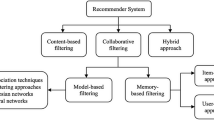
Abstract
Consumer behaviors (e.g., clicking products, adding products to favorites, adding products to carts, and purchasing products) play important roles in inferring consumers’ interests for product recommendation. Although studies have been conducted to incorporate the consumer behaviors for product recommendation, the heterogeneity of the behaviors and their composites were seldom explored for product recommendation. There is a need to capture the heterogeneity of the consumer behaviors and reveal their importance in the product recommendation because the behaviors indicate different consumer preferences for products. To bridge the gap, this research proposes a heterogeneous network-based approach to leverage the consumer behaviors for product recommendation. The proposed approach represents consumers and products as different types of nodes and behaviors as different types of edges. Meta paths that describe behavioral relationships between the consumers and products are used to calculate their similarities, which are further used to generate recommendations. To select informative meta paths for product recommendation, a heuristic selection mechanism is proposed. Besides, the research uses a non-negative matrix factorization method to learn the weights of the selected meta paths and then makes personalized recommendations for consumers. Experimental results based on real-world data demonstrate that the proposed approach not only helps to understand the roles of different consumer behaviors in product recommendation, but also achieves better recommendation performance than several baseline methods.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun, J., Ying, R., Jiang, Y., He, J., & Ding, Z. (2020). Leveraging friend and group information to improve social recommender system. Electronic Commerce Research, 20(1), 147–172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10660-019-09390-3.
Zhou, L. (2020). Product advertising recommendation in E-commerce based on deep learning and distributed expression. Electronic Commerce Research, 20(2), 321–342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10660-020-09411-6.
Wang, Q., Yu, J., & Deng, W. (2019). An adjustable re-ranking approach for improving the individual and aggregate diversities of product recommendations. Electronic Commerce Research, 19(1), 59–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10660-018-09325-4.
Mishra, R., Kumar, P., & Bhasker, B. (2015). A web recommendation system considering sequential information. Decision Support Systems, 75, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2015.04.004.
Wang, J., Huang, P., Zhao, H., Zhang, Z., Zhao, B., & Lee, D. L. (2018). Billion-scale commodity embedding for E-commerce recommendation in Alibaba. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining (pp. 839–848). New York, NY: ACM. https://doi.org/10.1145/3219819.3219869.
Wang, Q., Ma, J., Liao, X., & Du, W. (2017). A context-aware researcher recommendation system for university-industry collaboration on R&D projects. Decision Support Systems, 103, 46–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2017.09.001.
Xu, Y., Zhou, D., & Ma, J. (2019). Scholar-friend recommendation in online academic communities: An approach based on heterogeneous network. Decision Support Systems, 119, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2019.01.004.
Kang, D., & Seo, S. (2019). Personalized smart home audio system with automatic music selection based on emotion. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 78(3), 3267–3276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6733-7.
Oramas, S., Ostuni, V. C., Noia, T. D., Serra, X., & Sciascio, E. D. (2016). Sound and music recommendation with knowledge graphs. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 8(2), 21:1–21:21. https://doi.org/10.1145/2926718.
Xu, W., Sun, J., Ma, J., & Du, W. (2016). A personalized information recommendation system for R&D project opportunity finding in big data contexts. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 59, 362–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2015.01.003.
Liu, Y., Yang, C., Ma, J., Xu, W., & Hua, Z. (2019). A social recommendation system for academic collaboration in undergraduate research. Expert Systems, 36(2), e12365. https://doi.org/10.1111/exsy.12365.
Castro, J., Quesada, F. J., Palomares, I., & Martínez, L. (2015). A consensus-driven group recommender system. International Journal of Intelligent Systems, 30(8), 887–906. https://doi.org/10.1002/int.21730.
Castro, J., Barranco, M. J., Rodríguez, R. M., & Martínez, L. (2018). Group recommendations based on hesitant fuzzy sets. International Journal of Intelligent Systems, 33(10), 2058–2077. https://doi.org/10.1002/int.21922.
Pourgholamali, F., Kahani, M., Bagheri, E., & Noorian, Z. (2017). Embedding unstructured side information in product recommendation. Electronic Commerce Research and Applications, 25, 70–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elerap.2017.08.001.
Zhang, J., & Piramuthu, S. (2018). Product recommendation with latent review topics. Information Systems Frontiers, 20(3), 617–625. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-016-9697-z.
Zhang, M., Wei, X., Guo, X., Chen, G., & Wei, Q. (2019). Identifying complements and substitutes of products: A neural network framework based on product embedding. ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data, 13(3), 34:1–34:29. https://doi.org/10.1145/3320277.
Jing, N., Jiang, T., Du, J., & Sugumaran, V. (2018). Personalized recommendation based on customer preference mining and sentiment assessment from a Chinese e-commerce website. Electronic Commerce Research, 18(1), 159–179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10660-017-9275-6.
Sun, L., Guo, J., & Zhu, Y. (2018). A multi-aspect user-interest model based on sentiment analysis and uncertainty theory for recommender systems. Electronic Commerce Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10660-018-9319-6.
Linden, G., Smith, B., & York, J. (2003). Amazon.com recommendations: Item-to-item collaborative filtering. IEEE Internet Computing, 7(1), 76–80. https://doi.org/10.1109/MIC.2003.1167344.
Jia, R., Li, R., Yu, M., & Wang, S. (2017). E-commerce purchase prediction approach by user behavior data. In 2017 international conference on computer, information and telecommunication systems (CITS) (pp. 1–5). https://doi.org/10.1109/CITS.2017.8035294.
Hidasi, B., Karatzoglou, A., Baltrunas, L., & Tikk, D. (2016). Session-based recommendations with recurrent neural networks. arXiv:1511.06939 [cs]. Retrieved from http://arxiv.org/abs/1511.06939.
Wu, S., Tang, Y., Zhu, Y., Wang, L., Xie, X., & Tan, T. (2019). Session-based recommendation with graph neural networks. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 33(01), 346–353. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v33i01.3301346.
Wei, X., Zuo, X., & Yang, B. (2019). Sequential recommendation based on long-term and short-term user behavior with self-attention. In C. Douligeris, D. Karagiannis & D. Apostolou (Eds.), Knowledge science engineering and management (pp. 72–83). Cham: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-29551-6_7.
Shi, C., Hu, B., Zhao, W. X., & Yu, P. S. (2019). Heterogeneous information network embedding for recommendation. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 31(2), 357–370. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2018.2833443.
Yu, J., Gao, M., Li, J., Yin, H., & Liu, H. (2018). Adaptive implicit friends identification over heterogeneous network for social recommendation. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM international conference on information and knowledge management (pp. 357–366). Torino: Association for Computing Machinery. https://doi.org/10.1145/3269206.3271725.
He, X., Dong, Y., Zhen, Z., Wu, Y., Jiang, G., Meng, X., & Ma, S. (2019). Weighted meta paths and networking embedding for patent technology trade recommendations among subjects. Knowledge-Based Systems, 184, 104899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2019.104899.
DENG, W., & Ma, J. (2017). Leveraging heterogeneous information network for community recommendation. In ICIS 2017 proceedings. Retrieved from http://aisel.aisnet.org/icis2017/HCI/Presentations/4.
Hu, L., Wang, Y., Xie, Z., & Wang, F. (2017). Semantic preference-based personalized recommendation on heterogeneous information network. IEEE Access : Practical Innovations, Open Solutions, 5, 19773–19781. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2751682.
Wang, Q., Du, W., Ma, J., & Liao, X. (2019). Recommendation mechanism for patent trading empowered by heterogeneous information networks. International Journal of Electronic Commerce, 23(2), 147–178. https://doi.org/10.1080/10864415.2018.1564549.
Shi, C., Li, Y., Zhang, J., Sun, Y., & Yu, P. S. (2017). A survey of hinformation network analysis. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 29(1), 17–37. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2016.2598561.
Sun, Y., Han, J., Yan, X., Yu, P. S., & Wu, T. (2011). PathSim: Meta path-based top-k similarity search in heterogeneous information networks. In Proceedings of the 2011 international conference on very large data bases (VLDB’11).
Liu, H., Jiang, Z., Song, Y., Zhang, T., & Wu, Z. (2019). User preference modeling based on meta paths and diversity regularization in heterogeneous information networks. Knowledge-Based Systems, 181, 104784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2019.05.027.
Lao, N., & Cohen, W. W. (2010). Fast query execution for retrieval models based on path-constrained random walks. In Proceedings of the 16th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining (pp. 881–888). New York, NY: ACM. https://doi.org/10.1145/1835804.1835916.
Shi, C., Kong, X., Huang, Y., Yu, P. S., & Wu, B. (2014). HeteSim: a general framework for relevance measure in heterogeneous networks. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 26(10), 2479–2492. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2013.2297920.
Meng, X., Shi, C., Li, Y., Zhang, L., & Wu, B. (2014). Relevance measure in large-scale heterogeneous networks. In Web technologies and applications (pp. 636–643). Presented at the Asia-Pacific web conference. Cham: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-11116-2_61.
Lin, C.-J. (2007). Projected gradient methods for nonnegative matrix factorization. Neural Computation, 19(10), 2756–2779. https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.2007.19.10.2756.
Shani, G., & Gunawardana, A. (2011). Evaluating recommendation systems. In F. Ricci, L. Rokach, B. Shapira & P. B. Kantor (Eds.), Recommender systems handbook (pp. 257–297). Boston: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-85820-3_8.
Koren, Y., Bell, R., & Volinsky, C. (2009). Matrix factorization techniques for recommender systems. IEEE Computer Society, 42–49.
Cooper, C., Lee, S. H., Radzik, T., & Siantos, Y. (2014). Random walks in recommender systems: exact computation and simulations. In Proceedings of the 23rd international conference on world wide web (pp. 811–816). New York, NY: ACM. https://doi.org/10.1145/2567948.2579244.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, W. Leveraging consumer behaviors for product recommendation: an approach based on heterogeneous network. Electron Commer Res 22, 1079–1105 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10660-020-09441-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10660-020-09441-0