Abstract
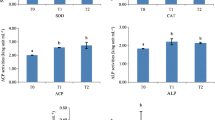
A 30-day feeding trial was conducted to investigate the effect of κ-selenocarrageenan on the growth performance, selenium accumulation, antioxidant capacity, and intestinal microbiota of sea cucumbers Apostichopus japonicus, with different sizes (70 g ± 10 g and 100 g ± 10 g). Sea cucumbers of each size were randomly assigned into two groups; a diet without supplemented κ-selenocarrageenan was referred to as a control diet, or supplemented with κ-selenocarrageenan at selenium (Se) levels of 2.0 μg/g. Selenium accumulation in the body wall and intestine was determined on days 0, 10, 20, and 30. The survival rate (SR) was significantly higher in the κ-selenocarrageenan-treated group (Se group) than in the control group. After 30 days of feeding, κ-selenocarrageenan supplementation increased the activities of glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) and total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC), and decreased malondialdehyde (MDA) levels in A. japonicus. Furthermore, the intestinal microbiota diversity of sea cucumbers was increased by dietary supplementation with κ-selenocarrageenan and the relative abundances of some probiotics (such as Sulfitobacter and Rhodobacteraceae) were also increased. It is suggested that κ-selenocarrageenan could increase the antioxidant capacity and modulate the intestinal microbiota of sea cucumbers A. japonicus. Further researches will be conducted for its optimal administration concentrations in vivo.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nan B, Min G (2017) Roles of zinc and selenium in protecting sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus coelomocytes against lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress in vitro. Aquac Res 48(4):1856–1865. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.13023
Deng H, He C, Zhou Z, Liu C, Tan K, Wang N, Jiang B, Gao X, Liu W (2009) Isolation and pathogenicity of pathogens from skin ulceration disease and viscera ejection syndrome of the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Aquaculture 287(1-2):18–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2008.10.015
Liu H, Zheng F, Sun X, Hong X, Dong S, Wang B, Tang X, Wang Y (2010) Identification of the pathogens associated with skin ulceration and peristome tumescence in cultured sea cucumbers Apostichopus japonicus (Selenka). J Invertebr Pathol 105(3):236–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jip.2010.05.016
Pohanka M (2013) Role of oxidative stress in infectious diseases. A review. Folia Microbiol 58(6):503–513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-013-0239-5
Valavanidis A, Vlahogianni T, Dassenakis M, Scoullos M (2006) Molecular biomarkers of oxidative stress in aquatic organisms in relation to toxic environmental pollutants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 64(2):178–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.03.013
Lushchak VI (2011) Environmentally induced oxidative stress in aquatic animals. Aquat Toxicol 101(1):13–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.10.006
Cui Y, Hou Z, Ren Y, Men X, Zheng B, Liu P, Xia B (2020) Effects of aerial exposure on oxidative stress, antioxidant and non-specific immune responses of juvenile sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus under low temperature. Fish Shellfish Immunol 101:58–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2020.03.050
Zenteno-Savín T, Saldierna R, Ahuejote-Sandoval M (2006) Superoxide radical production in response to environmental hypoxia in cultured shrimp. Comp Biochem Physiol Toxicol Pharmacol 142(3-4):301–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2005.11.001
Elia AC, Prearo M, Pacini N, Dörr AJ, Abete MC (2011) Effects of selenium diets on growth, accumulation and antioxidant response in juvenile carp. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74(2):166–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2010.04.006
Chen J, Han JH, Guan WT, Chen F, Wang CX, Zhang YZ, Lv YT, Lin G (2016) Selenium and vitamin E in sow diets: II. Effect on selenium status and antioxidant status of the progeny. Anim Feed Sci Technol 221:101–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2016.08.021
Li MY, Gao CS, Du XY, Zhao L, Niu XT, Wang GQ, Zhang DM (2020) Effect of sub-chronic exposure to selenium and astaxanthin on Channa argus: bioaccumulation, oxidative stress and inflammatory response. Chemosphere 244:125546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125546
Zhou N, Long H, Wang C, Yu L, Zhao M, Liu X (2020) Research progress on the biological activities of selenium polysaccharides. Food Funct 11(6):4834–4852. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9fo02026h
Jin W, Yu Y, Hou W, Wang G, Zhu Z, He J, Cheng S, Huang Q (2019) Molecular characteristics of kappa-selenocarrageenan and application in green synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Int J Biol Macromol 141:529–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.09.016
Wang JQ, Wang ZX, Zhang K, Zhang YM, Jiang YS, Liu CB, Yan-Qiang WU (2012) Effects of dietary selenomethionine levels on growth and some immune indices in juvenile sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. J Dalian Ocean Univ 27:110–115. https://doi.org/10.16535/j.cnki.dlhyxb.2012.02.009
Xiao-Qian LU, Zhang M, Yang YU, Wang ZF, Yang S, Dang ZQ, Liu JB, Zhou W (2015) Effects of dietary selenium methionine on feeding and growth in juvenile sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Chin J Fish 4:18–23
Zhou W, Cao Q, Wang ZF, Xiao-Jie HU, Zhang JY, Liu JB (2015) Effect of dietary methionine selenium on growth and digestive index of sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. J Dalian Ocean Univ 30:181–184. https://doi.org/10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-1388.2015.02.013
Xiumei LI, Tao XU, Sun G, Yang J, Genrui LI, Haizhou LI (2017) Effects of dietary selenium-enriched yeast levels on important physiological enzymes and enrichment of selenium in sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus). Prog Fish Sci 38(4):155–163. https://doi.org/10.11758/yykxjz.20140512003
Tremaroli V, Backhed F (2012) Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism. Nature 489(7415):242–249. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11552
Hsiao EY, McBride SW, Hsien S, Sharon G, Hyde ER, McCue T, Codelli JA, Chow J, Reisman SE, Petrosino JF, Patterson PH, Mazmanian SK (2013) Microbiota modulate behavioral and physiological abnormalities associated with neurodevelopmental disorders. Cell 155(7):1451–1463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.11.024
Zhou L, Li H, Qin JG, Wang X, Chen L, Xu C, Li E (2020) Dietary prebiotic inulin benefits on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, immune response and intestinal microbiota in Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) at low salinity. Aquaculture 518:734847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734847
Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, Gordon JI (2006) Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 444(7122):1022–1023. https://doi.org/10.1038/4441022a
Wang J, Ren T, Han Y, Zhao Y, Liao M, Wang F, Jiang Z (2015) Effects of dietary vitamin C supplementation on lead-treated sea cucumbers, Apostichopus japonicus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 118:21–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.04.009
Magoc T, Salzberg SL (2011) FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 27(21):2957–2963. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr507
Bokulich NA, Subramanian S, Faith JJ, Gevers D, Gordon JI, Knight R, Mills DA, Caporaso JG (2013) Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat Methods 10(1):57–59. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2276
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R (2011) UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27(16):2194–2200. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr381
Edgar RC (2013) UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 10(10):996–998. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2604
Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, Gerken J, Schweer T, Yarza P, Peplies J, Glockner FO (2013) The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res 41(Database issue):D590–D596. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1219
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32(5):1792–1797. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh340
Han D, Xie S, Liu M, Xiao X, Liu H, Zhu X, Yang Y (2011) The effects of dietary selenium on growth performances, oxidative stress and tissue selenium concentration of gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio). Aquac Nutr 17(3):e741–e749. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2095.2010.00841.x
Atencio L, Moreno I, Jos A, Prieto AI, Moyano R, Blanco A, Camean AM (2009) Effects of dietary selenium on the oxidative stress and pathological changes in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) exposed to a microcystin-producing cyanobacterial water bloom. Toxicon 53(2):269–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2008.11.011
De Riu N, Lee JW, Huang SS, Moniello G, Hung SS (2014) Effect of dietary selenomethionine on growth performance, tissue burden, and histopathology in green and white sturgeon. Aquat Toxicol 148:65–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2013.12.030
Zhang M, Xiao-Qian LU, Wang ZF, Yang S, Dang ZQ, Sang TC, Liu JB, Zhou W (2015) Accumulation of selenium in tissues of adult sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Chin J Fish 28(5):18–22
Ciardullo S, Aureli F, Coni E, Guandalini E, Iosi F, Raggi A, Rufo G, Cubadda F (2008) Bioaccumulation potential of dietary arsenic, cadmium, lead, mercury, and selenium in organs and tissues of rainbow trout (Oncorhyncus mykiss) as a function of fish growth. J Agric Food Chem 56(7):2442–2451. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf703572t
Fontagné-Dicharry S, Véron V, Larroquet L, Godin S, Wischhusen P, Aguirre P, Terrier F, Richard N, Bueno M, Bouyssière B, Antony Jesu Prabhu P, Tacon P, Kaushik SJ (2020) Effect of selenium sources in plant-based diets on antioxidant status and oxidative stress-related parameters in rainbow trout juveniles under chronic stress exposure. Aquaculture 529:735684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735684
Rider SA, Davies SJ, Jha AN, Fisher AA, Knight J, Sweetman JW (2009) Supra-nutritional dietary intake of selenite and selenium yeast in normal and stressed rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Implications on selenium status and health responses. Aquaculture 295(3-4):282–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2009.07.003
KÜÇÜKBAY FZ, Yazlak H, Karaca I, Sahin N, Tuzcu M, Cakmak MN, Sahin K (2009) The effects of dietary organic or inorganic selenium in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) under crowding conditions. Aquac Nutr 15(6):569–576. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2095.2008.00624.x
Lin YH, Shiau SY (2007) The effects of dietary selenium on the oxidative stress of grouper, Epinephelus malabaricus, fed high copper. Aquaculture 267(1-4):38–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2006.12.015
Penglase S, Hamre K, Rasinger JD, Ellingsen S (2014) Selenium status affects selenoprotein expression, reproduction, and F1 generation locomotor activity in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Br J Nutr 111(11):1918–1931. https://doi.org/10.1017/s000711451300439x
Fontagné-Dicharry S, Véron V, Larroquet L, Godin S, Kaushik SJ (2020) Effect of selenium sources in plant-based diets on antioxidant status and oxidative stress-related parameters in rainbow trout juveniles under chronic stress exposure. Aquaculture:735684. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735684
Del Rio AM, Davis BE, Fangue NA, Todgham AE (2019) Combined effects of warming and hypoxia on early life stage Chinook salmon physiology and development. Conserv Physiol 7(1):coy078. https://doi.org/10.1093/conphys/coy078
Wang L, Xiao J-X, Hua Y, Xiang X-W, Zhou Y-F, Ye L, Shao Q-J (2019) Effects of dietary selenium polysaccharide on growth performance, oxidative stress and tissue selenium accumulation of juvenile black sea bream, Acanthopagrus schlegelii. Aquaculture 503:389–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.01.033
Levander OA (2000) The selenium-coxsackievirus connection: chronicle of a collaboration. J Nutr 130(2S Suppl):485S–488S. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/130.2.485S
Hussein O, Rosenblat M, Refael G, Aviram M (1997) Dietary selenium increases cellular glutathione peroxidase activity and reduces the enhanced susceptibility to lipid peroxidation of plasma and low-density lipoprotein in kidney transplant recipients. Transplantation 63(5):679–685. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007890-199703150-00012
Prabhu KS, Nagaraja TP, Gandhi UH (2013) Selenoproteins and their role in oxidative stress and inflammation. Curr Chem Biol 7(1):65–73. https://doi.org/10.2174/2212796811307010007
Wang J, Ren T, Han Y, Zhao Y, Liao M, Wang F, Jiang Z (2015) The effects of dietary lead on growth, bioaccumulation and antioxidant capacity in sea cucumber, Apostichopus japonicus. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 40(2):535–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2015.08.012
Zhang Y, Meng D, Wang Z, Guo H, Wang Y (2012) Oxidative stress response in two representative bacteria exposed to atrazine. FEMS Microbiol Lett 334(2):95–101. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2012.02625.x
Dotan Y, Lichtenberg D, Pinchuk I (2004) Lipid peroxidation cannot be used as a universal criterion of oxidative stress. Prog Lipid Res 43(3):200–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2003.10.001
Chen H, Li J, Yan L, Cao J, Li D, Huang GY, Shi WJ, Dong W, Zha J, Ying GG, Zhong H, Wang Z, Huang Y, Luo Y, Xie L (2020) Subchronic effects of dietary selenium yeast and selenite on growth performance and the immune and antioxidant systems in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 97:283–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2019.12.053
Wang W, Mai K, Zhang W, Xu W, Ai Q, Liufu Z, Li H (2012) Dietary selenium requirement and its toxicity in juvenile abalone Haliotis discus hannai Ino. Aquaculture 330-333:42–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2011.11.032
Laparra JM, Sanz Y (2010) Interactions of gut microbiota with functional food components and nutraceuticals. Pharmacol Res 61(3):219–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2009.11.001
Zhu Y, Chen Y, Liu Y, Yang H, Liang G, Tian L (2012) Effect of dietary selenium level on growth performance, body composition and hepatic glutathione peroxidase activities of largemouth bass Micropterus salmoide. Aquac Res 43(11):1660–1668. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2011.02972.x
Bai Z, Ren T, Han Y, Rahman MM, Hu Y, Li Z, Jiang Z (2019) Influences of dietary selenomethionine exposure on tissue accumulation, blood biochemical profiles, gene expression and intestinal microbiota of Carassius auratus. Comp Biochem Physiol Toxicol Pharmacol 218:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2018.12.001
Sonnenburg ED, Zheng H, Joglekar P, Higginbottom SK, Firbank SJ, Bolam DN, Sonnenburg JL (2010) Specificity of polysaccharide use in intestinal bacteroides species determines diet-induced microbiota alterations. Cell 141(7):1241–1252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2010.05.005
Foster LH, Sumar S (2009) Selenium in health and disease: a review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 37(3):211–228. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408399709527773
Zhao Y, Liu H, Wang Q, Li B, Zhang H, Pi Y (2019) The effects of benzo[a]pyrene on the composition of gut microbiota and the gut health of the juvenile sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus Selenka. Fish Shellfish Immunol 93:369–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2019.07.073
Chen H, Li C, Liu T, Chen S, Xiao H (2019) A metagenomic study of intestinal microbial diversity in relation to feeding habits of surface and cave-dwelling Sinocyclocheilus species. Microb Ecol 79(2):299–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-019-01409-4
Gram L, Melchiorsen J, Spanggaard B, Huber I, Nielsen TF (1999) Inhibition of vibrio anguillarum by Pseudomonas fluorescens AH2, a possible probiotic treatment of fish. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(3):969–973
Sharifah EN, Eguchi M (2012) Benefits of live phytoplankton, Chlorella vulgaris, as a biocontrol agent against fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum. Fish Sci 78(2):367–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-011-0465-1
Yang G, Xu Z, Tian X, Dong S, Peng M (2015) Intestinal microbiota and immune related genes in sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) response to dietary beta-glucan supplementation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 458(1):98–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.01.074
Yamazaki Y, Meirelles PM, Mino S, Suda W, Oshima K, Hattori M, Thompson FL, Sakai Y, Sawabe T, Sawabe T (2016) Individual Apostichopus japonicus fecal microbiome reveals a link with polyhydroxybutyrate producers in host growth gaps. Sci Rep 6:21631. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep21631
Kasaikina MV, Kravtsova MA, Lee BC, Seravalli J, Peterson DA, Walter J, Legge R, Benson AK, Hatfield DL, Gladyshev VN (2011) Dietary selenium affects host selenoproteome expression by influencing the gut microbiota. FASEB J 25(7):2492–2499. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.11-181990
Acknowledgments
We thank the engineer Liu Yao at Public Technology Service Center, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, for contribution in the determination of selenium content.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFD0901103); the China Ocean Mineral Resources R&D Association (DY135-B2-14); Leading talent of Taishan Industry (tscy20190308); the Basic Scientific Fund for National Public Research Institutes of China (2020Q02); the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong (ZR2019BD023); the Key Research and Development Program of Shandong Province (2018GHY115034); and Ningbo Public Service Platform for High-Value Utilization of Marine Biological Resources (NBHY-2017-P2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, K., Liu, L., He, Y. et al. Effects of Dietary Supplementation with κ-Selenocarrageenan on the Selenium Accumulation and Intestinal Microbiota of the Sea Cucumbers Apostichopus japonicus. Biol Trace Elem Res 199, 2753–2763 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02393-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02393-4