman JH (2014) The role of Nrf1 and Nrf2 in the regulation of copper-responsive transcription. Exp Cell Res 322(1):39–50
Acknowledgments
This research was supported National Natural Science Foundation of China (31972740) and Major Science and Technology Innovation Project of Shandong Province (2019JZZY010735).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, B., Li, D., Chen, Y. et al. Curcumin Ameliorates Copper-Induced Neurotoxicity Through Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Apoptosis in SH-SY5Y Cells. Neurochem Res 46, 367–378 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03173-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03173-1