Abstract
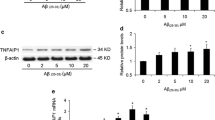
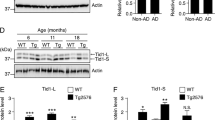
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) poses a significant threat to human life and health. The intraneuronal accumulation of β-amyloid (Aβ) plaques in the brains of AD patients results in neuronal cell death, which is a key factor that triggers multiple changes in the pathogenesis of AD. The inhibition of Aβ-induced neuronal cell death may potentially help in the intervention and treatment of AD. Our previous study reported that tumor necrosis factor α-induced protein 1 (TNFAIP1) is induced by and promotes Aβ25–35-induced neurotoxicity in mouse neuronal cells, but the roles and regulatory mechanisms of TNFAIP1 are still largely unknown. In this study, our experimental results show that TNFAIP1 and p-TNFAIP1 (phosphorylation of TNFAIP1 at Ser280) are overexpressed in the neurons of the cortex and hippocampus in the brains of APP/PS1 mice, and the transcription factor NF-κB is involved in the Aβ-induced upregulation of TNFAIP1. Moreover, our results suggest that TNFAIP1 contributes to the Aβ-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, decreased mitochondrial membrane potential (∆Ψm), and neuronal cell death in human SH-SY5Y cells. We further revealed that Aβ increases the binding of TNFAIP1 to RhoB, and knockdown of RhoB attenuates the TNFAIP1-induced apoptosis of human SH-SY5Y cells. These data suggest that TNFAIP1 is closely associated with AD pathogenesis, and overexpression of TNFAIP1 in the neurons of the brains of AD patients plays a role in apoptosis, at least in part, via RhoB signaling.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- TNFAIP1:
-
Tumor necrosis factor α-induced protein 1
- Aβ:
-
Amyloid beta
- Co-IP:
-
Co-immunoprecipitation
- siRNA:
-
Small interfering RNA
- NC siRNA:
-
Negative control small interfering RNA
References
Barberan S, McNair K, Iqbal K et al. (2011) Altered apoptotic responses in neurons lacking RhoB GTPase. EUR J NEUROSCI 34:1737–1746.
Burns A, Iliffe S (2009) Alzheimer’s disease. BMJ 338:b158.
Castillo-Carranza DL, Guerrero-Munoz MJ, Sengupta U et al. (2015) Tau immunotherapy modulates both pathological tau and upstream amyloid pathology in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. J NEUROSCI 35:4857–4868.
Chang L, Bakhos L, Wang Z et al. (2003) Femtomole immunodetection of synthetic and endogenous amyloid-beta oligomers and its application to Alzheimer’s disease drug candidate screening. J MOL NEUROSCI 20:305–313.
Chen JX, Yan SD (2007) Amyloid-beta-induced mitochondrial dysfunction J ALZHEIMERS DIS 12:177–184
Chen Y, Yang Z, Meng M et al (2009) Cullin mediates degradation of RhoA through evolutionarily conserved BTB adaptors to control actin cytoskeleton structure and cell movement. MOL CELL 35:841–855
Du S, Zhang Y, Yang J et al (2019) Curcumin alleviates beta amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in HT22 cells via upregulating SOD2. J MOL NEUROSCI 67:540–549
Eggler AL, Small E, Hannink M et al (2009) Cul3-mediated Nrf2 ubiquitination and antioxidant response element (ARE) activation are dependent on the partial molar volume at position 151 of Keap1. BIOCHEM J 422:171–180
Essers J, Theil AF, Baldeyron C et al (2005) Nuclear dynamics of PCNA in DNA replication and repair. MOL CELL BIOL 25:9350–9359
Gladwyn-Ng I, Huang L, Ngo L et al (2016) Bacurd1/Kctd13 and Bacurd2/Tnfaip1 are interacting partners to Rnd proteins which influence the long-term positioning and dendritic maturation of cerebral cortical neurons. NEURAL DEV 11:7
Gladwyn-Ng IE, Li SS, Qu Z et al (2015) Bacurd2 is a novel interacting partner to Rnd2 which controls radial migration within the developing mammalian cerebral cortex. NEURAL DEV 10:9
He D, Tan J, Zhang J (2017) miR-137 attenuates Abeta-induced neurotoxicity through inactivation of NF-kappaB pathway by targeting TNFAIP1 in Neuro2a cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 490:941–947
Jones SV, Kounatidis I (2017) Nuclear factor-kappa B and Alzheimer disease, unifying genetic and environmental risk factors from cell to humans. FRONT IMMUNOL 8:1805
Kadowaki H, Nishitoh H, Urano F et al (2005) Amyloid beta induces neuronal cell death through ROS-mediated ASK1 activation. CELL DEATH DIFFER 12:19–24
Kim DM, Chung KS, Choi SJ et al (2009) RhoB induces apoptosis via direct interaction with TNFAIP1 in HeLa cells. INT J CANCER 125:2520–2527
Li H, Zhu C, Wang B et al (2016) 17beta-estradiol protects the retinal nerve cells suppressing TLR2 mediated immune-inflammation and apoptosis from oxidative stress insult independent of PI3K. J MOL NEUROSCI 60:195–204
Lin MC, Lee NP, Zheng N et al (2005) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced protein 1 and immunity to hepatitis B virus. World J Gastroenterol 11:7564–7568
Link CD, Taft A, Kapulkin V et al (2003) Gene expression analysis in a transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans Alzheimer’s disease model. NEUROBIOL AGING 24:397–413
Liu H, Yang L, Zhao Y et al (2014) Estrogen is a novel regulator of Tnfaip1 in mouse hippocampus. INT J MOL MED 34:219–227
Liu N, Yu Z, Xun Y et al (2018) Amyloid-beta25-35 upregulates endogenous neuroprotectant neuroglobin via NFkappaB activation in vitro. J ALZHEIMERS DIS 64:1163–1174
Liu N, Wei K, Xun Y et al (2015) Transcription factor cyclic adenosine monophosphate responsive element binding protein negatively regulates tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 1 expression. MOL MED REP 12:7763–7769
Liu N, Yu Z, Xun Y et al (2016) TNFAIP1 contributes to the neurotoxicity induced by Abeta25-35 in Neuro2a cells. BMC NEUROSCI 17:51
Maga G, Hubscher U (2003) Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA): a dancer with many partners. J CELL SCI 116:3051–3060
Niu YL, Zhang WJ, Wu P et al (2010) Expression of the apoptosis-related proteins caspase-3 and NF-kappaB in the hippocampus of Tg2576 mice. NEUROSCI BULL 26:37–46
Pannaccione A, Secondo A, Scorziello A et al (2005) Nuclear factor-kappaB activation by reactive oxygen species mediates voltage-gated K+ current enhancement by neurotoxic beta-amyloid peptides in nerve growth factor-differentiated PC-12 cells and hippocampal neurones. J NEUROCHEM 94:572–586
Poirson J, Biquand E, Straub ML et al (2017) Mapping the interactome of HPV E6 and E7 oncoproteins with the ubiquitin-proteasome system. FEBS J 284:3171–3201
Qiu F, Zhou Y, Deng Y et al (2020) Knockdown of TNFAIP1 prevents di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate-induced neurotoxicity by activating CREB pathway. Chemosphere 241:125114
Redza-Dutordoir M, Averill-Bates DA (2016) Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen species. Biochim Biophys Acta 1863:2977–2992
Rehman SU, Shah SA, Ali T et al (2017) Anthocyanins reversed D-galactose-induced oxidative stress and neuroinflammation mediated cognitive impairment in adult rats. MOL NEUROBIOL 54:255–271
Salarinasab S, Salimi L, Alidadiani N et al (2020) Correction to: Interaction of opioid with insulin/IGFs signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. J MOL NEUROSCI 70:835
Skuli N, Monferran S, Delmas C et al (2006) Activation of RhoB by hypoxia controls hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha stabilization through glycogen synthase kinase-3 in U87 glioblastoma cells. CANCER RES 66:482–489
Snow WM, Albensi BC (2016) Neuronal gene targets of NF-kappaB and their dysregulation in Alzheimer’s disease. FRONT MOL NEUROSCI 9:118
Talebi M, Delpak A, Khalaj-Kondori M et al (2020) Correction to: ABCA7 and EphA1 genes polymorphisms in late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. J MOL NEUROSCI 70:174
Trapp T, Olah L, Holker I et al (2001) GTPase RhoB: an early predictor of neuronal death after transient focal ischemia in mice. MOL CELL NEUROSCI 17:883–894
Vega FM, Ridley AJ (2018) The RhoB small GTPase in physiology and disease. Small GTPases 9:384–393
Villeneuve NF, Lau A, Zhang DD (2010) Regulation of the Nrf2-Keap1 antioxidant response by the ubiquitin proteasome system: an insight into cullin-ring ubiquitin ligases. Antioxid Redox Signal 13:1699–1712
Wolf FW, Marks RM, Sarma V et al (1992) Characterization of a novel tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced endothelial primary response gene. J BIOL CHEM 267:1317–1326
Xiao Y, Huang S, Qiu F et al (2020) Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 1 as a novel tumor suppressor through selective downregulation of CSNK2B blocks nuclear factor-kappaB activation in hepatocellular carcinoma. EBIOMEDICINE 51:102603
Xun Y, Li Z, Tang Y et al (2018) Neuroglobin regulates Wnt/beta-catenin and NFkappaB signaling pathway through Dvl1. INT J MOL SCI 19(7):2133
Yang L, Liu N, Hu X et al (2010) CK2 phosphorylates TNFAIP1 to affect its subcellular localization and interaction with PCNA. MOL BIOL REP 37:2967–2973
Yi J, Zhu M, Qiu F et al (2020) TNFAIP1 mediates formaldehyde-induced neurotoxicity by inhibiting the Akt/CREB pathway in N2a cells. NEUROTOX RES 38:184–198
Zhang Q, Xia Y, Wang Y et al (2018) CK2 Phosphorylating I2(PP2A)/SET mediates tau pathology and cognitive impairment. FRONT MOL NEUROSCI 11:146
Zhao Y, Li S, Xia N et al (2018) Effects of XIST/miR-137 axis on neuropathic pain by targeting TNFAIP1 in a rat model. J CELL PHYSIOL 233:4307–4316
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully thank support from the ethical committee of Hunan Normal University.
Funding
This work was funded in part by the financial support from the China Natural Science Foundation (81601122, 81770389), Hunan Natural Science Foundation (2017JJ3205), the Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial
Education Department (17B162), and Hunan Provincial Department of Health (2016044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ning Liu, Shishan Yuan, and Shuanglin Xiang designed the experiments; Ning Liu, Ye Xiao, Yadan Li, Yinghua Jiang, Huihui Zhang, Chenxi Wei, Yu Xun, and Xing Feng performed the experiments; Ning Liu, Shishan Yuan, and Shuanglin Xiang helped in data analysis and paper writing. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
All animal care protocols and experiments were reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Hunan Normal University.
Informed Consent
The consent for publication was obtained from all authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, H. et al. TNFAIP1 Is Upregulated in APP/PS1 Mice and Promotes Apoptosis in SH-SY5Y Cells by Binding to RhoB. J Mol Neurosci 71, 1221–1233 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01748-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01748-9