Abstract
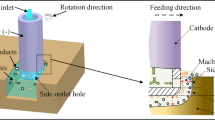
The industrial acceptance of ceramic materials is gradually increasing because of their attractive properties such as high strength, hot hardness, biocompatibility, insulating, and chemical stability over monolithic materials. The Zirconia (ZrO2) is a ceramic material of nonconductive and brittle in nature; thereby, it is very difficult to machine by very popular well-known machining methods like ECM, WEDM, EDM, etc. The machining problem resists its industrial applications. To overcome this problem, electrochemical discharge machining (ECDM) is a combination of electrochemical and electrical discharge machining methods used to machine the nonconductive ZrO2 material. The effects of machining parameters on machining responses were analysed through different graphs. Taguchi method-based L16 (45) orthogonal array was employed and utilized the acquired results to optimize the machining parameters. The experimental results reveal that the DC supply voltage and electrolyte concentration are the main governing factors in controlling the machining performance. The better material removal rate was identified at 65 V, 16 g/l electrolyte concentration, and 60-mm inter-electrode gap. FESEM images identified some of the micro-cracks on the machined hole surface when machining operations were carried out at a higher level of parameter setting. The presence of iron (Fe) was identified from EDS analysis, and it may be due to the diffused part of the steel cathode adhering to the machined surface.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AC:
-
Alternative current
- Adj MS:
-
Adjusted mean square
- Adj SS:
-
Adjusted sum of square
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- DC:
-
Direct current
- DF :
-
Duty factor
- DOF:
-
Degrees of freedom
- EC:
-
Electrolyte concentration
- ECDM:
-
Electrochemical discharge machining
- ECM:
-
Electrochemical machining
- EDM:
-
Electric discharge machining
- FESEM:
-
Field emission scanning electron microscope
- IEG:
-
Inter-electrode gap
- MEMS:
-
Micro-electromechanical system
- MOEMS:
-
Micro-optoelectromechanical system
- MRR:
-
Material removal rate
- MSD:
-
Mean square deviation
- NaOH:
-
Sodium hydroxide
- OA:
-
Orthogonal array
- S/N ratio:
-
Signal-to-noise ratio
- SR:
-
Surface roughness
- SS:
-
Stainless steel
- TWR:
-
Tool wear rate
- V:
-
DC supply voltage
- WC:
-
Tungsten carbide
- (W)OC:
-
(Width of) overcut
- %:
-
Percentage
References
Schünemann, F.H.; Galárraga-Vinueza, M.E.; Magini, R.; Fredel, M.; Silva, F.; Souza, J.C.M.; Zhang, Y.; Henriques, B.: Zirconia surface modifications for implant dentistry. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 98, 1294–1305, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.01.062.
Chevalier, J.: What future for zirconia as a biomaterial? Biomaterials 27, 535–543, 2006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.07.034.
Uwais, Z.A.; Hussein, M.A.; Samad, M.A.; Al-Aqeeli, N.: Surface modification of metallic biomaterials for better tribological properties: a review. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 42, 4493–4512, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2624-x.
Moradi, M.; Ghanbari, F.; Manshouri, M.; Angali, K.A.: Photocatalytic degradation of azo dye using nano-ZrO2/UV/Persulfate: response surface modeling and optimization. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 33, 539–546, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-015-0160-5.
Sudrajat, H.; Babel, S.; Sakai, H.; Takizawa, S.: Rapid enhanced photocatalytic degradation of dyes using novel N-doped ZrO2. J. Environ. Manag. 165, 224–234, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.09.036.
Das, S.; Doloi, B.; Bhattacharyya, B.: Fabrication of stepped hole on zirconia bioceramics by ultrasonic machining. Mach. Sci. Technol. 20, 681–700, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1080/10910344.2016.1224016.
Bian, R.; Ferraris, E.; He, N.; Reynaerts, D.: Process investigation on meso-scale hard milling of ZrO2 by diamond coated tools. Precis. Eng. 38, 82–91, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2013.07.007.
Kumar, S.; Dvivedi, A.: On machining of hard and brittle materials using rotary tool micro-ultrasonic drilling process. Mater. Manuf. Process., 2019. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2019.1594255.
Hu, P.; Zhang, J.M.; Pei, Z.J.; Treadwell, C.: lyde: modeling of material removal rate in rotary ultrasonic machining: designed experiments. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 129, 339–344, 2002. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(02)00686-6.
Abdo, B.M.A.; El-Tamimi, A.M.; Anwar, S.; Umer, U.; Alahmari, A.M.; Ghaleb, M.A.: Experimental investigation and multi-objective optimization of Nd:YAG laser micro-channeling process of zirconia dental ceramic. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 98, 2213–2230, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2374-2.
Dear, F.C.; Shephard, J.D.; Wang, X.; Jones, J.D.C.; Hand, D.P.: Pulsed laser micromachining of yttria-stabilized zirconia dental ceramic for manufacturing. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 5, 188–197, 2008. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7402.2008.02203.x.
Guo, Y.; Hou, P.; Shao, D.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Tang, L.: High-speed wire electrical discharge machining of insulating zirconia with a novel assisting electrode. Mater. Manuf. Process. 29, 526–531, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2014.892983.
Rona, N.; Yenisey, M.; Kucukturk, G.; Gurun, H.; Cogun, C.; Esen, Z.: Effect of electrical discharge machining on dental Y-TZP ceramic-resin bonding. J. Prosthodont. Res. 61, 158–167, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpor.2016.07.006.
Crichton, I.M.; McGeough, J.A.: Studies of the discharge mechanisms in electrochemical arc machining. J. Appl. Electrochem. 15, 113–119, 1985. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00617748.
Arab, J.; Mishra, D.K.; Kannojia, H.K.; Adhale, P.; Dixit, P.: Fabrication of multiple through-holes in non-conductive materials by electrochemical discharge machining for RF MEMS Packaging. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 271, 542–553, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2019.04.032.
Malik, A.; Manna, A.: An experimental investigation on developed WECSM during micro slicing of e-glass fibre epoxy composite. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 85, 2097–2106, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8858-z.
Yang, C.K.; Wu, K.L.; Hung, J.C.; Lee, S.M.; Lin, J.C.; Yan, B.H.: Enhancement of ECDM efficiency and accuracy by spherical tool electrode. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 51, 528–535, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2011.03.001.
He, S.; Tong, H.; Liu, G.: Spark assisted chemical engraving (SACE) mechanism on ZrO2 ceramics by analyzing processed products. Ceram. Int. 44, 7967–7971, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.01.236.
Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, S.; et al.: Experimental study of micro electrochemical discharge machining of ultra-clear glass with a rotating helical tool. Processes, 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7040195.
Elhami, S.; Razfar, M.R.: Effect of ultrasonic vibration on the single discharge of electrochemical discharge machining. Mater. Manuf. Process. 33, 444–451, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2017.1328113.
Chen, J.C.; Lin, Y.A.; Kuo, C.L.; et al.: An improvement in the quality of holes drilled in quartz glassby electrochemical discharge machining. Smart Sci. 00, 1–6, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1080/23080477.2019.1597579.
Sabahi, N.; Hajian, M.; Razfar, M.R.: Experimental study on the heat-affected zone of glass substrate machined by electrochemical discharge machining (ECDM) process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2027-5.
Sundaram, M.; Chen, Y.J.; Rajurkar, K.: Pulse electrochemical discharge machining of glass-fiber epoxy reinforced composite. CIRP Ann. 68, 169–172, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2019.04.113.
Elhami, S.; Razfar, M.R.: Numerical and experimental study of discharge mechanism in the electrochemical discharge machining process. J. Manuf. Process. 50, 192–203, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.12.040.
Singh, T.; Dvivedi, A.: On prolongation of discharge regime during ECDM by titrated flow of electrolyte. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 107, 1819–1834, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05126-y.
Uthayakumar, M.; Thirumalai Kumaran, S.; Adam Khan, M.; Skoczypiec, S.; Bizon, W.: Microdrilling of AA (6351)-SiC-B4C composite using hybrid micro-ECDM process. J. Test. Eval. 48, 20180216, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1520/jte20180216.
Kumar, M.; Vaishya, R.O.; Oza, A.D.; Suri, N.M.: Experimental investigation of wire-electrochemical discharge machining (WECDM) performance characteristics for quartz material. Silicon, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-019-00309-z.
Oza, A.D.; Kumar, A.; Badheka, V.; Arora, A.: Traveling wire electrochemical discharge machining (TW-ECDM) of quartz using zinc coated brass wire : investigations on material removal rate and kerf width characteristics. Silicon, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-019-0070-y.
Kumar, M.; Vaishya, R.O.; Suri, N.M.: Machinability study of zirconia material by micro-ECDM. In: Sharma, V.; Dixit, U.; Sørby, K.; Bhardwaj, A.; Trehan, R. (eds.) Manufacturing Engineering. Lecture Notes on Multidisciplinary Industrial Engineering, pp. 195–209. Springer, Singapore (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-4619-8_15
Singh, J.; Vaishya, R.; Kumar, M.: Fabrication of micro features on quartz glass using developed WECDM setup . ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 14, 725–731, 2019
Tang, W.; Kang, X.; Zhao, W.: Experimental investigation of gas evolution in electrochemical discharge machining process. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 14, 970–984, 2019. https://doi.org/10.20964/2019.01.68.
Li, D.; Li, W.; Wang, R.; Kou, H.: High-temperature strength of zirconia and its sensitivity to surface defects. Mater. Res. Express., 2019. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab1525.
Rattan, N.; Mulik, R.S.: Improvement in material removal rate (MRR) using magnetic field in TW-ECSM process. Mater. Manuf. Process. 32, 101–107, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2016.1176197.
Verma, M.; Manna, A.: Experimental investigation of the effects of electrode shape on ECSM performance during machining of alumina ceramics. Int. J. Eng. Manag. Res. 8, 65–72, 2018
Kumar, S.; Batra, U.: Surface modification of die steel materials by EDM method using tungsten powder-mixed dielectric. J. Manuf. Process. 14, 35–40, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2011.09.002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, M., Vaishya, R.O., Suri, N.M. et al. An Experimental Investigation of Surface Characterization for Zirconia Ceramic Using Electrochemical Discharge Machining Process. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 2269–2281 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05059-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05059-4