Abstract
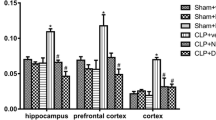
Sepsis-related encephalopathy (SAE), which causes a series of brain injuries and long-term, potentially irreversible cognitive dysfunction, is closely associated with increased morbidity and mortality. Hydrogen (H2) is a new type of medical gas molecule that has been widely used in the treatment of various diseases in recent years. The aim of the present study was to explore the protective effects of H2 inhalation on brain injury and long-term cognitive impairment in an improved chronic septic mouse model. Male C57BL/6J mice were randomized into four groups: Control, Control + H2, SAE and SAE + H2. The SAE and Control models were established by intraperitoneal injection of human stool suspension or saline in mice. H2 (2%) was inhaled for 60 min at 1 h and 6 h after SAE or Control treatment. The survival rates were recorded for 14 days (days 1–14) and the Morris Water Maze was performed for 7 days (days 8–14). To assess the severity of the brain injury, hematoxylin and eosin staining, Nissl staining, Evans blue (EB) extravasation and the wet/dry weight ratio of brain tissue were detected 24 h after SAE or Control treatment. In addition, inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin 6 (IL-6), high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1), as well as the protein levels of nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) and Occludin, were measured 6, 12 and 24 h after SAE or Control treatment. The results showed that H2 treatment increased survival rates, mitigated cognitive impairment, reduced hippocampal histological damage, decreased EB and water content, and decreased the levels of TNF-α, IL-6, HMGB1, Nrf2, HO-1, ZO-1 and Occludin, as compared with the SAE group. These data revealed that 2% H2 could suppress brain damage and improve cognitive function in septic mice by inhibiting oxidative stress, inflammatory response and the sepsis-induced blood–brain barrier (BBB) disruption.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balboa E, Saavedra-Leiva F, Cea LA et al (2018) Sepsis-induced channelopathy in skeletal muscles is associated with expression of non-selective channels. Shock 49:221–228. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0000000000000916
Barichello T, Martins MR, Reinke A, Feier G, Ritter C, Quevedo J, Dal-Pizzol F (2005) Cognitive impairment in sepsis survivors from cecal ligation and perforation. Crit Care Med 33:221–223. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ccm.0000150741.12906.bd (discussion 262–223)
Bian Y, Qin C, Xin Y et al (2018) Itraq-based quantitative proteomic analysis of lungs in murine polymicrobial sepsis with hydrogen gas treatment. Shock 49:187–195. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0000000000000927
Chen H, Xie K, Chen Y et al (2019) Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway participated in the protection of hydrogen sulfide on neuropathic pain in rats. Int Immunopharmacol 75:105746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105746
Cui HY, Zhang XJ, Yang Y, Zhang C, Zhu CH, Miao JY, Chen R (2018) Rosmarinic acid elicits neuroprotection in ischemic stroke via Nrf2 and heme oxygenase 1 signaling. Neural Regen Res 13:2119–2128. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.241463
Danielski LG, Giustina AD, Badawy M, Barichello T, Quevedo J, Dal-Pizzol F, Petronilho F (2018) Brain barrier breakdown as a cause and consequence of neuroinflammation in sepsis. Mol Neurobiol 55:1045–1053. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0356-7
Fang H, Hua C, Weiss S et al (2018) Modulation of innate immunity by G-CSF and inflammatory response by LBPK95A improves the outcome of sepsis in a rat model. J Immunol Res 2018:6085095. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6085095
Gonnert FA, Recknagel P, Seidel M et al (2011) Characteristics of clinical sepsis reflected in a reliable and reproducible rodent sepsis model. J Surg Res 170:e123-134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2011.05.019
Gonnert FA, Kunisch E, Gajda M et al (2012) Hepatic fibrosis in a long-term murine model of sepsis. Shock 37:399–407. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0b013e31824a670b
Hong Y, Sun LI, Sun R, Chen H, Yu Y, Xie K (2016) Combination therapy of molecular hydrogen and hyperoxia improves survival rate and organ damage in a zymosan-induced generalized inflammation model. Exp Ther Med 11:2590–2596. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2016.3231
Hubbard WJ, Choudhry M, Schwacha MG, Kerby JD, Rue LW 3rd, Bland KI, Chaudry IH (2005) Cecal ligation and puncture. Shock 24(Suppl 1):52–57. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.shk.0000191414.94461.7e
Iacobone E, Bailly-Salin J, Polito A, Friedman D, Stevens RD, Sharshar T (2009) Sepsis-associated encephalopathy and its differential diagnosis. Crit Care Med 37:S331-336. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181b6ed58
Jesus AA, Passaglia P, Santos BM et al (2020) Chronic molecular hydrogen inhalation mitigates short and long-term memory loss in polymicrobial sepsis. Brain Res 1739:146857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2020.146857
Li Y, Li Q, Chen H et al (2015) Hydrogen gas alleviates the intestinal injury caused by severe sepsis in mice by increasing the expression of heme oxygenase-1. Shock 44:90–98. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0000000000000382
Li Y, Xie K, Chen H, Wang G, Yu Y (2015) Hydrogen gas inhibits high-mobility group box 1 release in septic mice by upregulation of heme oxygenase 1. J Surg Res 196:136–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2015.02.042
Liu L, Xie K, Chen H et al (2014) Inhalation of hydrogen gas attenuates brain injury in mice with cecal ligation and puncture via inhibiting neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis. Brain Res 1589:78–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2014.09.030
Maes M, Sirivichayakul S, Kanchanatawan B, Vodjani A (2019) Breakdown of the paracellular tight and adherens junctions in the gut and blood brain barrier and damage to the vascular barrier in patients with deficit schizophrenia. Neurotox Res 36:306–322. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-00054-6
Maier S, Traeger T, Entleutner M et al (2004) Cecal ligation and puncture versus colon ascendens stent peritonitis: two distinct animal models for polymicrobial sepsis. Shock 21:505–511. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.shk.0000126906.52367.dd
McCarron EP, Williams DP, Antoine DJ, Kipar A, Lemm J, Stehr S, Welters ID (2015) Exploring the translational disconnect between the murine and human inflammatory response: analysis of LPS dose-response relationship in murine versus human cell lines and implications for translation into murine models of sepsis. J Inflamm Res 8:201–209. https://doi.org/10.2147/JIR.S89097
Ohsawa I, Ishikawa M, Takahashi K et al (2007) Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat Med 13:688–694. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1577
Onodera H, Sato G, Kogure K (1986) Lesions to schaffer collaterals prevent ischemic death of CA1 pyramidal cells. Neurosci Lett 68:169–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3940(86)90136-9
Rittirsch D, Hoesel LM, Ward PA (2007) The disconnect between animal models of sepsis and human sepsis. J Leukoc Biol 81:137–143. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.0806542
Steiner E, Enzmann GU, Lyck R, Lin S, Ruegg MA, Kroger S, Engelhardt B (2014) The heparan sulfate proteoglycan agrin contributes to barrier properties of mouse brain endothelial cells by stabilizing adherens junctions. Cell Tissue Res 358:465–479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-014-1969-7
Tang Y, Soroush F, Sun S et al (2018) Protein kinase C-delta inhibition protects blood-brain barrier from sepsis-induced vascular damage. J Neuroinflammation 15:309. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-018-1342-y
Tian M, Qingzhen L, Zhiyang Y, Chunlong C, Jiao D, Zhang L, Li W (2019) Attractylone attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy and cognitive dysfunction by inhibiting microglial activation and neuroinflammation. J Cell Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27983
Wang B, Cao W, Biswal S, Dore S (2011) Carbon monoxide-activated Nrf2 pathway leads to protection against permanent focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 42:2605–2610. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.607101
Xie K, Yu Y, Zhang Z et al (2010) Hydrogen gas improves survival rate and organ damage in zymosan-induced generalized inflammation model. Shock 34:495–501. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0b013e3181def9aa
Xie K, Liu L, Yu Y, Wang G (2014) Hydrogen gas presents a promising therapeutic strategy for sepsis. Biomed Res Int 2014:807635. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/807635
Xie K, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Meng X, Wang Y, Yu Y, Chen H (2020) Hydrogen attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy by NRF2 mediated NLRP3 pathway inactivation. Inflamm Res 69:697–710. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-020-01347-9
Yan M, Yu Y, Mao X et al (2019) Hydrogen gas inhalation attenuates sepsis-induced liver injury in a FUNDC1-dependent manner. Int Immunopharmacol 71:61–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2019.03.021
Yang S, Gu C, Mandeville ET et al (2017) Anesthesia and surgery impair blood-brain barrier and cognitive function in mice. Front Immunol 8:902. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.00902
Yu Y, Yang Y, Bian Y et al (2017) Hydrogen gas protects against intestinal injury in wild type but not NRF2 knockout mice with severe sepsis by regulating HO-1 and HMGB1 release. Shock 48:364–370. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0000000000000856
Yu Y, Yang Y, Yang M, Wang C, Xie K, Yu Y (2019) Hydrogen gas reduces HMGB1 release in lung tissues of septic mice in an Nrf2/HO-1-dependent pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 69:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2019.01.022
Yu Y, Feng J, Lian N et al (2020) Hydrogen gas alleviates blood-brain barrier impairment and cognitive dysfunction of septic mice in an Nrf2-dependent pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 85:106585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106585
Zhou J, Tian H, Du X et al (2017) Population-based epidemiology of sepsis in a subdistrict of Beijing. Crit Care Med 45:1168–1176. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000002414
Zhuang X, Yu Y, Jiang Y et al (2020) Molecular hydrogen attenuates sepsis-induced neuroinflammation through regulation of microglia polarization through an mTOR-autophagy-dependent pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 81:106287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106287
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Chinese National Natural Science Foundation (Grant nos. 81671888 and 81600962), the Tianjin Natural Science Foundation (Grant nos. 18JCZDJC35100 and 18JCYBJC94400) and The Science and Technology Development Fund of Tianjin Education Commission for Higher Education (Grant no. 2017KJ194).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by Sreedharan Sajikumar.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Y., Zhang, K., Yu, Y. et al. Molecular hydrogen alleviates brain injury and cognitive impairment in a chronic sequelae model of murine polymicrobial sepsis. Exp Brain Res 238, 2897–2908 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-020-05950-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-020-05950-4