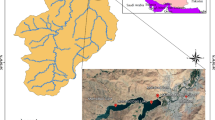
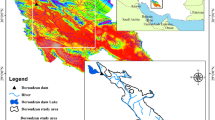
Abstract
Evaporation is a primary component of the hydrological cycle, water resources management and forward planning. The succeed management for the dam system is based on the accurate prediction of the reservoir evaporation magnitude. Physical models applied in the prediction of evaporation can encounter obstacles in respect to accurate estimations of evaporation due to the inherent challenges in respect to the mathematical procedure that could fail to address the natural processes and initial conditions that drive the evaporation patterns. To address these limitations, the present study aims to design a new model using the modified Coactive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (CANFIS) algorithm to improve feature extraction process in a purely data-driven model. The new approach comprised of the adjustments made to the back-propagation algorithm, allowing the automatic updating of the membership rules and hence, providing the center-weighted set rather than the global weight sets for input-target feature mapping. The predictive ability of the modified CANIFIS model is benchmarked in respect to the conventional ANFIS, SVR and RBF-NN model by statistical performance metrics. To explore its efficiency, the modified CANFIS method is applied for evaporation prediction in two diverse climatic environments. The results revealed the superiority of the modified CANFIS model for evaporation prediction in both Aswan High Dam (AHD) and Timah Tasoh Dam (TTD). The statistical indicators supported the better performance of the modified CANFIS model, which significantly outperforms other proposed models to attain relative error value less than (23% for AHD, 20% for TTD), MAE (12.72 mm month−1 for AHD, 7.63 mm month−1 for TTD), RMSE (15.42 mm month−1 for AHD, 8.53 mm month−1 for TTD) and a relative large coefficient of determination (0.96 for AHD, 0.91 for TTD).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alecsandru C, Ishak S (2004) Hybrid model-based and memory-based traffic prediction system. Transp Res Rec J Transp Res Board 1879:59–70. https://doi.org/10.3141/1879-08
Aljanabi QA, Chik Z, Allawi MF et al (2017) Support vector regression-based model for prediction of behavior stone column parameters in soft clay under highway embankment. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2807-5
Allawi MF, El-Shafie A (2016) Utilizing RBF-NN and ANFIS methods for multi-lead ahead prediction model of evaporation from reservoir. Water Resour Manag 30:4773–4788. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1452-1
Allawi MF, Jaafar O, Mohamad Hamzah F et al (2017) Reservoir inflow forecasting with a modified coactive neuro-fuzzy inference system: a case study for a semi-arid region. Theor Appl Climatol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-017-2292-5
Allawi MF, Jaafar O, Ehteram M et al (2018a) Synchronizing artificial intelligence models for operating the dam and reservoir system. Water Resour Manag. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-018-1996-3
Allawi MF, Jaafar O, Mohamad Hamzah F et al (2018b) Review on applications of artificial intelligence methods for dam and reservoir-hydro-environment models. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1867-8
Behzad M, Asghari K, Eazi M, Palhang M (2009) Generalization performance of support vector machines and neural networks in runoff modeling. Expert Syst Appl 36:7624–7629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2008.09.053
Bozorg-Haddad O, Zarezadeh-Mehrizi M, Abdi-Dehkordi M et al (2016) A self-tuning ANN model for simulation and forecasting of surface flows. Water Resour Manag 30:2907–2929. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1301-2
Broomhead D, Lowe D (1988) Multivariable functional interpolation and adaptive networks. Complex Syst 2:327–355
Budu K (2014) Comparison of wavelet-based ANN and regression models for reservoir inflow forecasting. J Hydrol Eng 19:1385–1400. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000892
Cooley KR (1983) Evaporation reduction: summary of long-term tank studies. J Irrig Drain Eng 109:89–98. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9437(1983)109:1(89)
Deo RC, Samui P (2017) Forecasting evaporative loss by least-square support-vector regression and evaluation with genetic programming, Gaussian process, and minimax probability machine regression: case study of Brisbane City. J Hydrol Eng 22:5017003. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0001506
Deo RC, Samui P, Kim D (2016) Estimation of monthly evaporative loss using relevance vector machine, extreme learning machine and multivariate adaptive regression spline models. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 30:1769–1784. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-015-1153-y
El-Shafie A, Noureldin A (2011) Generalized versus non-generalized neural network model for multi-lead inflow forecasting at Aswan High Dam. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 15:841–858. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-15-841-2011
Eray O, Mert C, Kisi O (2017) Comparison of multi-gene genetic programming and dynamic evolving neural-fuzzy inference system in modeling pan evaporation. Hydrol Res nh2017076. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.2017.076
Ghorbani MA, Deo RC, Yaseen ZM et al (2017) Pan evaporation prediction using a hybrid multilayer perceptron-firefly algorithm (MLP-FFA) model: case study in North Iran. Theor Appl Climatol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-017-2244-0
Guo J, Zhou J, Qin H et al (2011) Monthly streamflow forecasting based on improved support vector machine model. Expert Syst Appl 38:13073–13081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2011.04.114
Guven A, Kişi Ö (2011) Daily pan evaporation modeling using linear genetic programming technique. Irrig Sci 29:135–145
Hanafy TOS, Hanafy TOS (2014) A new algorithm to model highly nonlinear system based coactive neuro fuzzy inference system. Int J Comput Appl 94:9–20
Hidalgo IG, Barbosa PSF, Francato AL et al (2015) Management of inflow forecasting studies. Water Pract Technol 10:402. https://doi.org/10.2166/wpt.2015.050
Hosseinzadeh Talaee P, Tabari H, Abghari H (2014) Pan evaporation and reference evapotranspiration trend detection in western Iran with consideration of data persistence. Hydrol Res 45:213. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.2013.058
Izadbakhsh MA, Javadikia H (2014) Application of hybrid FFNN-genetic algorithm for predicting evaporation in storage dam reservoirs. Agric Commun 2:57–62
Jang JSR, Sun CT (1997) Neuro-fuzzy and soft computing: a computational approach to learning and machine intelligence. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ
Kashiwao T, Nakayama K, Ando S et al (2017) A neural network-based local rainfall prediction system using meteorological data on the Internet: a case study using data from the Japan Meteorological Agency. Appl Soft Comput J 56:317–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.03.015
Keshtegar B, Allawi MF, Afan HA, El-Shafie A (2016) Optimized river stream-flow forecasting model utilizing high-order response surface method. Water Resour Manag 30:3899–3914. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1397-4
Keskin ME, Terzi Ö (2006) Artificial neural network models of daily pan evaporation. J Hydrol Eng 11:65–70. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0699(2006)11:1(65)
Keskin ME, Terzi Ö, Taylan D (2004) Fuzzy logic model approaches to daily pan evaporation estimation in western Turkey (Estimation de l’évaporation journalière du bac dans l’Ouest de la Turquie par des modèles à base de logique floue). Hydrol Sci J 4:9. https://doi.org/10.1623/hysj.49.6.1001.55718
Kişi Ö (2006) Daily pan evaporation modelling using a neuro-fuzzy computing technique. J Hydrol 329:636–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.03.015
Kişi Ö, Tombul M (2013) Modeling monthly pan evaporations using fuzzy genetic approach. J Hydrol 477:203–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.11.030
Koza JR (1992) Genetic programming: on the programming of computers by means of natural selection. MIT Press, Cambridge
Lohani AK, Kumar R, Singh RD (2012) Hydrological time series modeling: a comparison between adaptive neuro-fuzzy, neural network and autoregressive techniques. J Hydrol 442:23–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.03.031
Lu X, Ju Y, Wu L et al (2018) Daily pan evaporation modeling from local and cross-station data using three tree-based machine learning models. J Hydrol 566:668–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.09.055
Maier HR, Dandy GC (2000) Neural networks for the prediction and forecasting of water resources variables: a review of modelling issues and applications. Environ Model Softw 15:101–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1364-8152(99)00007-9
Majhi B, Naidu D (2020) Pan evaporation modeling in different agroclimatic zones using functional link artificial neural network. Inf Process Agric. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inpa.2020.02.007
Majhi B, Naidu D, Mishra AP, Satapathy SC (2019) Improved prediction of daily pan evaporation using Deep-LSTM model. Neural Comput Appl 32:7823–7838. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04127-7
Mekanik F, Imteaz MA, Talei A (2016) Seasonal rainfall forecasting by adaptive network-based fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) using large scale climate signals. Clim Dyn 46:3097–3111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2755-2
Memarian H, Pourreza Bilondi M, Rezaei M (2016) Drought prediction using co-active neuro-fuzzy inference system, validation, and uncertainty analysis (case study: Birjand, Iran). Theor Appl Climatol 125:541–554. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-015-1532-9
Moghaddamnia A, Ghafari M, Piri J, Han D (2009a) Evaporation estimation using support vector machines technique. Int J Eng Appl Sci 5:415–423
Moghaddamnia A, Ghafari Gousheh M, Piri J et al (2009b) Evaporation estimation using artificial neural networks and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system techniques. Adv Water Resour 32:88–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2008.10.005
Mohamadi S, Ehteram M, El-Shafie A (2020) Accuracy enhancement for monthly evaporation predicting model utilizing evolutionary machine learning methods. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17:3373–3396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02619-6
Nourani V, Fard M (2012) Sensitivity analysis of the artificial neural network outputs in simulation of the evaporation process at different climatologic regimes. Adv Eng Softw 47:127–146
Nourani V, Kisi Ö, Komasi M (2011) Two hybrid Artificial Intelligence approaches for modeling rainfall–runoff process. J Hydrol 402:41–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.03.002
Nourani V, Sayyah Fard M (2012) Sensitivity analysis of the artificial neural network outputs in simulation of the evaporation process at different climatologic regimes. Adv Eng Softw 47:127–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ADVENGSOFT.2011.12.014
Omar MH, El-Bakry MM (1981) Estimation of evaporation from the lake of the Aswan High Dam (Lake Nasser) based on measurements over the lake. Agric Meteorol 23:293–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-1571(81)90115-1
Patil S, Valunjkar S (2016) Utility of coactive neuro-fuzzy inference system for runoff prediction in comparison with multilayer perception. Int J Eng Res 8:156–160. https://doi.org/10.17950/ijer/v5i1/036
Penman H (1948) Natural evaporation from open water, bare soil and grass. Proc R Soc Lond 193:120–145
Piri J, Amin S, Moghaddamnia A (2009) Daily pan evaporation modeling in a hot and dry climate. J Hydrol 14:803–81
Saemi M, Ahmadi M (2008) Integration of genetic algorithm and a coactive neuro-fuzzy inference system for permeability prediction from well logs data. Transp Porous Media 71:273–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-007-9125-4
Salih SQ, Allawi MF, Yousif AA et al (2019) Viability of the advanced adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system model on reservoir evaporation process simulation: case study of Nasser Lake in Egypt. Eng Appl Comput Fluid Mech 13:878–891. https://doi.org/10.1080/19942060.2019.1647879
Tabari H, Marofi S, Sabziparvar A (2010a) Estimation of daily pan evaporation using artificial neural network and multivariate non-linear regression. Irrig Sci 28:399–406
Tabari H, Marofi S, Sabziparvar A-A (2010b) Estimation of daily pan evaporation using artificial neural network and multivariate non-linear regression. Irrig Sci 28:399–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-009-0201-0
Tabari H, Hosseinzadeh Talaee P, Abghari H (2012) Utility of coactive neuro-fuzzy inference system for pan evaporation modeling in comparison with multilayer perceptron. Meteorol Atmos Phys 116:147–154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-012-0184-x
Wu L, Huang G, Fan J et al (2020) Hybrid extreme learning machine with meta-heuristic algorithms for monthly pan evaporation prediction. Comput Electron Agric 168:105115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2019.105115
Acknowledgements
The authors greatly acknowledge the datasets provided by Nile Water Authority (NWA) and Aswan High Dam Authority (AHDA), Ministry of Water Resources and Irrigation, Egypt and Water Resources Management and Hydrology Division, Department of Irrigation and Drainage (DID), Malaysia. We would like to thank the University of Malaya Research Grant (UMRG) coded RP025A-18SUS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allawi, M.F., Ahmed, M.L., Aidan, I.A. et al. Developing reservoir evaporation predictive model for successful dam management. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 35, 499–514 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-020-01918-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-020-01918-6