Abstract
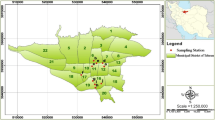
Urban green space is a special space for urban life and natural contact and has an important impact on human health. However, little information is available on dioxin-like persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in the soils from the specific areas. We measured the concentrations of polychlorinated naphthalenes (PCNs), polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs), and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in the soils from urban green space in a metropolis, North China, and found total concentrations of PCDD/Fs, PCBs, and PCNs in the range of 11.5–91.4, 14.7–444, and 82.5–848 pg/g, respectively. It was worth to notice that the concentrations of PCDD/Fs in public park soil from urban center were significantly higher than those in the road greenbelts and resident lawns (Kruskal-Wallis test, p = 0.004). The source analysis indicated that sewage sludge from wastewater treatment plants were important sources of PCNs and PCDD/Fs in urban green land soils, and atmospheric deposition from municipal solid waste incinerator (MSWI) also play an important role in PCDD/F sources. The rough exposure risk evaluation showed that the residents were at a safe level with the daily doses being 0.172–3.144 fg/kg BW/day for children and 0.022–0.406 fg/kg BW/day for adult. Due to the complex and variable sources of PCDD/Fs in urban areas, dioxin-like POPs in urban green land should be given more attention to weaken human exposure.




Similar content being viewed by others

Availability of data and materials
The dataset used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Alcock RE, Behnisch PA, Jones KC, Hagenmaier H (1998) Dioxin-like PCBs in the environment - human exposure and the significance of sources. Chemosphere 37:1457–1472
Aries E, Anderson DR, Fisher R, Fray TAT, Hemfrey D (2006) PCDD/F and “dioxin-like” PCB emissions from iron ore sintering plants in the UK. Chemosphere 65:1470–1480
Banu C (2016) Investigation of PAHs, PCBs and PCNs in soils around a heavily industrialized area in Kocaeli, Turkey: concentrations, distributions, sources and toxicological effects. Sci Total Environ 560-561:160–169
Barone G, Storelli A, Quaglia NC, Dambrosio A, Garofalo R, Chiumarulo R, Storelli MM (2019) Dioxin and PCB residues in meats from Italy: consumer dietary exposure. Food Chem Toxicol 133:110717
Biasioli M, Ajmone-Marsan F (2007) Organic and inorganic diffuse contamination in urban soils: the case of Torino (Italy). J Environ Monit 9:862–868
Cachada A, Pato P, Rocha-Santos T, Silva EFD, Duarte AC (2012) Levels, sources and potential human health risks of organic pollutants in urban soils. Sci Total Environ 430:184–192
Cappelletti N, Astoviza M, Morrone M, Tatone L (2018) Urban geochemistry and potential human health risks in the Metropolitan Area of Buenos Aires: PAHs and PCBs in soil, street dust, and bulk deposition. Environ Geochem Health 41:699–713
Dai J, Xu M, Chen J, Yang X, Ke Z (2007) PCDD/F, PAH and heavy metals in the sewage sludge from six wastewater treatment plants in Beijing, China. Chemosphere 66:353–361
Dat ND, Huang YJ, Hsu YC, Chang MB (2020) Emission characteristics of dl-PCNs, PCDD/Fs, and dl-PCBs from secondary copper metallurgical plants: control technology and policy. Chemosphere 253:126651
Die Q, Nie Z, Liu F, Tian Y, Fang Y, Gao H, Tian S, He J, Huang Q (2015) Seasonal variations in atmospheric concentrations and gas–particle partitioning of PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs around industrial sites in Shanghai, China. Atmos Environ 119:220–227
Die Q, Nie Z, Fang Y, Yang Y, Gao X, Tian Y, He J, Liu F, Huang Q, Tian S (2016) Seasonal and spatial distributions of atmospheric polychlorinated naphthalenes in Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 144:2134–2141
Die Q, Nie Z, Yue B, Zhu X, Gao X, Wang J, Yang Y, Fang Y, Huang Q (2017) Assessment of the temporal and spatial distribution of atmospheric PCNs and their air–soil exchange using passive air samplers in Shanghai, East China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:14365–14375
Falandysz J, Fernandes A, Gregoraszczuk E, Rose M (2014) The Toxicological effects of halogenated naphthalenes: a review of aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated (dioxin-like) relative potency factors. J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev 32:239–272
Fang Y, Nie Z, Yang J, Die Q, He J, Yu H, Zhou Q, Huang Q (2019) Polychlorinated naphthalene emissions to the atmosphere from typical secondary aluminum smelting plants in southwestern China: concentrations, characterization, and risk evaluation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:12731–12740
Fernandes A, Mortimer D, Gem M, Smith F, Rose M, Panton S, Carr M (2010) Polychlorinated naphthalenes (PCNs): congener specific analysis, occurrence in food, and dietary exposure in the UK. Environ Sci Technol 44:3533–3538
Fu S, Yang Z-Z, Li K, Xu X-B (2008) Polychlorinated biphenyl residues in sandstorm depositions in Beijing, China. Chemosphere 73:962–966
Fu S, Cheng HX, Liu YH, Yang ZZ, Xu XB (2009) Spatial character of polychlorinated biphenyls from soil and respirable particulate matter in Taiyuan, China. Chemosphere 74:1477–1484
Gandhi N, Bhavsar SP, Reiner EJ, Chen T, Morse D, Arhonditsis GB, Drouillard KG (2015) Evaluation and interconversion of various indicator PCB schemes for ∑PCB and dioxin-like PCB toxic equivalent levels in fish. Environ Sci Technol 49:123–131
González N, Marquès M, Nadal M, Domingo JL (2018) Levels of PCDD/Fs in foodstuffs in Tarragona County (Catalonia, Spain): spectacular decrease in the dietary intake of PCDD/Fs in the last 20 years. Food Chem Toxicol 121:109–114
Gueguen F, Stille P, Millet M (2011) Air quality assessment by tree bark biomonitoring in urban, industrial and rural environments of the Rhine Valley: PCDD/Fs PCBs and trace metal evidence. Chemosphere 85:195–202
Guéguen F, Stille P, Maurice M (2013) Persistent organic pollutants in the atmosphere from urban and industrial environments in the Rhine Valley: PCBs, PCDD/Fs. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:3852–3862
Hooth MJ, Nyska A, Fomby LM, Vasconcelos DY, Vallant M, DeVito MJ, Walker NJ (2012) Repeated dose toxicity and relative potency of 1,2,3,4,6,7-hexachloronaphthalene (PCN 66) 1,2,3,5,6,7-hexachloronaphthalene (PCN 67) compared to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) for induction of CYP1A1, CYP1A2 and thymic atrophy in female Harlan Sprague–Dawley rats. Toxicology 301:85–93
Hu J, Zheng M, Liu W, Li C, Nie Z, Liu G, Zhang B, Xiao K, Gao L (2013) Characterization of polychlorinated naphthalenes in stack gas emissions from waste incinerators. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:2905–2911
Im SH, Kannan K, Giesy JP, Matsuda M, Wakimoto T (2002) Concentrations and profiles of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in soils from Korea. Environ Sci Technol 36:3700–3705
Kim SJ, Moon HB (2013) Occurrence and human exposure of PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs in house dust from Busan, Korea: comparison with seafood consumption. Toxicol Environ Heal Sci 5:155–162
Kumar B, Verma VK, Mishra M, Kumar S, Sharma CS, Akolkar AB (2014) Persistent organic pollutants in residential soils of North India and assessment of human health hazard and risks. Toxicol Environ Chem 96:255–272
Le LTH, Dat ND, Minh NH, Nguyen K-A (2019) Characteristics of PCDD/Fs in soil and sediment samples collected from A-So former airbase in Central Vietnam. Sci Total Environ 661:27–34
Li H, Yu L, Sheng G, Fu J, Peng Pa (2007) Severe PCDD/F and PBDD/F pollution in air around an electronic waste dismantling area in China. Environ Sci Technol 41:5641–5646
Li G, Bing Z, Ke X, QingHua Z, MingHui Z (2008a) Levels and distributions of polychlorinated naphthalenes in sewage sludge of urban wastewater treatment plants. Chin Sci Bull 053:508–513
Li H, Feng J, Sheng G, Lü S, Fu J, Peng Pa, Man R (2008b) The PCDD/F and PBDD/F pollution in the ambient atmosphere of Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 70:576–583
Li Y, Jiang G, Wang Y, Cai Z, Zhang Q (2008c) Concentrations, profiles and gas–particle partitioning of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in the ambient air of Beijing, China. Atmos Environ 42:2037–2047
Li C, Zheng MH, Zhang B, Gao LR, Liu LD, Jiang XX, Liu ZT (2012) Levels of PCDD/Fs, Dl-PCBs and HCB in air, soils and sediments from a city with multiple thermal-related industries in China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 89:542–546
Li W, Li C, Chen Z, Ding N, Cai Z (2014) Levels of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in mountainous and park soils in Beijing, China. Int J Environ Anal Chem 94:691–711
Li J, Huang Y, Ye R, Yuan G-L, Wu H-Z, Han P, Fu S (2015a) Source identification and health risk assessment of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in the topsoils of typical petrochemical industrial area in Beijing, China. J Geochem Explor 158:177–185
Li L, Sun S, Dong S, Jiang X, Liu G, Zheng M (2015b) Polychlorinated naphthalene concentrations and profiles in cheese and butter, and comparisons with polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin, polychlorinated dibenzofuran and polychlorinated biphenyl concentrations. Int J Environ Anal Chem 95:203–216
Li J, Zhang Y, Sun T, Hao H, Wu H, Wang L, Chen Y, Xing L, Niu Z (2018) The health risk levels of different age groups of residents living in the vicinity of municipal solid waste incinerator posed by PCDD/Fs in atmosphere and soil. Sci Total Environ 631-632:81–91
Liu G, Zheng M, Du B, Nie Z, Zhang B, Liu W, Li C, Hu J (2012) Atmospheric emission of polychlorinated naphthalenes from iron ore sintering processes. Chemosphere 89:467–472
Liu G, Cai Z, Zheng M (2014a) Sources of unintentionally produced polychlorinated naphthalenes. Chemosphere 94:1–12
Liu G, Lv P, Jiang X, Nie Z, Zheng M (2014b) Identifying iron foundries as a new source of unintentional polychlorinated naphthalenes and characterizing their emission profiles. Environ Sci Technol 48:13165–13172
Liu G, Zheng M, Cai Z (2014c) Occurrence, profile and possible sources of PCNs in Hong Kong soils, and a comparison with PCBs, PCDDs and PCDFs. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:13656–13663
Liu G, Zhan J, Zhao Y, Li L, Jiang X, Fu J, Li C, Zheng M (2016) Distributions, profiles and formation mechanisms of polychlorinated naphthalenes in cement kilns co-processing municipal waste incinerator fly ash. Chemosphere 155:348–357
Lohmann R, Muir D (2010) Global aquatic passive sampling (AQUA-GAPS): using passive samplers to monitor POPs in the waters of the world. Environ Sci Technol 44:860–864
Lundin L, Jansson S (2014) The effects of fuel composition and ammonium sulfate addition on PCDD, PCDF, PCN and PCB concentrations during the combustion of biomass and paper production residuals. Chemosphere 94:20–26
Ma WL, Li YF, Sun DZ, Qi H (2009) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and polychlorinated biphenyls in topsoils of Harbin, China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 57:670–678
Mahmood A, Malik RN, Li J, Zhang G, Jones KC (2014) PCNs (polychlorinated napthalenes): dietary exposure via cereal crops, distribution and screening-level risk assessment in wheat, rice, soil and air along two tributaries of the River Chenab, Pakistan. Sci Total Environ 481:409–417
Mai TA, Doan TV, Tarradellas J, de Alencastro LF, Grandjean D (2007) Dioxin contamination in soils of Southern Vietnam. Chemosphere 67:1802–1807
Meijer SN, Ockenden WA, Sweetman A, Breivik K, Grimalt JO, Jones KC (2003) Global Distribution and Budget of PCBs and HCB in background surface soils: implications for sources and environmental processes. Environ Sci Technol 37:667–672
Minh NH, Anh DH, Tri TM, Anh HQ, Mai PTN, Nam VD, Viet PH, Minh TB (2016) Persistent Toxic substances in Vietnam: a review of environmental contamination and human exposure. Persistent Organic Chemicals in the Environment: Status and Trends in the Pacific Basin Countries I Contamination Status American Chemical Society, 55-83
Nadal M, Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL (2007) Levels of metals, PCBs, PCNs and PAHs in soils of a highly industrialized chemical/petrochemical area: temporal trend. Chemosphere 66:267–276
Ngo TH, Tsou HH, Chen YF, Chen YW, Chi KH (2018) Sources identification of PCDD/Fs in soil and atmospheric deposition in Taiwan. Chemosphere 208:374–381
Nie Z, Zheng M, Liu W, Zhang B, Liu G, Su G, Lv P, Xiao K (2011) Estimation and characterization of PCDD/Fs, dl-PCBs, PCNs, HxCBz and PeCBz emissions from magnesium metallurgy facilities in China. Chemosphere 85:1707–1712
Nieuwoudt C, Quinn LP, Pieters R, Jordaan I, Visser M, Kylin H, Borgen AR, Giesy JP, Bouwman H (2009) Dioxin-like chemicals in soil and sediment from residential and industrial areas in central South Africa. Chemosphere 76:774–783
Noma Y, Yamamoto T, Sakai S-I (2004) Congener-specific composition of polychlorinated naphthalenes, coplanar PCBs, dibenzo-p-dioxins, and dibenzofurans in the Halowax series. Environ Sci Technol 38:1675–1680
Odabasi M, Ozgunerge Falay E, Tuna G, Altiok H, Kara M, Dumanoglu Y, Bayram A, Tolunay D, Elbir T (2015) Biomonitoring the spatial and historical variations of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in an industrial region. Environ Sci Technol 49:2105–2114
Petriello MC, Hoffman JB, Vsevolozhskaya O, Morris AJ, Hennig B (2018) Dioxin-like PCB 126 increases intestinal inflammation and disrupts gut microbiota and metabolic homeostasis. Environ Pollut 242:1022–1032
Pokhrel B, Gong P, Wang X, Chen M, Wang C, Gao S (2018) Distribution, sources, and air-soil exchange of OCPs, PCBs and PAHs in urban soils of Nepal. Chemosphere 200:532–541
Qu C, Albanese S, Lima A, Hope D, Pond P, Fortelli A, Romano N, Cerino P, Pizzolante A, De Vivo B (2019) The occurrence of OCPs, PCBs, and PAHs in the soil, air, and bulk deposition of the Naples metropolitan area, southern Italy: implications for sources and environmental processes. Environ Int 124:89–97
Ren N, Que M, Li Y-F, Liu Y, Wan X, Xu D, Sverko E, Ma J (2007) Polychlorinated biphenyls in Chinese surface soils. Environ Sci Technol 41:3871–3876
Rey MD, Font R, Aracil I (2014) PCDD/F emissions from light-duty diesel vehicles operated under highway conditions and a diesel-engine based power generator. J Hazard Mater 278:116–123
Rusin M, Dziubanek G, Marchwińska-Wyrwał E, Ćwieląg-Drabek M, Razzaghi M, Piekut A (2019) PCDDs, PCDFs and PCBs in locally produced foods as health risk factors in Silesia Province, Poland. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 172:128–135
Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL, Hagberg J, Lindström G (2004a) PCDD/F and non-ortho PCB concentrations in adipose tissue of individuals living in the vicinity of a hazardous waste incinerator. Chemosphere 57:357–364
Schuhmacher M, Nadal M, Domingo JL (2004b) Levels of PCDD/Fs, PCBs, and PCNs in soils and vegetation in an area with chemical and petrochemical industries. Environ Sci Technol 38:1960–1969
Shen H, Guan R, Ding G, Chen Q, Lou X, Chen Z, Zhang L, Xing M, Han J, Wu Y (2017) Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins/furans (PCDD/Fs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in Zhejiang foods (2006–2015): market basket and polluted areas. Sci Total Environ 574:120–127
Ssebugere P, Sillanpää M, Matovu H, Mubiru E (2019) Human and environmental exposure to PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs in Africa: A review. Chemosphere 223:483–493
Takasuga T, Inoue T, Ohi E, Senthil Kumar K (2004) Formation of polychlorinated naphthalenes, dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans, biphenyls, and organochlorine pesticides in thermal processes and their occurrence in ambient air. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 46:419–431
Tian Y, Nie Z, Tian S, Liu F, He J, Yang Y, Wang X, Die Q, Fang Y, Huang Q (2015) Passive air sampling for determining the levels of ambient PCDD/Fs and their seasonal and spatial variations and inhalation risk in Shanghai, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:13243–13250
Tian Y, Nie Z, He J, Die Q, Fang Y, Liu F, Yang Y, Gao X, Huang Q (2016) Seasonal variations in concentrations, distributions, and air–soil exchange fluxes of dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls in Shanghai, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:3376–3384
Vives I, Müller A, Umlauf G, Christoph EH, Mariani G, Skejo H, Cenci RM, Sena F, Beone GM (2008) Levels of PCDD/Fs and trace elements in superficial soils of Pavia Province (Italy). Environ Int 34:994–1000
Wang DG, Yang M, Jia HL, Zhou L, Li YF (2008) Levels, distributions and profiles of polychlorinated biphenyls in surface soils of Dalian, China. Chemosphere 73:38–42
Wang Y, Cheng Z, Li J, Luo C, Xu Y, Li Q, Liu X, Zhang G (2012) Polychlorinated naphthalenes (PCNs) in the surface soils of the Pearl River Delta, South China: distribution, sources, and air-soil exchange. Environ Pollut 170:1–7
Wu S, Xia X, Yang L, Liu H (2011) Distribution, source and risk assessment of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in urban soils of Beijing, China. Chemosphere 82:732–738
Wu J, Hu J, Wang S, Jin J, Wang R, Wang Y, Jin J (2018) Levels, sources, and potential human health risks of PCNs, PCDD/Fs, and PCBs in an industrial area of Shandong Province, China. Chemosphere 199:382–389
Wyrzykowska B, Hanari N, Orlikowska A, Bochentin I, Rostkowski P, Falandysz J, Taniyasu S, Horii Y, Jiang Q, Yamashita N (2007) Polychlorinated biphenyls and -naphthalenes in pine needles and soil from Poland – concentrations and patterns in view of long-term environmental monitoring. Chemosphere 67:1877–1886
Xu Y, Li J, Chakraborty P, Syed JH, Malik RN, Wang Y, Tian C, Luo C, Zhang G, Jones KC (2014) Atmospheric polychlorinated naphthalenes (PCNs) in India and Pakistan. Sci Total Environ 466-467:1030–1036
Xu Y, Li J, Zheng Q, Pan S, Luo C, Zhu H, Nizzetto L, Zhang G (2015) Polychlorinated naphthalenes (PCNs) in Chinese forest soil: will combustion become a major source? Environ Pollut 204:124–132
Xu C, Hu J, Wu J, Wei B, Zhu Z, Yang L, Zhou T, Jin J (2020) Polychlorinated naphthalenes, polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans, and polychlorinated biphenyls in soils in an industrial park in Northwestern China: levels, source apportionment, and potential human health risks. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 188:109895
Xue L, Zhang L, Yan Y, Dong L, Huang Y, Li X (2016) Concentrations and patterns of polychlorinated naphthalenes in urban air in Beijing, China. Chemosphere 162:199–207
Yang L, Liu G, Zheng M, Jin R, Zhu Q, Zhao Y, Zhang X, Xu Y (2017) Atmospheric occurrence and health risks of PCDD/Fs, polychlorinated biphenyls, and polychlorinated naphthalenes by air inhalation in metallurgical plants. Sci Total Environ 580:1146–1154
Yang L, Liu G, Zhu Q, Zheng M (2019a) Small-scale waste incinerators in rural China: potential risks of dioxin and polychlorinated naphthalene emissions. Emerging Contaminants 5:31–34
Yang L, Zheng M, Zhao Y, Yang Y, Li C, Liu G (2019b) Unintentional persistent organic pollutants in cement kilns co-processing solid wastes. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 182:109373
Yang L, Zheng M, Zhu Q, Yang Y, Li C, Liu G (2020a) Inventory of polychlorinated naphthalene emissions from waste incineration and metallurgical sources in China. Environ Sci Technol 54:842–850
Yang Y, Wu G, Jiang C, Zheng M, Yang L, Xie J, Wang Q, Wang M, Li C, Liu G (2020b) Variations of PCDD/Fs emissions from secondary nonferrous smelting plants and towards to their source emission reduction. Environ Pollut 260:113946
Yu L, Mai B, Meng X, Bi X, Sheng G, Fu J, Peng Pa (2006) Particle-bound polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in the atmosphere of Guangzhou, China. Atmos Environ 40:96–108
Yuan G-L, Wu H-Z, Fu S, Han P, Lang X-X (2014) Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in the topsoil of typical urban renewal area in Beijing, China: status, sources and potential risk. J Geochem Explor 138:94–103
Zhang S, Peng Pa, Huang W, Li X, Zhang G (2009) PCDD/PCDF pollution in soils and sediments from the Pearl River Delta of China. Chemosphere 75:1186–1195
Zhang L, Li J, Liu X, Zhao Y, Li X, Wen S, Wu Y (2013) Dietary intake of PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs from the Chinese total diet study in 2007. Chemosphere 90:1625–1630
Zhang H, Xiao K, Liu J, Wang T, Liu G, Wang Y, Jiang G (2014) Polychlorinated naphthalenes in sewage sludge from wastewater treatment plants in China. Sci Total Environ 490:555–560
Zhang C, Li X, Zhou Z (2019) Spatial and temporal variation, source profile of PCDD/Fs in the atmosphere of a municipal waste incinerator in China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 184:109615
Acknowledgments
We appreciated Prof. Zhenwu Tang for suggestion on drafting the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (8182021), the Research Foundation of Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences (KJCX20180407), National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFD0801404), and the Open Fund of The State Key Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology (KF2018-06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qingqi Die and Cheng Li jointly initiated and designed the study. Haifeng Li, Hongling Kong, and Bingru Li jointly collected the samples and carried out chemical analysis. Qingqi Die drafted the manuscript with assist from Anxiang Lu and Cheng Li. Qingqi Die revised and completed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Kitae Baek
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 179 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Die, Q., Lu, A., Li, C. et al. Occurrence of dioxin-like POPs in soils from urban green space in a metropolis, North China: implication to human exposure. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 5587–5597 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10953-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10953-3