Abstract
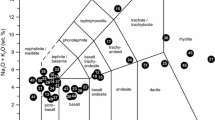
In ancient times, the most widely used rocks, especially in construction of roads and monuments, were sedimentary and magmatic rocks. Natural stones used in the buildings and historical monuments are subjected to atmospheric effects such as freeze-thaw, salt crystalisation and wetting and drying cycles which accelerates abrasion. Therefore, wear resistance of natural stone materials is important for selection of suitable materials in engineering projects. In order to investigate the effect of deterioration on abrasion properties of natural rock samples, three different abrasion tests (Böhme abrasion (BA), wide wheel abrasion (WWA) and aggregate impact value (AIV)) were applied to undeteriorated and artificially deteriorated (samples were subjected to accelerated weathering tests (AWT)) natural rock samples in this study. For the first time, the relationship between AIV-WWA and BA-AIV tests was experimentally investigated. Consequently, the relationships among BA-WWA, BA-AIV and AIV-WWA values were examined, the empirical formulas showing these relationships were developed and high correlations (R2 > 0.80) were obtained. Finally, an abrasion class was proposed using classification of WWA for determining BA and AIV of natural rock samples in this study.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akın M, Özsan A (2011) Evaluation of the long-term durability of yellow travertineusing accelerated weathering tests. Bull Eng Geol Environ 70:101–114
Akın M, Özvan A, Dinçer İ, Topal T (2017) Evaluation of the physico-mechanical parameters affecting the deterioration rate of Ahlat ignimbrites (Bitlis, Turkey). Environ Earth Sci 76:827
ASTM C131/C131M-14 (2006) Standard test method for resistance to degradation of small-size coarse aggregate by abrasion and impact in the Los Angeles machine. ASTM International, West Conshohocken
ASTM C241–290 (2005) Standard test method abrasion resistance stone subjected foot traffic. ASTM International, West Conshohocken
BS 812–112 (1990) Testing aggregates. Method for determination of aggregate impact value (AIV), British Standarts Institution
Çobanoğlu İ, Çelik SB (2017) Assessments on the usability of wide wheel (capon) test as reference abrasion test method for building stones. Constr Build Mater 151:319–330
CS3 (2013) Aggregates for concrete. Construction Standard 141
EN 1926 (2006) Natural stone test methods – determination of uniaxial compressive strength. European Commitee for Standardization, 20
EN 1936 (2006) Natural stone test methods – determination of real density and apparent density and of total and open porosity. European Committee for Standardization, 11
Erdoğan O, Özvan A (2015) Evaluation of strength parameters and quality assessment of different lithotype levels of Edremit (Van) Travertine (Eastern Turkey). J Afr Earth Sci 106:108–117
ISRM (2007) The complete ISRM suggested methods for rock characterization, testing and monitoring: 1974–2006. In: Ulusay R, Hudson JA (eds) Suggested Methods Prepared by the ISRM Commission on Testing Methods. Compilation arranged by the ISRM Turkish National Group, Ankara
ISRM (2015) The ISRM suggested methods for rock characterization, testing and monitoring: 2007-2014, in: R.Ulusay, J.A.Hudson (Eds.), Suggested Methods Prepared by the Commission on Testing Methods. International Society for Rock Mechanics, Springer, 293
Karaca Z, Yılmaz NG, Göktan RM (2012) Considerations on the European Standard EN 14157 Test Methods: abrasion resistance of natural stones used for flooring in buildings. Rock Mech Rock Eng 45:103–111
Mac Gregor ID, Chiu KY (2000) Porosity and wear resistance in stone flooring tiles. J.v Test Eval 28:149–154
Marradi A, Secchiari L, Lezzerini M (2008) The qualification of materials for their application in road stone pavements. Second Int Congr Dimens Stones 29-31(May):225–235
Özvan Erdeve E, Akkaya İ, Özvan A, Tapan M, Bor M (2018) Evaluation of different types of limestones used as marble by nondestructive test methods, Çukurova Üniversitesi Mühendislik-Mimarlık Fakültesi Dergisi, vol. 33, 229–240
Özvan A, Dinçer İ, Acar A (2011) Quality assessment of geo-materials for coastal structures (Yumurtalık, Turkey). Marine Georesour Geotechnol 29(4):299–316
Özvan A, Dinçer İ, Akın M, Oyan V, Tapan M (2015) Experimental studies on ignimbrite and the effect of lichens and capillarity on the deterioration of Seljuk Gravestones. Eng Geol 185:81–95
RILEM (1980) Recommended tests to measure the deterioration of stone and to assess the effectiveness of treatment methods. Commission 25-PEM. Mater Struct 13:175–253
Sousa LMO (2013) The influence of the characteristics of quartz and mineral deterioration on the strength of granitic dimensional stones. Environ Earth Sci 69:1331–1346
Sousa LMO (2014) Petrophysical properties and durability of granites employed as building stone: acomprehensive evaluation. Bull Eng Geol Environ 73:569–588
Sutton DC, Limbert G, Stewart D, Wood RJK (2014) A functional form for wear depth of a ball and a flat surface. Tribol Lett 53:173–179
TS EN 12371 (2002) Natural stones-testing methods-determination of frost resistance. Turkish Standards Institute, Ankara
TS EN 1367–2 (2010) Agregaların termal ve bozunma özellikleri için deneyler – bölüm 2: Magnezyum sülfat deneyi Türk Standartları Enstitüsü. Ankara (in Turkish)
TS EN 14157 (2004) Natural stones-determination of abrasion resistance, Turkey
TS EN 14157 (2017) Natural stones test methods-determination of abrasion resistance, Turkey
Yavuz AB, Turk N, Koca MY (2005) Material properties of the Menderes massif marbles from SW Turkey. Eng Geol 82:91–106
Yavuz H, Ugur I, Demirdag S (2008) Abrasion resistance of carbonate rocks used in dimension stone industry and correlations between abrasion and rock properties. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 45:260–267
Yılmaz NG, Göktan RM, Onargan T (2017) Correlative relations between three-body abrasion wear resistance and petrographic properties of selected granites used as floor coverings. Wear 372-373:197–207
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank to Geological Engineer Mesut BOR (MSc), Dr. İsmail Akkaya and Dr. Vural Oyan considering their support during different stages of this study. Prof. Dr. Mücip Tapan is gratefully acknowledged for his review on the use of English.
Funding
The Scientific Research Projects Office of Van Yüzüncü Yıl University (FLY-2017-6449) financially supported this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Özvan, A., Direk, N. The relationships among different abrasion tests on deteriorated and undeteriorated rocks. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80, 1745–1756 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-02041-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-02041-0