Abstract
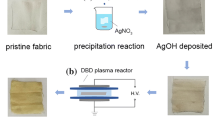
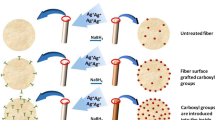
In-situ preparation of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) into plasma-pretreated cotton substrates adds novel functional properties and expands their potential applications. Herein, we report a new approach toward the assembly of multifunctional coated technical textiles. AgNPs was in-situ prepared onto plasma-pretreated cotton fibers using the simple pad-dry-cure method to impart ultraviolet protection, brilliant colors, antimicrobial and photocatalytic self-cleaning properties. AgNPs was produced by thermal reduction of excess Ag+ from an aqueous solution of silver N-(2-ethylhexyl)carbamate on the fibrous cotton surface at 130 °C. The immobilization of the generated AgNPs onto the fibers was improved by plasma activation. Both morphology and elemental content of the treated fabrics were investigated by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, energy dispersive X-ray analysis and scanning electron microscopy (EDX-SEM). The morphology of the generated AgNPs was also investigated by means of transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The generated AgNPs exhibited a homogeneous distribution and high depositing density with a nanoparticle size between 35 and 80 nm. AgNPs incorporated onto cotton fibers endowed with brownish-yellow color for plasma-untreated fibers and brown for plasma-pretreated fibers. The colorfastness and color strength of the AgNPs-coated fabrics were explored. The colored cotton fibers demonstrated persistent antimicrobial performance to S. aureus, E. coli and C. albicans pathogens. AgNPs/cotton displayed excellent photocatalysis and self-cleaning properties to the photochemical decomposition of methylene blue.











Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
14 November 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04891-1
References
Abdelgawad AM, El-Naggar ME, Eissa WH, Rojas OJ (2017) Clean and high-throughput production of silver nanoparticles mediated by soy protein via solid state synthesis. J Clean Prod 144:501–510
Abdelrahman MS, Khattab TA (2019) Development of one-step water-repellent and flame-retardant finishes for cotton. ChemistrySelect 4:3811–3816
Abdelrahman MS, Nassar SH, Mashaly H et al (2020) Studies of polylactic acid and metal oxide nanoparticles-based composites for multifunctional textile prints. Coatings 10:58
Ahmed H, Khattab TA, Mashaly HM et al (2020) Plasma activation toward multi-stimuli responsive cotton fabric via in situ development of polyaniline derivatives and silver nanoparticles. Cellulose 27:2913–2926
Airoudj A, Ploux L, Roucoules V (2015) Effect of plasma duty cycle on silver nanoparticles loading of cotton fabrics for durable antibacterial properties. J Appl Polym Sci 132:41279
Almeida APC, Canejo JP, Fernandes SN et al (2018) Cellulose-based biomimetics and their applications. Adv Mater 30:1703655
Butola BS, Verma D (2019) Facile synthesis of chitosan-silver nanoparticles onto linen for antibacterial activity and free-radical scavenging textiles. Int J Biol Macromol 133:1134–1141
Czaja WK, Young DJ, Kawecki M, Brown RM (2007) The future prospects of microbial cellulose in biomedical applications. Biomacromolecules 8:1–12
Du H, Liu W, Zhang M et al (2019) Cellulose nanocrystals and cellulose nanofibrils based hydrogels for biomedical applications. Carbohydr Polym 209:130–144
El-Naggar ME, Shaarawy S, Hebeish AA (2018) Bactericidal finishing of loomstate, scoured and bleached cotton fibres via sustainable in-situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Int J Biol Macromol 106:1192–1202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.08.127
El-Naggar ME, Al-Joufi F, Anwar M et al (2019) Curcumin-loaded PLA-PEG copolymer nanoparticles for treatment of liver inflammation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 177:389–398
Elshaarawy RFM, Seif GA, El-Naggar ME et al (2019) In-situ and ex-situ synthesis of poly-(imidazolium vanillyl)-grafted chitosan/silver nanobiocomposites for safe antibacterial finishing of cotton fabrics. Eur Polym J 116:210–221
Fu L-H, Qi C, Ma M-G, Wan P (2019) Multifunctional cellulose-based hydrogels for biomedical applications. J Mater Chem B 7:1541–1562
Gorjanc M, Mozetič M, Vesel A (2018) Natural dyeing and UV protection of plasma treated cotton. Eur Phys J D 72:1–6
Haslinger S, Ye Y, Rissanen M et al (2019) Cellulose fibers for high-performance textiles functionalized with incorporated gold and silver nanoparticles. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8:649–658
Hebeish A, El-Naggar ME, Fouda MMG et al (2011) Highly effective antibacterial textiles containing green synthesized silver nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.05.048
Hebeish A, El-Rafie MH, EL-Sheikh MA, et al (2014) Antimicrobial wound dressing and anti-inflammatory efficacy of silver nanoparticles. Int J Biol Macromol 65:509–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.01.071
Hussein J, El Naggar ME, Latif YA et al (2018) Solvent-free and one pot synthesis of silver and zinc nanoparticles: Activity toward cell membrane component and insulin signaling pathway in experimental diabetes. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 170:76–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.05.058
Islam MS, Akter N, Rahman MM et al (2018) Mussel-inspired immobilization of silver nanoparticles toward antimicrobial cellulose paper. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:9178–9188
Jayathilaka WADM, Qi K, Qin Y et al (2019) Significance of nanomaterials in wearables: a review on wearable actuators and sensors. Adv Mater 31:1805921
Kamel S, Khattab TA (2020) Recent advances in cellulose-based biosensors for medical diagnosis. Biosensors 10:67
Khalil-Abad MS, Yazdanshenas ME, Nateghi MR (2009) Effect of cationization on adsorption of silver nanoparticles on cotton surfaces and its antibacterial activity. Cellulose 16:1147
Khattab TA, Mowafi S, El-Sayed H (2019) Development of mechanically durable hydrophobic lanolin/silicone rubber coating on viscose fibers. Cellulose 26:9361–9371
Kim T-S, Cha J-R, Gong M-S (2017) Preparation of silver-coated silk fabrics with antibacterial activity using silver carbamate and hydrogen reduction. Macromol Res 25:856–863
Kim T-S, Cha J-R, Gong M-S (2018) Investigation of the antimicrobial and wound healing properties of silver nanoparticle-loaded cotton prepared using silver carbamate. Text Res J 88:766–776
Kwak W-G, Oh MH, Gong M-S (2015a) Preparation of silver-coated cotton fabrics using silver carbamate via thermal reduction and their properties. Carbohydr Polym 115:317–324
Kwak W-G, Oh MH, Son S-Y, Gong M-S (2015b) Silver loading on poly (ethylene terephthalate) fabrics using silver carbamate via thermal reduction. Macromol Res 23:509–517
Kwak W-G, Cha J-R, Gong M-S (2016) Surface modification of polyester fibers by thermal reduction with silver carbamate complexes. Fibers Polym 17:1146–1153
Liu H, Lv M, Deng B et al (2014) Laundering durable antibacterial cotton fabrics grafted with pomegranate-shaped polymer wrapped in silver nanoparticle aggregations. Sci Rep 4:5920
Lund A, van der Velden NM, Persson N-K et al (2018) Electrically conducting fibres for e-textiles: an open playground for conjugated polymers and carbon nanomaterials. Mater Sci Eng R Rep 126:1–29
Magesh G, Bhoopathi G, Nithya N et al (2018) Tuning effect of polysaccharide chitosan on structural, morphological, optical and photoluminescence properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Superlattices Microstruct 117:36–45
Mitrano DM, Rimmele E, Wichser A et al (2014) Presence of nanoparticles in wash water from conventional silver and nano-silver textiles. ACS Nano 8:7208–7219
Nguyen-Tri P, Altiparmak F, Nguyen N et al (2019) Robust superhydrophobic cotton fibers prepared by simple dip-coating approach using chemical and plasma-etching pretreatments. ACS Omega 4:7829–7837
OhadiFar P, Shahidi S, Dorranian D (2020) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles and exhaustion on cotton fabric simultaneously using laser ablation method. J Nat Fibers 17:1295–1306
Perera S, Bhushan B, Bandara R et al (2013) Morphological, antimicrobial, durability, and physical properties of untreated and treated textiles using silver-nanoparticles. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 436:975–989
Petkova P, Francesko A, Fernandes MM et al (2014) Sonochemical coating of textiles with hybrid ZnO/chitosan antimicrobial nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:1164–1172
Pulit-Prociak J, Chwastowski J, Kucharski A, Banach M (2016) Functionalization of textiles with silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 385:543–553
Rehan M, El-Naggar ME, Mashaly HM, Wilken R (2018a) Nanocomposites based on chitosan/silver/clay for durable multi-functional properties of cotton fabrics. Carbohydr Polym 182:29–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.11.007
Rehan M, Khattab TA, Barohum A et al (2018b) Development of Ag/AgX (X= Cl, I) nanoparticles toward antimicrobial, UV-protected and self-cleanable viscose fibers. Carbohydr Polym 197:227–236
Rehan M, Barhoum A, Khattab TA et al (2019) Colored, photocatalytic, antimicrobial and UV-protected viscose fibers decorated with Ag/Ag2CO3 and Ag/Ag3PO4 nanoparticles. Cellulose 26:5437–5453
Revaiah RG, Kotresh TM, Kandasubramanian B (2019) Technical textiles for military applications. J Text Inst 111:273–308
Shabbir M, Mohammad F (2018) Multifunctional AgNPs@ Wool: colored, UV-protective and antioxidant functional textiles. Appl Nanosci 8:545–555
Shaheen TI, El-Naggar ME, Hussein JS et al (2016) Antidiabetic assessment; in vivo study of gold and core-shell silver-gold nanoparticles on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Biomed Pharmacother 83:865–875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.07.052
Tao G, Liu L, Wang Y et al (2016) Characterization of silver nanoparticle in situ synthesis on porous sericin gel for antibacterial application. J Nanomater 2016:1–8
Textor T, Mahltig B (2010) A sol–gel based surface treatment for preparation of water repellent antistatic textiles. Appl Surf Sci 256:1668–1674
Vigneshwaran N, Arputharaj A (2020) Functional finishing of cotton textiles using nanomaterials. In: Advances in functional finishing of textiles. Springer, pp 43–56
Wang C, Lv J, Ren Y et al (2016) Cotton fabric with plasma pretreatment and ZnO/Carboxymethyl chitosan composite finishing for durable UV resistance and antibacterial property. Carbohydr Polym 138:106–113
Wang X, Yao C, Wang F, Li Z (2017) Cellulose-based nanomaterials for energy applications. Small 13:1702240
Xu Q, Xie L, Diao H et al (2017) Antibacterial cotton fabric with enhanced durability prepared using silver nanoparticles and carboxymethyl chitosan. Carbohydr Polym 177:187–193
J Yan, AM Abdelgawad, ME El-Naggar, OJ Rojas (2016) Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized In-situ by Solution Spraying onto Cellulose. Carbohydr Polym 147:500–508
Yang J, Pu Y, Miao D, Ning X (2018) Fabrication of durably superhydrophobic cotton fabrics by atmospheric pressure plasma treatment with a siloxane precursor. Polymers (Basel) 10:460
Yasin S, Sun D (2019) Propelling textile waste to ascend the ladder of sustainability: EOL study on probing environmental parity in technical textiles. J Clean Prod 233:1451–1464
Youssef AM, El-Naggar ME, Malhat FM, El Sharkawi HM (2019) Efficient removal of pesticides and heavy metals from wastewater and the antimicrobial activity of f-MWCNTs/PVA nanocomposite film. J Clean Prod 206:315–325
Yuranova T, Mosteo R, Bandara J et al (2006) Self-cleaning cotton textiles surfaces modified by photoactive SiO2/TiO2 coating. J Mol Catal A Chem 244:160–167
Zhang M, Pang J, Bao W et al (2017) Antimicrobial cotton textiles with robust superhydrophobicity via plasma for oily water separation. Appl Surf Sci 419:16–23
Zhou Y, Tang R-C (2018) Facile and eco-friendly fabrication of AgNPs coated silk for antibacterial and antioxidant textiles using honeysuckle extract. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 178:463–471
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, for funding this work through Researchers Supporting Project Number (RSP-2020/30), Additionally, Technical supports from National Research Centre are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: Figure 5 is updated.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
El-Naggar, M.E., Khattab, T.A., Abdelrahman, M.S. et al. Development of antimicrobial, UV blocked and photocatalytic self-cleanable cotton fibers decorated with silver nanoparticles using silver carbamate and plasma activation. Cellulose 28, 1105–1121 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03537-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03537-4