Abstract
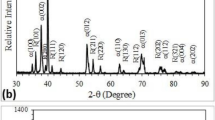
The effects of Ti addition on the microstructure and tribological properties of in situ composite carbide WC-TiC/FeNi coating were studied using XRD, SEM, EDS, and friction and dry sliding wear tests. The results show that the composite carbide WC-TiC was successfully in situ synthesized in the coating, and with Ti addition increased by 0.1 from 0.1 to 0.4 wt.%, the in situ carbide TiC increased from 3.4 to 24.4 vol.%, while the carbide WC decreased from 32.5 to 24.2 vol.%, and the coating hardness increased from 1027 to 1196 HV4.9. The friction and dry sliding wear tests show that for WC-TiC/FeNi composite coating, the addition of Ti can not only reduce the friction coefficient, the mass loss of both the coatings and its counterpart but also improve the friction stability, service life, and wear rate (WR). The relationship between the Ti addition and the coating wear rate fits the exponential decay equation WR = 10.6 − 0.089 \(\times\) e (Ti/0.098). The main wear mechanisms of in situ WC-TiC/FeNi composite carbide coating are abrasive wear, oxidative wear, and micro-plow wear.















Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Z.H. Qiao, J. Rathel, L.M. Berger, and M. Herrmann, Investigation of Binderless WC-TiC-Cr3C2 Hard Materials Prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS), Int. J. Refract. Met. H., 2013, 38, p 7–14.
Z.X. Guo, J. Xiong, M. Yang, X.Y. Song, and C.J. Jiang, Effect of Mo2C on the Microstructure and Properties of WC-TiC-Ni Cemented Carbide, Int. J. Refract. Met. H., 2008, 26(6), p 601–605.
H.C. Kim, D.K. Kim, K.D. Woo, I.Y. Ko, and I.J. Shon, Consolidation of Binderless WC-TiC by High Frequency Induction Heating Sintering, Int. J. Refract. Met. H., 2008, 26(1), p 48–54.
K.H. Lee, S.I. Cha, B.K. Kim, and S.H. Hong, Effect of WC/TiC Grain Size Ratio on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of WC-TiC-Co Cemented Carbides, Int. J. Refract. Met. H., 2006, 24(1–2), p 109–114.
D. Duman, H. Gokce, and H. Cimenoglu, Synthesis, Microstructure, and Mechanical Properties of WC-TiC-Co Ceramic Composites, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2012, 32(7), p 1427–1433.
J.J. Roa, E. Jimenez-Pique, C. Verge, J.M. Tarrago, A. Mateo, J. Fair, and L. Llanes, Intrinsic Hardness of Constitutive Phases in WC-Co Composites: Nanoindentation Testing, Statistical Analysis, WC Crystal Orientation Effects and Flow Stress for the Constrained Metallic Binder, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2015, 35(13), p 3419–3425.
M. Zhang, M. Li, J. Chi, S. Wang, L. Ren, M. Fang, and C. Zhou, Microstructure Evolution, Recrystallization and Tribological Behavior of TiC/WC Composite Ceramics Coating, Vacuum, 2019, 166, p 64–71.
B. Fotovvati, N. Namdari, and A. Dehghanghadikolaei, On Coating Techniques for Surface Protection: A Review, J. Manuf. Mater. Process., 2019, 3(1), p 28.
A. Garcia, M.R. Fernandez, J.M. Cuetos, R. Gonzalez, A. Ortiz, and M. Cadenas, Study of the Sliding Wear and Friction Behavior of WC plus NiCrBSi Laser Cladding Coatings as a Function of Actual Concentration of WC Reinforcement Particles in Ball-on-Disk Test, Tribol. Lett., 2016, 63(3), p 41.
D. Shu, Z. Li, K. Zhang, C. Yao, D. Li, and Z. Dai, In Situ Synthesized High Volume Fraction WC Reinforced Ni-Based Coating by Laser Cladding, Mater. Lett., 2017, 195, p 178–181.
D. Gu and W. Meiners, Microstructure Characteristics and Formation Mechanisms of in situ WC Cemented Carbide Based Hardmetals Prepared by Selective Laser Melting, Mat. Sci. Eng. A-Struct., 2010, 527(29–30), p 7585–7592.
M. Zhang, M. Li, J. Chi, S. Wang, L. Ren, and M. Fang, Microstructure and Tribology Properties of In-Situ MC(M:Ti, Nb) Coatings Prepared Via PTA Technology, Vacuum, 2019, 160, p 264–271.
M. Zhang, M. Li, J. Chi, S. Wang, S. Yang, J. Yang, and Y. Wei, Effect of Ti on Microstructure Characteristics, Carbide Precipitation Mechanism and Tribological Behavior of Different WC Types Reinforced Ni-Based Gradient Coating, Surf. Coat. Tech., 2019, 374, p 645–655.
T. Liyanage, G. Fisher, and A.P. Gerlich, Microstructures and Abrasive Wear Performance of PTAW Deposited Ni–WC Overlays Using Different Ni-alloy Chemistries, Wear, 2012, 274, p 345–354.
P. Skarvelis, G.D. Papadimitriou, and M. Perraki, Self Lubricating Composite Coatings Containing TiC-MnS or WC-MnS Compounds Prepared by the Plasma Transferred Arc (PTA) Technique, J. Tribol-T Asme., 2010, 132(3), p 1–8.
D.X. Peng, Optimizing wear Resistance of Ceramic (TiN, WC and TiC) Clad Layer by Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), Ind. Lubr. Tribol., 2014, 66(3), p 452–458.
P. Yu, X. Chai, D. Landwehr, and S. Kou, Ni-WC Hardfacing by Gas Metal Arc Welding, Weld J., 2016, 95(12), p 451–466.
N. Vashishtha, R.K. Khatirkar, and S.G. Sapate, Tribological Behaviour of HVOF Sprayed WC-12Co, WC-10Co-4Cr and Cr3C2-25NiCr Coatings, Tribol. Int., 2017, 105, p 55–68.
P.C. Du, X.P. Zhu, Y. Meng, H. Feng, Q.F. Wang, and M.K. Lei, Water-Lubricated Tribological Behavior of WC-Ni Coatings Deposited by Off-Angle HVOF Spraying, Surf. Coat. Tech., 2017, 309, p 663–670.
X.B. Zhao, Y.G. Zhuo, S. Liu, Y.F. Zhou, C.C. Zhao, C.X. Wang, and Q.X. Yang, Investigation on WC/TiC Interface Relationship in Wear-Resistant Coating by First-Principles, Surf. Coat. Tech., 2016, 305, p 200–207.
L.B. Niu, Y.H. Xu, and X.G. Wang, Fabrication of WC/Fe Composite Coating by Centrifugal Casting Plus In-Situ Synthesis Techniques, Surf. Coat. Tech., 2010, 205(2), p 551–556.
Y. Yuan, H. Wu, M. You, Z. Li, and Y. Zhang, Improving Wear Resistance and Friction Stability of FeNi Matrix Coating by In-Situ Multi-Carbide WC-TiC via PTA Metallurgical Reaction, Surf. Coat. Tech., 2019, 378, p 124957.
Y. Yuan and Z. Li, A Novel Approach of In-Situ Synthesis of WC Particulate-Reinforced Fe-30Ni Ceramic Metal Coating, Surf. Coat. Tech., 2017, 328, p 256–265.
Y. Yuan and Z. Li, Microstructure and Tribology Behaviors of In-Situ WC/Fe Carbide Coating Fabricated by Plasma Transferred Arc Metallurgic Reaction, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017, 423(Supplement C), p 13–24.
J.B. Roerdink and A. Meijster, The Watershed Transform: Definitions, Algorithms and Parallelization Strategies, Fund. Inform., 2000, 41(1,2), p 187–228.
Y. Yuan and Z. Li, Microstructure and Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of Fe-Based (Cr, Fe)7C3 Composite Coating Fabricated by PTA Welding Process, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2013, 22(11), p 3439–3449.
Y. Yuan and Z. Li, Effects of Rod Carbide Size, Content, Loading and Sliding Distance on the Friction and Wear Behaviors of (Cr, Fe)7C3-Reinforced α-Fe Based Composite Coating Produced Via PTA Welding Process, Surf. Coat. Tech., 2014, 248, p 9–22.
B. Kaplan, S. Norgren, M. Schwind, and M. Selleby, Thermodynamic Calculations and Experimental Verification in the WC-Co-Cr Cemented Carbide System, Int. J. Refract. Met. H., 2015, 48, p 257–262.
T.S. Eyre, Wear Resistance of Metals, Treatise on Materials Science & Technology. D. Scott, Ed., Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1979, p 363–442
N. Lin, Y.H. He, C.H. Wu, S.F. Liu, X.H. Xiao, and Y. Jiang, Influence of TiC Additions on the Corrosion Behaviour of WC-Co Hardmetals in Alkaline Solution, Int. J. Refract. Met. H., 2014, 46, p 52–57.
J.A. Fouts, P.J. Shiller, K.K. Mistry, R.D. Evans, and G.L. Doll, Additive Effects on the Tribological Performance of WC/a-C: H and TiC/a-C: H Coatings in Boundary Lubrication, Wear, 2017, 372, p 104–115.
J. Pirso, M. Viljus, and S. Letunovits, Friction and Dry Sliding Wear Behaviour of Cermets, Wear, 2006, 260(7–8), p 815–824.
M. Guo-zheng, X. Bin-shi, W. Hai-dou, S. Hong-juan, and Y. Da-xiang, Effect of Surface Nanocrystallization on the Tribological Properties of 1Cr18Ni9Ti Stainless Steel, Mater. Lett., 2011, 65(9), p 1268–1271.
A. Emamian, S.F. Corbin, and A. Khajepour, Tribology Characteristics of In-Situ Laser Deposition of Fe-TiC, Surf. Coat. Tech., 2012, 206(22), p 4495–4501.
J. Liu, S. Yang, W.S. Xia, X. Jiang, and C.B. Gui, Microstructure and Wear Resistance Performance of Cu-Ni-Mn Alloy Based Hardfacing Coatings Reinforced by WC Particles, J. Alloy Compd., 2016, 654, p 63–70.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51171116), the Research Foundation of Hubei Key Laboratory of Hydroelectric Machinery Design & Maintenance (2019KJX03), and the Open Fund of Shanghai Key Laboratory of Materials Laser Processing and Modification (MPLM2018-2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, Y., Li, Y., Zhou, X. et al. Effects of Ti Addition on Microstructure and Tribological Properties of In Situ Composite Carbide Coating WC-TiC/FeNi Fabricated by Plasma Transferred Arc Metallurgical Reaction. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 29, 8093–8106 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-05275-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-05275-x