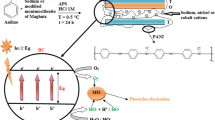
Abstract
Metal–organic frameworks (MOF) have attracted great attention in the field of wastewater treatment. When MOF nanoparticles are used for adsorption applications, the nanoparticles normally have to be separated from the dispersed suspension by filtration or centrifugation for regeneration or recycling. In order to avoid this costly and time consuming process, MOF (NH2-MIL-125) nanofibrous hybrid membranes with photocatalytic properties were successfully fabricated in this study. The MOF membranes were characterized by using XRD, SEM, FTIR, TGA, BET, and UV–Vis. The adsorption (including capacity, mechanism, dynamic, and isotherm) of dyes by the membranes is studied in great detail. The membranes exhibit great adsorption capacity to methylene blue and sodium fluorescein, and the adsorption is dominated by steric hindrance of dye molecule, not the π–π interactions and the zeta potential. Most importantly, the MOF membranes could be easily separated from the dyes solution and regenerated via a visible light catalytic degradation process for recycling, and the photocatalytic mechanism is discussed.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang S, Peng Y (2010) Natural zeolites as effective adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment. Chem Eng J 156:11–24
Brillas E, Martínez-Huitle CA (2015) Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods. An updated review. Appl Catal B Environ 166:603–643
Saratale RG, Saratale GD, Kalyani DC, Chang JS, Govindwar SP (2009) Enhanced decolorization and biodegradation of textile azo dye Scarlet R by using developed microbial consortium-GR. Bioresour Technol 100:2493–2500
Robinson T, McMullan G, Marchant R, Nigam P (2001) Remediation of dyes in textile effluent: a critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Bioresour Technol 77:247–255
Salleh MAM, Mahmoud DK, Karim WAWA, Idris A (2011) Cationic and anionic dye adsorption by agricultural solid wastes: a comprehensive review. Desalination 280:1–13
Adeyemo AA, Adeoye IO, Bello OS (2012) Metal organic frameworks as adsorbents for dye adsorption: overview, prospects and future challenges. Toxicol Environ Chem 94:1846–1863
Zhou H, Long JR, Yaghi OM (2012) Introduction to metal–organic frameworks. Chem Rev 112:673–674
Li H, Eddaoudi M, O’Keeffe M, Yaghi OM (1999) Design and synthesis of an exceptionally stable and highly porous metal-organic framework. Nature 402:276–279
Chen Q, He Q, Lv M et al (2015) Selective adsorption of cationic dyes by UiO-66-NH2. Appl Surf Sci 327:77–85
Oveisi M, Asli MA, Mahmoodi NM (2018) MIL-Ti metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) nanomaterials as superior adsorbents: synthesis and ultrasound-aided dye adsorption from multicomponent wastewater systems. J Hazard Mater 347:123–140
Ahmed I, Khan NA, Yoon JW, Chang J-S, Jhung SH (2017) Protonated MIL-125-NH2: remarkable adsorbent for the removal of Quinoline and Indole from liquid fuel. ACS Appl Mater Inter 9:20938–20946
Efome JE, Rana D, Matsuura T, Lan CQ (2018) Insight studies on metal-organic framework nanofibrous membrane adsorption and activation for heavy metal ions removal from aqueous solution. ACS Appl Mater Inter 10:18619–18629
Wang C, Zheng T, Luo R et al (2018) In Situ growth of ZIF-8 on PAN fibrous filters for highly efficient U(VI) removal. ACS Appl Mater Inter 10:24164–24171
Wang C, Wang H, Luo R et al (2017) Metal–organic framework one-dimensional fibers as efficient catalysts for activating peroxymonosulfate. Chem Eng J 330:262–271
Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Wang X, Yu J, Ding B (2018) Ultrahigh metal–organic framework loading and flexible nanofibrous membranes for efficient CO2 capture with long-term, ultrastable recyclability. ACS Appl Mater Inter 10:34802–34810
Gu Z, Zhang J (2019) Epitaxial growth and applications of oriented metal–organic framework thin films. Coord Chem Rev 378:513–532
Liu C, Wu Y, Morlay C et al (2016) General deposition of metal–organic frameworks on highly adaptive organic–inorganic hybrid electrospun fibrous substrates. ACS Appl Mater Inter 8:2552–2561
Jeremias F, Lozan V, Henninger SK, Janiak C (2013) Programming MOFs for water sorption: amino-functionalized MIL-125 and UiO-66 for heat transformation and heat storage applications. Dalton Trans 42:15967–15973
Kim S-N, Kim J, Kim H-Y, Cho H-Y, Ahn W-S (2013) Adsorption/catalytic properties of MIL-125 and NH2-MIL-125. Catal Today 204:85–93
Sun D, Ye L, Li Z (2015) Visible-light-assisted aerobic photocatalytic oxidation of amines to imines over NH2-MIL-125(Ti). Appl Catal B Environ 164:428–432
Fu Y, Sun D, Chen Y et al (2012) An amine-functionalized titanium metal–organic framework photocatalyst with visible-light-induced activity for CO2 reduction. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:3364–3367
Liu C, Wu Y, Yu A, Li F (2014) Cooperative fabrication of ternary nanofibers with remarkable solvent and temperature resistance by electrospinning. RSC Adv 4:31400–31408
Hendon CH, Tiana D, Fontecave M et al (2013) Engineering the optical response of the titanium-MIL-125 metal-organic framework through ligand functionalization. J Am Chem Soc 135:10942–10945
Kawase Y, Isaka Y, Kuwahara Y, Mori K, Yamashita H (2019) Ti cluster-alkylated hydrophobic MOFs for photocatalytic production of hydrogen peroxide in two-phase systems. Chem Commun 55:6743–6746
Peterson GW, Lu AX, Epps TH (2017) Tuning the morphology and activity of electrospun polystyrene/UiO-66-NH2 metal–organic framework composites to enhance chemical warfare agent removal. ACS Appl Mater Inter 9:32248–32254
Wu GM, Lin SJ, Yang CC (2006) Preparation and characterization of PVA/PAA membranes for solid polymer electrolytes. J Membr Sci 275:127–133
Pirzada T, Arvidson SA, Saquing CD, Shah SS, Khan SA (2012) Hybrid Silica–PVA Nanofibers via Sol-Gel Electrospinning. Langmuir 28:5834–5844
Bibi R, Wei L, Shen Q et al (2017) Effect of amino functionality on the uptake of cationic dye by titanium-based metal organic frameworks. J Chem Eng Data 62:1615–1622
Dan-Hardi M, Serre C, Frot T et al (2009) A new photoactive crystalline highly porous titanium(IV) dicarboxylate. J Am Chem Soc 131:10857–10859
Andrew Lin K-Y, Chang H-A (2015) A zeolitic imidazole framework (ZIF)–sponge composite prepared via a surfactant-assisted dip-coating method. J Mater Chem A 3:20060–20064
Pei R, Fan L, Zhao F et al (2020) 3D-printed metal-organic frameworks within biocompatible polymers as excellent adsorbents for organic dyes removal. J Hazard Mater 384:121418
Silveira JV, Moraes EC, Moura JVB et al (2020) Mo-doped WO3 nanowires for adsorbing methylene blue dye from wastewater. J Mater Sci 55:6429–6440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-04472-2
Zhang W, Zhang R-Z, Huang Y-Q, Yang J-M (2018) Effect of the synergetic interplay between the electrostatic interactions, size of the dye molecules, and adsorption sites of MIL-101(Cr) on the adsorption of organic dyes from aqueous solutions. Cryst Growth Des 18:7533–7540
Kim J, Kang T, Kim H, Shin HJ, Oh S-G (2019) Preparation of PVA/PAA nanofibers containing thiol-modified silica particles by electrospinning as an eco-friendly Cu (II) adsorbent. J Ind Eng Chem 77:273–279
Foo KY, Hameed BH (2010) Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem Eng J 156:2–10
Wang Y, Katepalli H, Gu T, Hatton TA, Wang Y (2018) Functionalized magnetic silica nanoparticles for highly efficient adsorption of Sm3+ from a dilute aqueous solution. Langmuir 34:2674–2684
Hasan Z, Choi E-J, Jhung SH (2013) Adsorption of naproxen and clofibric acid over a metal–organic framework MIL-101 functionalized with acidic and basic groups. Chem Eng J 219:537–544
Yan J, Huang Y, Miao Y-E, Tjiu WW, Liu T (2015) Polydopamine-coated electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol)/poly(acrylic acid) membranes as efficient dye adsorbent with good recyclability. J Hazard Mater 283:730–739
Shen L, Luo M, Huang L, Feng P, Wu L (2015) A clean and general strategy to decorate a titanium metal–organic framework with noble-metal nanoparticles for versatile photocatalytic applications. Inorg Chem 54:1191–1193
Yang Z, Ding J, Feng J et al (2018) Preparation of BiVO4/MIL-125(Ti) composite with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity for dye degradation. Appl Organomet Chem 32:e4285
Wang H, Yuan X, Wu Y et al (2015) Facile synthesis of amino-functionalized titanium metal-organic frameworks and their superior visible-light photocatalytic activity for Cr(VI) reduction. J Hazard Mater 286:187–194
Rodríguez NA, Savateev A, Grela MA, Dontsova D (2017) Facile synthesis of potassium poly(heptazine imide) (PHIK)/Ti-based metal-organic framework (MIL-125-NH2) composites for photocatalytic applications. ACS Appl Mater Inter 9:22941–22949
Tomita O, Ohtani B, Abe R (2014) Highly selective phenol production from benzene on a platinum-loaded tungsten oxide photocatalyst with water and molecular oxygen: selective oxidation of water by holes for generating hydroxyl radical as the predominant source of the hydroxyl group. Catal Sci Technol 4:3850–3860
Sun Z, Chen Y, Ke Q, Yang Y, Yuan J (2002) Photocatalytic degradation of a cationic azo dye by TiO2/bentonite nanocomposite. J Photochem Photobiol, A 149:169–174
Liu Y, Zhu Y, Xu J, Bai X, Zong R, Zhu Y (2013) Degradation and mineralization mechanism of phenol by BiPO4 photocatalysis assisted with H2O2. Appl Catal B: Environ 142:561–567
Hu Q, Di J, Wang B et al (2019) In-situ preparation of NH2-MIL-125(Ti)/BiOCl composite with accelerating charge carriers for boosting visible light photocatalytic activity. Appl Surf Sci 466:525–534
Acknowledgements
Financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 21802036) and the Science and Technology Department of Hubei Province (grant no. 218CFB110) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Chris Cornelius.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, J., Huang, D., Zeng, F. et al. Photocatalytic MOF fibrous membranes for cyclic adsorption and degradation of dyes. J Mater Sci 56, 3127–3139 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05473-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05473-x