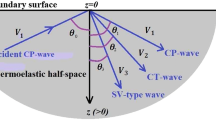
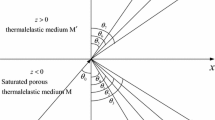
Abstract
In this article, the propagation of Rayleigh surface waves in a piezothermoelastic transversely isotropic layer lying over a piezothermoelastic transversely isotropic half-space is investigated in the context of the Green–Naghdi model type III of hyperbolic thermoelasticity. The secular equation of Rayleigh surface waves is derived, and different cases are discussed. Phase velocity, attenuation coefficient and specific loss of surface waves are computed and presented graphically with respect to frequency, and a comparison of different wave characteristics for classical and generalized thermoelastic models is presented in the figures.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biot, M.: Thermoelsticity and irreversible thermodynamics. J. Appl. Phys. 27, 240–253 (1956)
Lord, H., Shulman, Y.: A generalized dynamic theory of thermoelasticity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 15, 299–309 (1967)
Green, A.E., Lindsay, K.A.: Thermoelasticity. J. Elast. 2, 1–7 (1972)
Green, A.E., Naghdi, P.M.: A re-examination of the basic properties of thermomechanics. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 432, 171–194 (1991)
Green, A.E., Naghdi, P.M.: On damped heat waves in an elastic solid. J. Therm. Stresses 15, 252–264 (1992)
Green, A.E., Naghdi, P.M.: Thermoelasticity without energy dissipation. J. Elast. 31, 189–208 (1993)
Chandrasekharaih, D.S.: Hyperbolic thermoelasticity: a review of recent literature. Appl. Mech. Rev. 51(11), 705–729 (1998)
Ignaczak, J., Ostoja-Starzewski, M.: Thermoelasticity with Finite Wave Speeds. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2010)
Curie, J., Curie, P.: Développement par compression de l’électricité polaire dans les cristaux hemledres a faces inclines. bulletin no. 4 de la societee minearalogique de france 3, 1880
Mindlin, R.D.: On the equations of motion of piezoelectric crystals problems of continuum mechanics. SIAM Philadelphia N.I Muskelishvili’s Birthday 70, 282–290 (1961)
Mindlin, R.D.: Equation of High Frequency Vibrations of Thermo-Piezo-Electric Plates, Interactions in Elastic Solids. Springer, Wein (1979)
Gates, W.D.: Vibrating angular rate sensor may threaten the gyroscope. Electronic 41, 103–134 (1968)
Soderkvist, J.: Micro machined gyroscopes. Sens. Actuators A 43, 65–71 (1994)
Wren, T., Burdess, J.S.: Surface waves perturbed by rotation. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 54, 464–468 (1987)
Clarke, N.S., Burdess, J.S.: A rotation rate sensor based upon a Rayleigh resonator. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 61, 139–143 (1994)
Fang, H., Yang, J.S., Jiang, Q.: Rotation sensitivity of waves propagating in a piezoelectric plate. Int. J. Solids Struct. 39, 5241–51 (2000)
Chen, T.Y.: Further correspondences between plane piezoelectricity and generalized plane strain in elasticity. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 454, 873–884 (1971)
Chizhikov, S.I., Sorokin, N.G., Petrakov, V.S.: The elastoelectric effect in the non-centrosymmetric crystal. In: Taylor, G.W., et al. (eds.) Piezoelectricity, pp. 75–91. Gordon & Breach Science publishers, New York (1985)
He, J.H.: Coupled variational principles of piezoelectricity. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 39, 323–341 (2001)
Maugin, G.A.: The Mechanical Behaviour of Electromagnetic Solid Continua. North-Holland, Amsterdam (1984)
Maugin, G.A.: Continuum Mechanics of Electromagnetic Solid. North-Holland, Amsterdam (1988)
Nowacki, W.: Some general theorems of thermo-piezoelectricity. J. Therm. Stresses 1, 171–182 (1978)
Nowacki, W.: Foundations of linear piezoelectricity. In: Parkus, H. (ed.) Electromagnetic Interactions in Elastic Solids. Springer, Wien (1979). (Chapter 1)
Nowacki, W.: Mathematical models of phenomenological piezoelectricity. In: New Problems in Mechanics of Continua. University of Waterloo Press, Ontario, pp. 29–49 (1983)
Chandrasekharaiah, D.S.: A temperature rate dependent theory of piezoelectricity. J. Therm. Stresses 7, 293–306 (1984)
Chandrasekharaiah, D.S.: A generalized linear thermoelastic theory of piezoelectric media. Acta Mech. 71, 39–49 (1988)
Sharma, J.N., Pal, M., Chand, D.: Propagation characteristics of Rayleigh waves in transversely isotropic piezothermoelastic materials. J. Sound Vib. 284, 227–248 (2005)
Sharma, J.N., Walia, V.: Further investigations on Rayleigh waves in piezothermoelastic materials. J. Sound Vib. 301, 189–206 (2007)
Sharma, J.N., Walia, V.: Effect of rotation on Rayleigh waves in piezothermoelastic half space. Int. J. Solids Struct. 44, 1060–1072 (2007)
Sharma, J.N., Pal, M.: Propagation of Lamb waves in transversely isotropic piezothermoelastic plate. J. Sound Vib. 270, 587–610 (2004)
Sharma, J.N., Walia, V.: Straight and circular crested Lamb waves in generalized piezothermoelastic plates. J. Therm. Stresses 29, 529–551 (2006)
Sharma, J.N., Pal, M., Chand, D.: Thermoelastic Lamb waves in electrically shorted transversely isotropic piezothermoelastic plate. J. Therm. Stresses 27, 33–58 (2004)
Pramanik, A.S., Biswas, S.: Surface waves in nonlocal thermoelastic medium with state space approach. J. Therm. Stresses 43(6), 667–686 (2020)
Biswas, S.: Surface waves in porous nonlocal thermoelastic orthotropic medium. Acta Mech. 231(7), 2741–2760 (2020)
Biswas, S., Mukhopadhyay, B., Shaw, S.: Rayleigh surface wave propagation in orthotropic thermoelastic solids under three-phase-lag model. J. Therm. Stresses 40(4), 403–419 (2017)
Biswas, S., Abo-Dahab, S.M.: Effect of phase-lags on Rayleigh waves in initially stressed magneto-thermoelastic orthotropic medium. Appl. Math. Model. 59, 713–727 (2018)
Biswas, S.: Stroh analysis of Rayleigh waves in anisotropic thermoelastic medium. J. Therm. Stresses 41(5), 627–644 (2018)
Biswas, S., Mukhopadhyay, B.: Eigenfunction expansion method to characterize Rayleigh wave propagation in orthotropic medium with phase-lags. Waves Random Complex Media 29(4), 722–742 (2019)
Kolsky, H.: Stress Waves in Solids. Dover Press, New York (1963)
Acknowledgements
The author is grateful to the reviewer for his valuable suggestion for the improvement of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
where
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biswas, S. Surface waves in piezothermoelastic transversely isotropic layer lying over piezothermoelastic transversely isotropic half-space. Acta Mech 232, 373–387 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-020-02848-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-020-02848-8