Abstract
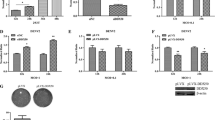
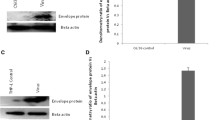
Dengue virus (DV) is the most rapidly spreading arbovirus in the world. Our previous studies indicated that Rac1, a kind of Rho GTPase, was related with the increased vascular permeability in DV infection. However, the molecular mechanisms that regulate the activity of the Rac1 pathway during DV infection is not fully understood yet. Recently, Rho-specific guanine nucleotide dissociated inhibitors (Rho GDIs), as a pivotal upstream regulator of Rho GTPase, attract our attention. To identify the role of GDI-1 in DV2 infection, the expression of GDI in Eahy926 cells was detected. Moreover, a GDI-1 down-regulated cell line was constructed to explore the correlation between GDI-1 and Rac1 and to further evaluate the function of GDI in DV life cycle. Our results indicated that DV2 infection could up-regulate GDI-1 expression, and down-regulation of GDI enhanced the activity of Rac1. In addition, down-regulated GDI-1 significantly inhibited all steps of DV2 replication cycle. GDI-1 plays an important role in DV2 infection via negatively regulating the activation of the Rac1-actin pathway. These results not only contribute to our further understanding of the pathogenesis of severe dengue but also provide further insight into the development of antiviral drugs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhatt S, Gething PW, Brady OJ, Messina JP, Farlow AW, Moyes CL, Drake JM, Brownstein JS, Hoen AG, Sankoh O, Myers MF, George DB, Jaenisch T, Wint GR, Simmons CP, Scott TW, Farrar JJ, Hay SI (2013) The global distribution and burden of dengue. Nature 496(7446):504–507. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12060
Vervaeke P, Vermeire K, Liekens S (2015) Endothelial dysfunction in dengue virus pathology. Rev Med Virol 25(1):50–67. https://doi.org/10.1002/rmv.1818
Dalrymple NA, Mackow ER (2012) Roles for endothelial cells in dengue virus infection. Adv Virol 2012:840654. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/840654
Srikiatkhachorn A, Kelley JF (2014) Endothelial cells in dengue hemorrhagic fever. Antiviral Res 109:160–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2014.07.005
Angelini MM, Akhlaghpour M, Neuman BW, Buchmeier MJ (2013) Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus nonstructural proteins 3, 4, and 6 induce double-membrane vesicles. mBio. doi: https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00524-13
Gondar V, Molina-Jimenez F, Hishiki T, Garcia-Buey L, Koutsoudakis G, Shimotohno K, Benedicto I, Majano PL (2015) Apolipoprotein E, but Not Apolipoprotein B, is essential for efficient cell-to-cell transmission of Hepatitis C virus. J Virol 89(19):9962–9973. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00577-15
Stein KR, Gardner TJ, Hernandez RE, Kraus TA, Duty JA, Ubarretxena-Belandia I, Moran TM, Tortorella D (2019) CD46 facilitates entry and dissemination of human cytomegalovirus. Nat Commun 10(1):2699. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10587-1
Mailler E, Waheed AA, Park SY, Gershlick DC, Freed EO, Bonifacino JS (2019) The autophagy protein ATG9A promotes HIV-1 infectivity. Retrovirology 16(1):18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12977-019-0480-3
Baggen J, Thibaut HJ, Strating J, van Kuppeveld FJM (2018) The life cycle of non-polio enteroviruses and how to target it. Nat Rev Microbiol 16(6):368–381. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-018-0005-4
Moller LLV, Klip A, Sylow L (2019) Rho GTPases-emerging regulators of glucose homeostasis and metabolic health. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8050434
Zhang J, Wu N, Gao N, Yan W, Sheng Z, Fan D, An J (2016) Small G Rac1 is involved in replication cycle of dengue serotype 2 virus in EAhy926 cells via the regulation of actin cytoskeleton. Sci China Life Sci 59(5):487–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-016-5042-5
Dransart E, Olofsson B, Cherfils J (2005) RhoGDIs revisited: novel roles in Rho regulation. Traffic 6(11):957–966. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2005.00335.x
Garcia-Mata R, Boulter E, Burridge K (2011) The “invisible hand”: regulation of RHO GTPases by RHOGDIs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12(8):493–504. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3153
Scherle P, Behrens T, Staudt LM (1993) Ly-GDI, a GDP-dissociation inhibitor of the RhoA GTP-binding protein, is expressed preferentially in lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(16):7568–7572. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.90.16.7568
Lelias JM, Adra CN, Wulf GM, Guillemot JC, Khagad M, Caput D, Lim B (1993) cDNA cloning of a human mRNA preferentially expressed in hematopoietic cells and with homology to a GDP-dissociation inhibitor for the rho GTP-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(4):1479–1483. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.90.4.1479
Adra CN, Manor D, Ko JL, Zhu S, Horiuchi T, Van Aelst L, Cerione RA, Lim B (1997) RhoGDIgamma: a GDP-dissociation inhibitor for Rho proteins with preferential expression in brain and pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94(9):4279–4284. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.94.9.4279
Boulter E, Garcia-Mata R (2010) RhoGDI: A rheostat for the Rho switch. Small GTPases 1(1):65–68. https://doi.org/10.4161/sgtp.1.1.12990
Sasaki T, Takai Y (1998) The Rho small G protein family-Rho GDI system as a temporal and spatial determinant for cytoskeletal control. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 245(3):641–645. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1998.8253
Zhang Y, Zhang B (2006) D4-GDI, a Rho GTPase regulator, promotes breast cancer cell invasiveness. Can Res 66(11):5592–5598. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4004
Harding MA, Theodorescu D (2010) RhoGDI signaling provides targets for cancer therapy. Eur J Cancer 46(7):1252–1259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2010.02.025
Said N, Sanchez-Carbayo M, Smith SC, Theodorescu D (2012) RhoGDI2 suppresses lung metastasis in mice by reducing tumor versican expression and macrophage infiltration. J Clin Investig 122(4):1503–1518. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI61392
Peng XC, Chen XX, Zhang YU, Wang HJ, Feng Y (2015) A novel inhibitor of Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor alpha improves the therapeutic efficacy of paclitaxel in Lewis lung carcinoma. Biomed Rep 3(4):473–477. https://doi.org/10.3892/br.2015.475
Ngo AT, Thierheimer ML, Babur O, Rocheleau AD, Huang T, Pang J, Rigg RA, Mitrugno A, Theodorescu D, Burchard J, Nan X, Demir E, McCarty OJ, Aslan JE (2017) Assessment of roles for the Rho-specific guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor Ly-GDI in platelet function: a spatial systems approach. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 312(4):C527–C536. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00274.2016
Watanabe T, Urano E, Miyauchi K, Ichikawa R, Hamatake M, Misawa N, Sato K, Ebina H, Koyanagi Y, Komano J (2012) The hematopoietic cell-specific Rho GTPase inhibitor ARHGDIB/D4GDI limits HIV type 1 replication. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 28(8):913–922. https://doi.org/10.1089/AID.2011.0180
Kramer SR, Goregaoker SP, Culver JN (2011) Association of the Tobacco mosaic virus 126kDa replication protein with a GDI protein affects host susceptibility. Virology 414(2):110–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2010.12.030
Wang JL, Zhang JL, Chen W, Xu XF, Gao N, Fan DY, An J (2010) Roles of small GTPase Rac1 in the regulation of actin cytoskeleton during dengue virus infection. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0000809
(2019). https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dengue-and-severe-dengue
Trejo-Cerro O, Aguilar-Hernandez N, Silva-Ayala D, Lopez S, Arias CF (2019) The actin cytoskeleton is important for rotavirus internalization and RNA genome replication. Virus Res 263:27–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2019.01.003
Lv X, Li Z, Guan J, Hu S, Zhang J, Lan Y, Zhao K, Lu H, Song D, He H, Gao F, He W (2019) Porcine hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus activation of the Integrin alpha5beta1-FAK-Cofilin pathway causes cytoskeletal rearrangement to promote its invasion of N2a cells. J Virol. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01736-18
Ni B, Wen LB, Wang R, Hao HP, Huan CC, Wang X, Huang L, Miao JF, Fan HJ, Mao X (2015) The involvement of FAK-PI3K-AKT-Rac1 pathway in porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus entry. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 458(2):392–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.01.126
Ospina Stella A, Turville S (2018) All-round manipulation of the actin cytoskeleton by HIV. Viruses. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10020063
Boulter E, Garcia-Mata R, Guilluy C, Dubash A, Rossi G, Brennwald PJ, Burridge K (2010) Regulation of Rho GTPase crosstalk, degradation and activity by RhoGDI1. Nat Cell Biol 12(5):477–483. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2049
Griner EM, Theodorescu D (2012) The faces and friends of RhoGDI2. Cancer Metastasis Rev 31(3–4):519–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-012-9376-6
Fiorillo M, Peiris-Pages M, Sanchez-Alvarez R, Bartella L, Di Donna L, Dolce V, Sindona G, Sotgia F, Cappello AR (1859) Lisanti MP (2018) Bergamot natural products eradicate cancer stem cells (CSCs) by targeting mevalonate, Rho-GDI-signalling and mitochondrial metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 9:984–996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2018.03.018
Fang Y, Yi J, Lizhi L, Qiucheng C (2014) Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor beta promotes cell proliferation and invasion by modulating the AKT pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. DNA Cell Biol 33(11):781–786. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2014.2545
Barone I, Brusco L, Gu G, Selever J, Beyer A, Covington KR, Tsimelzon A, Wang T, Hilsenbeck SG, Chamness GC, Ando S, Fuqua SA (2011) Loss of Rho GDIalpha and resistance to tamoxifen via effects on estrogen receptor alpha. J Natl Cancer Inst 103(7):538–552. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djr058
Griner EM, Dancik GM, Costello JC, Owens C, Guin S, Edwards MG, Brautigan DL, Theodorescu D (2015) RhoC is an unexpected target of RhoGDI2 in prevention of lung colonization of bladder cancer. Mol Cancer Res 13(3):483–492. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-14-0420
Yamashita T, Okamura T, Nagano K, Imai S, Abe Y, Nabeshi H, Yoshikawa T, Yoshioka Y, Kamada H, Tsutsumi Y, Tsunoda S (2012) Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor alpha is associated with cancer metastasis in colon and prostate cancer. Pharmazie 67(3):253–255
Coiras M, Camafeita E, Urena T, Lopez JA, Caballero F, Fernandez B, Lopez-Huertas MR, Perez-Olmeda M, Alcami J (2006) Modifications in the human T cell proteome induced by intracellular HIV-1 Tat protein expression. Proteomics 6(Suppl 1):S63-73. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.200500437
Saxena R, Gupta S, Singh K, Mitra K, Tripathi AK, Tripathi RK (2015) Proteomic profiling of SupT1 cells reveal modulation of host proteins by HIV-1 Nef variants. PLoS ONE 10(4):e0122994. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0122994
Cossart P, Helenius A (2014) Endocytosis of viruses and bacteria. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a016972
Stradal TEB, Schelhaas M (2018) Actin dynamics in host-pathogen interaction. FEBS Lett 592(22):3658–3669. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.13173
Leffers H, Nielsen MS, Andersen AH, Honore B, Madsen P, Vandekerckhove J, Celis JE (1993) Identification of two human Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor proteins whose overexpression leads to disruption of the actin cytoskeleton. Exp Cell Res 209(2):165–174. https://doi.org/10.1006/excr.1993.1298
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81671971, 81871641, 81972979, U1602223 and U1902210), Key Project of Beijing Natural Science Foundation B (KZ201810025035), the Scientific Research Plan of the Beijing Municipal Education Committee (KM201710025002) and the Foundation of Capital Medical University (PYZ19064).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NG designed the study. DYF, NW, JZ and NG performed the experiments. ZYW analyzed the data. NG wrote the paper. PGW and JA reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, D., Wu, N., Zhang, J. et al. Effect of the Rho GTPase inhibitor-1 on the entry of dengue serotype 2 virus into EAhy926 cells. Mol Biol Rep 47, 9739–9747 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05980-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05980-9