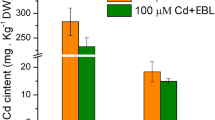
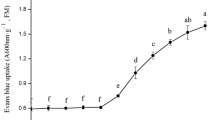
Abstract
Experiments were conducted to determine how exogenous abscisic acid (ABA) mediates the tolerance of plants to cadmium (Cd) exposure. Cd stress strongly reduced all the growth parameters of mung bean seedlings. Cd significantly increased ascorbate peroxidase (APX) and catalase (CAT) activities in roots and stems, and peroxidase (POD) activities in roots, stems, and leaves of mung bean seedlings. Cd caused remarkable increases in the levels of leaf chlorophyll and carotenoid, root polyphenols, and malondialdehyde (MDA) and proline in the three organs. However, Cd greatly decreased leaf CAT activity, root and leaf ascorbic acid (AsA) levels, and stem and leaf polyphenol levels. Foliar application of ABA partially alleviated Cd toxicity on the seedlings. ABA could restore most of the changed biochemical parameters caused by Cd, suggesting that ABA played roles in the protection of membrane lipid peroxidation and the modulation of antioxidative defense systems in response to Cd stress. Our results also implied the differential physiological and biochemical responsive patterns of roots, stems, and leaves to Cd and ABA in mung bean seedlings. The great changes in many biochemical parameters in roots suggested that roots were the first to be affected by Cd and play pivotal roles in response to Cd, especially in chelating Cd and reducing Cd absorption.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas G, Saqib M, Akhtar J, Murtaza G (2017) Physiological and biochemical characterization of Acacia stenophylla and Acacia albida exposed to salinity under hydroponic conditions. Can J For Res 47:1293–1301
Adie BAT, Pérez-Pérez J, Pérez-Pérez MM, Godoy M, Sánchez-Serrano JJ, Schmelz EA, Solano R (2007) ABA is an essential signal for plant resistance to pathogens affecting JA biosynthesis and the activation of defenses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19:1665–1681
Agarwal S, Sairam RK, Srivastava GC, Tyagi A, Meena RC (2005) Role of ABA, salicylic acid, calcium and hydrogen peroxide on antioxidative enzymes induction in wheat seedlings. Plant Sci 169:559–570
Ali B, Qian P, Jin R, Ali S, Khan M, Aziz R, Tian T, Zhou W (2014) Physiological and ultra-structural changes in Brassica napus seedlings induced by cadmium stress. Biol Plant 58:131–138
Ammar WB, Mediouni C, Tray B, Ghorbel MH, Jemal F (2008) Glutathione and phytochelatin contents in tomato plants exposed to cadmium. Biol Plant 52:314–320
An Y, Zhou P, Liang J (2014) Effects of exogenous application of abscisic acid on membrane stability, osmotic adjustment, photosynthesis and hormonal status of two Lucerne (Medicago sativa L.) genotypes under high temperature stress and drought stress. Crop Pasture Sci 65:274–286
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24:1–15
Bandurska H (2001) Does proline accumulated in leaves of water deficit stressed barley plants confine cell membrane injuries? II. Proline accumulation during hardening and its involvement in reducing membrane injuries in leaves subjected to severe osmotic stress. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum 23:483–490
Bashandy T, Guilleminot J, Vernoux T, Caparros-Ruiz D, Ljung K, Meyer Y, Reichheld JP (2010) Interplay between the NADP-linked thioredoxin and glutathione systems in Arabidopsis auxin signaling. Plant Cell 22:376–391
Bates L, Waldren RP, Teare JD (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Benyó D, Horváth E, Németh E, Leviczky T, Takács K, Lehotai N, Feigl G, Kolbert Z, Ördög A, Gallé R, Csiszár J, Szabados L, Erdei L, Gallé Á (2016) Physiological and molecular responses to heavy metal stresses suggest different detoxification mechanism of Populus deltoides and P. canadensis. J Plant Physiol 201:62–70
Cao X, Wu L, Wu M, Zhu C, Jin Q, Zhang J (2020) Abscisic acid mediated proline biosynthesis and antioxidant ability in roots of two different rice genotypes under hypoxic stress. BMC Plant Biol 20:198
Chen Z, Gallie DR (2004) The ascorbic acid redox state controls guard cell signaling and stomatal movement. Plant Cell 16:1143–1162
Chen F, Wang F, Wu FB, Mao WH, Zhang GP, Zhou MX (2010) Modulation of exogenous glutathione in antioxidant defense system against Cd stress in the two barley genotypes differing in Cd tolerance. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:663–672
Clemens S (2006) Toxic metal accumulation, responses to exposure and mechanisms of tolerance in plants. Biochimie 88:1707–1719
Cobbett CS (2000) Phytochelatins and their roles in heavy metal detoxification. Plant Physiol 123:825–832
Cobbett C, Goldsbrough P (2002) Phytochelatins and metallothioneins: roles in heavy metal detoxification and homeostasis. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:159–182
Dai M, Liu W, Hong H, Lu H, Liu J, Jia H, Yan C (2018) Exogenous phosphorus enhances cadmium tolerance by affecting cell wall polysaccharides in two mangrove seedlings Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh and Kandelia obovata (S., L.) Yong differing in cadmium accumulation. Mar Pollut Bull 126:86–92
Das S, Kar RK (2018) Abscisic acid mediated differential growth responses of root and shoot of Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek seedlings under water stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 123:213–221
Ding Y, Feng R, Wang R, Guo J, Zheng X (2014) A dual effect of Se on Cd toxicity: evidence from plant growth, root morphology and responses of the antioxidative systems of paddy rice. Plant Soil 375:289–301
Dong J, Wu F, Zhang G (2006) Influence of cadmium on antioxidant capacity and four microelement concentrations in tomato seedlings (Lycopersicon esculentum). Chemosphere 64:1659–1666
Ekmekçi Y, Tanyolaç D, Ayhan B (2008) Effects of cadmium on antioxidant enzyme and photosynthetic activities in leaves of two maize cultivars. J Plant Physiol 165:600–611
Fan SK, Fang XZ, Guan MY, Ye YQ, Lin XY, Du ST, Jin CW (2014) Exogenous abscisic acid application decreases cadmium accumulation in Arabidopsis plants, which is associated with the inhibition of IRT1-mediated cadmium uptake. Front Plant Sci 5:721
Farooq MA, Niazi A, Akhtar J, Saifullah FM, Souri Z, Karimi N, Rengel Z (2019) Acquiring control: the evolution of ROS-induced oxidative stress and redox signaling pathways in plant stress responses. Plant Physiol Biochem 141:353–369
Foyer CH, Noctor G (2011) Ascorbate and glutathione: the heart of the redox hub. Plant Physiol 155:2–18
Freeman JI, Persans MW, Nieman K, Albrecht C, Peer W, Pickering IJ, Salt DE (2004) Increased glutathione biosynthesis plays a role in nickel tolerance in Thalpsi nickel hyperaccumulator. Plant Cell 16:2176–2191
Gallego SM, Pena LB, Barcia RA, Azpilicueta CE, Iannone MF, Rosales EP, Zawoznik MS, Groppa MD, Benavides MP (2012) Unravelling cadmium toxicity and tolerance in plants: insight into regulatory mechanisms. Environ Exp Bot 83:33–46
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:909–930
Guo JJ, Qin SY, Reng Z, Gao W, Nie ZJ, Liu HG, Li C, Zhao P (2019) Cadmium stress increases antioxidant enzyme activities and decreases endogenous hormone concentrations more in Cd-tolerant than Cd-sensitive wheat varieties. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 172:380–387
Hartung W, Sauter A, Hose E (2002) Abscisic acid in the xylem: where does it come from, where does it go to? J Exp Bot 53(366):27–32
Hassan MJ, Shao G, Zhang G (2006) Influence of Cadmium Toxicity on Growth and Antioxidant Enzyme Activity in Rice Cultivars with Different Grain Cadmium Accumulation. Journal of Plant Nutrition 28:1259–1270
Hassan MJ, Shafi M, Zhang G, Zhu Z, Qaisar M (2008) The growth and some physiological responses of rice to Cd toxicity as affected by nitrogen form. Plant Growth Regul 54:125–132
Hauser F, Li Z, Waadt R, Schroeder JI (2017) SnapShot: abscisic acid signaling. Cell 171:1708–1708e0
Hodges DM, DeLong JM, Forney CF, Prange RK (1999) Improving the thiobarbituric acid-reactive-substances assay for estimating lipid peroxidation in plant tissues containing anthocyanin and other interfering compounds. Planta 207:604–611
Hsu YT, Kao CH (2003) Role of abscisic acid in cadmium tolerance of rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Plant Cell Environ 26:867–874
Hsu YT, Kao CH (2005) Abscisic acid accumulation and cadmium tolerance in rice seedlings. Physiol Plant 124:71–80
Hu ZB, Cools T, De Veylder L (2016) Mechanisms used by plants to cope with DNA damage. Annu Rev Plant Biol 67:439–462
Huang D, Wu W, Abrams SR, Cutler AJ (2008) The relationship of drought-related gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana to hormonal and environmental factors. J Exp Bot 59:2991–3007
Jahan MS, Nozulaidi M, Khairi M, Mat N (2016) Light-harvesting complexes in photosystem II regulate glutathione-induced sensitivity of Arabidopsis guard cells to abscisic acid. J Plant Physiol 195:1–8
Jaleel CA, Riadh K, Gopi R, Manivannan P, Ines J, Al-Juburi H, Zhao CX, Shao HB, Panneerselvam R (2009) Antioxidant defense responses: physiological plasticity in higher plants under abiotic constraints. Acta Physiol Plant 31:427–436
Jia L, Liu Z, Chen W, Ye Y, Yu S, He X (2015) Hormesis effects induced by cadmium on growth and photosynthetic performance in a hyperaccumulator, Lonicera japonica thunb. J Plant Growth Regul 34:13–21
Jiang M, Zhang J (2001) Effect of abscisic acid on active oxygen species, antioxidative defence system and oxidative damage in leaves of maize seedlings. Plant Cell Physiol 42:1265–1273
Jiang MY, Cai XY, Liao JR, Yang YX, Chen QB, Gao SYXF, Luo ZH, Lei T, Lv BY, Liu SL (2020) Different strategies for lead detoxification in dwarf bamboo tissues. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 193:110329
Jin X, Yang X, Mahmood Q, Islam E, Liu D, Li H (2008) Response of antioxidant enzymes, ascorbate and glutathione metabolism towards cadmium in hyperaccumulator and nonhyperaccumulator ecotypes of Sedum alfredii H. Environ Toxicol 23:517
Jun M, Fu HY, Hong J, Wan X, Yang CS, Ho CT (2003) Comparison of antioxidant activities of isoflavones from kudzu root (Pueraria lobata Ohwi). J Food Sci 68:2117–2122
Kuromori T, Sugimoto E, Shinozaki K (2014) Intertissue signal transfer of abscisic acid from vascular cells to guard cells. Plant Physiol 164:1587–1592
Li SW, Leng Y, Feng L, Zeng XY (2014) Involvement of abscisic acid in regulating antioxidative defense systems and IAA-oxidase activity and improving adventitious rooting in mung bean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek] seedlings under cadmium stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:525–537
Li SW, Zeng XY, Leng Y, Feng L, Kang XH (2018) Indole-3-butyric acid mediates antioxidative defense systems to promote adventitious rooting in mung bean seedlings under cadmium and drought stresses. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 161:332–341
Lin R, Wang X, Luo Y, Du W, Guo H, Yin D (2007) Effects of soil cadmium on growth, oxidative stress and antioxidant system in wheat seedlings (Triticum aestivum L.). Chemosphere 69:89–98
Mahmud JA, Hasanuzzaman M, Nahar K, Bhuyan MHMB, Fujita M (2018) Insights into citric acid-induced cadmium tolerance and phytoremediation in Brassica juncea L.: coordinated functions of metal chelation, antioxidant defense and glyoxalase systems. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:990–1001
Matysik J, Alia BB, Mohanty P (2002) Molecular mechanism of quenching of reactive oxygen species by proline under stress in plants. Curr Sci 82:525–532
Meng Y, Zhang L, Wang LQ, Zhou CJ, Shangguan YX, Yang Y (2019) Antioxidative enzymes activity and thiol metabolism in three leafy vegetables under Cd stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 173:214–224
Menguer PK, Farthing E, Peaston KA, Ricachenevsky FK, Fett JP, Williams LE (2013) Functional analysis of the rice vacuolar zinc transporter OsMTP1. J Exp Bot 64:2871–2883
Milner MJ, Seamon J, Craft E, Kochian LV (2013) Transport properties of members of the ZIP family in plants and their role in Zn and Mn homeostasis. J Exp Bot 64:369–381
Mittler R (2002) Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 7:405–410
Nahar K, Hasanuzzamanc M, Alam MM, Rahman A, Suzukid T, Fujita M (2016) Polyamine and nitric oxide crosstalk: antagonistic effects on cadmium toxicity in mung bean plants through upregulating the metal detoxification, antioxidant defense and methylglyoxal detoxification systems. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 126:245–255
Naimah N, Jahan MS (2017) Signaling behaviour of abscisic acid on physiological activities in plants under stress. Pertanika J Trop Agric Sci 40:485–496
Nasibeh P, Tommy L, Parviz E, Maria G (2019) Different response to Cd stress in domesticated and wild safflower (Carthamus spp.). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 171:321–328
Nouairi I, Ammar WB, Youssef NB, Miled DDB, Ghorbal MH, Zarrouk M (2009) Antioxidant defense system in leaves of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea) and rape (Brassica napus) under cadmium stress. Acta Physiol Plant 31:237–247
Osakabe Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K, Tran LSP (2014) ABA control of plant macroelement membrane transport systems in response to water deficit and high salinity. New Phytol 202:35–49
Ozfidan C, Turkan I, Sekmen AH, Seckin B (2012) Abscisic acid-regulated responses of aba2-1 under osmotic stress: the abscisic acid-inducible antioxidant defence system and reactive oxygen species production. Plant Biol 14:337–346
Parrotta L, Guerriero G, Sergeant K, Cai G, Hausman JF (2015) Target or barrier? The cell wall of early- and later-diverging plants vs cadmium toxicity: differences in the response mechanisms. Front Plant Sci 6:133
Peng JS, Gong JM (2014) Vacuolar sequestration capacity and long-distance metal transport in plants. Front Plant Sci 5:19
Pereira A (2016) Plant abiotic stress challenges from the changing environment. Front Plant Sci 7:1123
Pirie A, Mullins MG (1976) Changes in anthocyanin and phenolics content of grapevine leaf and fruit tissues treated with sucrose, nitrate, and abscisic acid. Plant Physiol 58:468–472
Polle A, Otter T, Seifert F (1994) Apoplastic peroxidases and lignification in needles of Norway spruce (Piceaabies L.). Plant Physiol 106:53–60
Pongrac P, Zhao FJ, Razinger J, Zrimec A, Regvar M (2009) Physiological responses to Cd and Zn in two Cd/Zn hyperaccumulating Thlaspi species. Environ Exp Bot 66:479–486
Popova L, Maslenkova L, Yordanova R, Krantev A, Szalai G, Janda T (2013) Salicylic acid protects photosynthesis against cadmium toxicity in pea plants. Bulg J Plant Physiol 34:133–148
Qin HY, Liu HG, Nie ZJ, Gao W, Li C, Lin YH, Zhao P (2018) AsA–GSH cycle and antioxidant enzymes play important roles in Cd tolerance of wheat. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 101:684–690
Rao MV, Paliyath G, Ormrod DP, Murr DO, Watkins CB (1997) Influence of salicylic acid on H2O2 production, oxidative, stress, and H2O2-metabolizing enzymes. Plant Physiol 115:137–149
Sadia R, Ghulam A, Muhammad S, Muhammad S, Abu BUF, Munawar H, Behzad M, Muhammad A, Muhammad AN, Amjad F (2019) Effect of salinity on cadmium tolerance, ionic homeostasis and oxidative stress responses in conocarpus exposed to cadmium stress: implications for phytoremediation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 171:146–153
Semane B, Cuypers A, Smeets K, Van BF, Horemans N, Schat H, Vangronsveld J (2007) Cadmium responses in Arabidopsis thaliana: glutathione metabolism and antioxidative defence system. Physiol Plant 129:519–528
Shahid M, Dumat C, Khalid S, Schreck E, Xiong TT, Niazi NK (2017) Foliar heavy metal uptake, toxicity and detoxification in plants: a comparison of foliar and root metal uptake. J Hazard Mater 325:36–58
Sharma A, Shahzad B, Rehman A, Bhardwaj R, Landi M, Zheng BS (2019) Response of phenylpropanoid pathway and the role of polyphenols in plants under abiotic stress. Molecules 24:2452
Shen GM, Niu JK, Deng ZX (2017) Abscisic acid treatment alleviates cadmium toxicity in purple flowering stalk (Brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis var. purpurea Hort.) seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 118:471–478
Simões CC, Melo JO, Magalhaes JV, Guimarães CT (2012) Genetic and molecular mechanisms of aluminum tolerance in plants. Genet Mol Res 11:1949–1957
Singh S, Parihar P, Singh R, Singh VP, Prasad SM (2016) Heavy metal tolerance in plants: role of transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and lonomics. Front Plant Sci 6:1143
Smeets K, Ruytinx J, Semane B, Belleghem FV, Remans T, Sanden SV, Vangronsveld J, Cuypers A (2008) Cadmium-induced transcriptional and enzymatic alteration related to oxidative stress. Environ Exp Bot 63:1–8
Song WY, Yang HC, Shao HB, Zheng AZ, Brestic M (2014) The alleviative effects of salicylic acid on the activities of catalase and superoxide dismutase in malting barley (Hordeum uhulgare L.) seedling leaves stressed by heavy metals. Clean-Soil Air Water 42:88–97
Spychalla JP, Desborough SL (1990) Superoxide dismutase, catalase and alpha tocopherol content of stored potato tubers. Plant Physiol 94:1214–1218
Suzuki N, Koussevitzky S, Mittler R, Miller G (2012) ROS and redox signalling in the response of plants to abiotic stress. Plant Cell Environ 35:259–270
Sytar O, Kumari P, Yadav S, Brestic M, Rastogi A (2019) Phytohormone priming: regulator for heavy metal stress in plants. J Plant Growth Regul 38:739–752
Szabados L, Savoure A (2010) Proline: a multifunctional amino acid. Trends Plant Sci 15:89–97
Tanaka K, Fujimaki S, Fujiwara T, Yoneyama T, Hayashi H (2007) Quantitative estimation of the contribution of the phloem in cadmium transport to grains in rice plants. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 53:72–77
Tang Y, Wang L, Xie Y, Yu X, Li H, Lin L, Liao MA, Wang Z, Sun G, Wang X, Liang D, Xia H, Tu L (2020) Effects of exogenous abscisic acid on the growth and cadmium accumulation of lettuce under cadmium-stress conditions. Int J Environ Anal Chem 100:720–731
Tyburski J, Tretyn A (2010) Glutathione and glutathione disulfide affect adventitious root formation and growth in tomato seedling cuttings. Acta Physiol Plant 32:411–417
Uraguchi S, Mori S, Kuramata M, Kawasaki A, Arao T, Ishikawa S (2009) Root-to-shoot Cd translocation via the xylem is the major process determining shoot and grain cadmium accumulation in rice. J Exp Bot 60:2677–2688
Verbruggen N, Hermans C (2008) Proline accumulation in plants: a review. Amino Acids 35:753–759
Verbruggen N, Hermans C, Schat H (2009) Mechanisms to cope with arsenic or cadmium excess in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 2:364–372
Wang J, Chen J, Pan K (2013) Effect of exogenous abscisic acid on the level of antioxidants in Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz under lead stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:1441–1449
Wang J, Lin LJ, Luo L, Liao MA, Lv XL, Wang ZH, Liang D, Xia H, Wang X, Lai YS, Tang Y (2016) The effects of abscisic acid (ABA) addition on cadmium accumulation of two ecotypes of Solanum photeinocarpum. Environ Monit Assess 188:182
Wu FB, Chen F, Wei K, Zhang GP (2004) Effect of cadmium on free amino acid, glutathione and ascorbic acid concentrations in two barley genotypes (Hordeum vulgare L.) differing in cadmium tolerance. Chemosphere 57:447–454
Wu K, Wu ZH, Tai FJ, Han Y, Xie BE, Yuan ZL (2011) Effects of cadmium on the contents of phytohormones, photosynthetic performance and fluorescent characteristics in tobacco leaves. Acta Ecol Sin 31:4517–4524
Wu M, Luo Q, Zhao Y, Long Y, Liu S, Pan Y (2018) Physiological and biochemical mechanisms preventing Cd toxicity in the new hyperaccumulator Abelmoschus manihot. J Plant Growth Regul 37:709–718
Yang SL, Lan SS, Gong M (2009) Hydrogen peroxide-induced proline and metabolic pathway of its accumulation in maize seedlings. J Plant Physiol 166:1694–1699
Yuan ZL, Wu ZH (2010) Effect of cadmium on antioxidative capability and phytohormone level in tobacco roots. Acta Ecol Sin 30:4109–4118
Zhang FQ, Wang YS, Lou ZP, Dong JD (2007) Effect of heavy metal stress on antioxidative enzymes and lipid peroxidation in leaves and roots of two mangrove plant seedlings (Kandelia candel and Bruguiera gymnorrhiza). Chemosphere 67:44–50
Zhao L, Xiong J, Li LP, Zhu C (2009) Low concentration of exogenous abscisic acid increases lead tolerance in rice seedlings. Biol Plant 53:728–732
Zhu HH, Chen L, Xing W, Ran SM, Wei ZH, Amee M, Wassie M, Niu H, Tang DY, Sun J, Du DY, Yao J, Hou HB, Chen K, Sun J (2020) Phytohormones-induced senescence efficiently promotes the transport of cadmium from roots into shoots of plants: a novel strategy for strengthening of phytoremediation. J Hazard Mater 388:122080
Funding
This work was supported through funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31760110 and 31560121) and Young Scholars Science Foundation of Lanzhou Jiaotong University (2020048).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leng, Y., Li, Y., Ma, YH. et al. Abscisic acid modulates differential physiological and biochemical responses of roots, stems, and leaves in mung bean seedlings to cadmium stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 6030–6043 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10843-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10843-8