Abstract
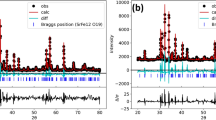
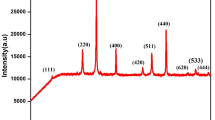
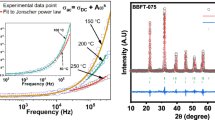
Ba1-xPbxFe12O19 (x = 0.0 to 1.0) was synthesized by a co-precipitation method at room temperature. Parent compounds used were oxides of iron and lead, while barium was used in a carbonated form. Acids and Di-H2O were used as a solute. Na-Alkaline solution with molarity 5 was used for fertilization. Iron to barium ratio was kept 12. Washing played a vital role to minimize the impurities. It also improved the homogeneity. Semi-liquid-type material was obtained after overnight drying in an oven. It was further transformed into powder form which further processed, and pellets were formed for characterizations. These pellets were sintered for 3 h in a box furnace at 965 ± 5 °C. Growth along with its surface and dimensional modifications were analyzed by X-ray diffractometry (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). It showed almost 70% phase purity. Lead physical properties like higher mobility, ionic radii (Pb2+ = 1.76 Å & Ba = 1.37 Å), and occupancy preference were the important reasons for the investigation during heat treatment. Lead doping in R blocks was another big reason for these variations. SEM showed modification in all respect in each successive composition. Frequency-based analysis of whole composition from room temperature to 973 K with a step of 100 has discussed. Frequency precession analyzer was used from 20 Hz to 3 MHz for each sample. Obtained data was used to calculate dielectric constant, dielectric loss and dielectric loss factor, and AC conductivity. Determined parameters were further studied with respect to respective temperatures during whole applied frequency spectrum. The study contains almost different behaviors from each other. Prime factors were heat treatment, impurities, dopant (x), and variation of applied electric field. These behaviors and trends could be useful for today’s modern IT applications and other related electrical and electronic components like capacitors. It could also be useful for high frequency microwave and related network applications.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Trukhanov, S.V., Trukhanov, A.V., Turchenko, V.A., Kostishyn, V.G., Panina, L.V., Kazakevich, I.S., Balagurov, A.M.: Structure and magnetic properties of BaFe11.9In0.1O19 hexaferrite in a wide temperature range. J. Alloys Compd. 689, 383–393 (2016)
Trukhanov, S.V., Trukhanov, A.V., Kostishin, V.G., Panina, L.V., Kazakevich, I.S., Turchenko, V.A., Kochervinskii, V.V.: Coexistence of spontaneous polarization and magnetization in substituted M-type hexaferrites BaFe12 – xAlxO19 (x ≤ 1.2) at room temperature. JETP Lett. 103, 106–112 (2016)
Trukhanov, S.V., Trukhanov, A.V., Turchenko, V.A., Trukhanov, A.V., Tishkevich, D.I., Trukhanova, E.L., Zubar, T.I., Karpinsky, D.V., Kostishyn, V.G., Panina, L.V., Vinnik, D.A., Gudkova, S.A., Trofimov, E.A., Thakur, P., Thakur, A., Yang, Y.: Magnetic and dipole moments in indium doped barium hexaferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 457, 83–96 (2018)
Trukhanov, S.V., Trukhanov, A.V., Kostishyn, V.G., Panina, L.V., Trukhanov, A.V., Turchenko, V.A., Tishkevich, D.I., Trukhanova, E.L., Yakovenko, O.S., Matzui, L.Y.: Investigation into the structural features and microwave absorption of doped barium hexaferrites by Cite this: Dalton Trans. R. Soc. Chem. 46, 9010–9021 (2017)
Turchenkoa, V.A., Trukhanovc, S.V., Balagurov, A.M., Kostishyn, V.G., Trukhanovc, A.V., Panina, L.V., Trukhanova, E.L.: Features of crystal structure and dual ferroic properties of BaFe Me O 12 19 −x x ( = + Me In3) and Ga+3 : ( x = 0.1–1.2). 464, 139–147 (2018)
Sebastian, M.T.: Dielectric materials for wireless communication. In: NIIT, India Book, 3rd edn, (2008)
Jie, L., et al.: Transformation behavior of M type barium ferrites due to Co–Ti substitution. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26, 4668–4674 (2015)
Cheng, Y., Ren, X.: Permeability and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of sintered barium hexaferrite with substitution of Co2+ − Zr4+. J. Mater. (2015)
Abbas, S.M., Chatterjeea, R., Dixit, A.K., Kumar, A.V.R.: Electromagnetic and microwave absorption properties of Co2+ − Si4+ substituted barium hexaferrites and its polymer composite. J. Appl. Phys. 101, 74–81 (2007)
Fujiwara, T.: Barium Ferrite media for perpendicular recording. IEEE Trans. Magn. 21, 1480–1485 (1985)
Buschow, K.H.J.: High-Density Digital Recording, vol. 182. Kluwer, Dordrecht (1992)
Cho, et al.: Pb cation induced low-temperature crystallization of (Ba·Pb) hexaferrite thin films. J. Electroceram. 17, 365–368 (2006)
Ali, I., Awan, M.U., Ahmad, M.: Effects of heat treatment time on structural, dielectric, electrical and magnetic properties of BaM hexaferrite. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 22(7), 2104–2114 (2013)
Haq, A., Anis-ur-Rehman, M.: Effect of Pb on structural and magnetic properties of Ba-hexaferrite. J. Phys. B. 407, 822–826 (2012)
Ashima, S.S., Agarwal, A.: Rietveld refinement, electrical properties and magnetic characteristics of Ca–Sr substituted barium hexaferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 513, 436–444 (2011)
J.C. Maxwell. Electricity and Magnetism. Oxford University Press, Section Vol 1, Vol 2 (1973) p. 328, (1929) p. 828 (2012)
Koops, C.G.: On the dispersion of resistivity and dielectric constant of some semiconductors at audio frequencies. Phys. Rev. 83, 117–121 (1951)
Wagner, K.W.: Dielectric relaxation in distributed dielectric layers. J. Ann. Phys. 345(5), 815–817 (1913)
Chandra, M.J.: Science of engineering materials. 3, (1980)
Batoo, K.M., Kumar, S.: Influence of Al doping on electrical properties of Ni-Cd nano ferrites. Curr. Appl. Phys. 9, 826–832 (2009)
Mangalaraja, R.V., Manohar, P.: Electrical and magnetic properties of Ni0.8Zn0.2Fe2O4/silica composite prepared by sol-gel method. J. Mater. Sci. 39, 2037–2042 (2004)
Verma, A., Thakur, O.P., Prakash, C., Goel, T.C., Mendiratta, R.G.: Temperature dependence of electrical properties of nickel–zinc ferrites processed by the citrate precursor technique. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. 116, 1–6 (2005)
Narang, S.B., Singh, A., Singh, K.: High-frequency dielectric behavior of rare earth substituted Sr-M hexaferrite. J. Ceram. Process. Res. 8, 347–351 (2007)
Bellad, S.S., Coagula, B.K.: Composition and frequency dependent dielectric properties of Li-Mg-Ti ferrites. J. Mater. Chem. Phys. 66, 55–58 (2000)
Chauhan, C.C., Jotania, R.B., Jotania, K.R.: Conductivity and dielectric properties of M-type barium magnesium hexaferrite powder. I(IV), 25–27 (2012)
Che, S., Wang, J., Chen, Q.: Soft magnetic nanoparticles of BaFe12O19 fabricated under mild conditions. J. Phys. 15, L335–L339 (2003)
Hudson, A.S.: Ferrite devices for magnetron protection in microwave power systems. J. Microwave Power. 10, 257–264 (1975)
Iqbal, M.J., Farooq, S.: Enhancement of electrical resistivity of Sr0.5Ba0.5Fe12O19 nanomaterials by doping with lanthanum and nickel. Mater. Chem. Phys. 118, 308–313 (2009)
Iqbal, M.J., Ashiq, M.N., Gómez, P.H.: Influence of annealing temperature and doping rate on the magnetic properties of Zr-Mn substituted Sr-hexaferrite nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 500, 113–116 (2010)
Anis-ur-Rehman, M., Mahmood, W., Ghazanfar, H., Khan, M.A.A., Haq, A.: Structural and Electrical Dependence in Zn-Doped Li-Ferrite Nanostructures. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 4–9 (2019)
Mahmood, W., Haq, A., Anis-ur-Rehman, M.: Electrical behavior of lead-doped Ba-hexaferrite for smart applications. Iran J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Sci. 1–5 (2019)
Che, S., Wang, J., Chen, Q.: Soft magnetic nanoparticules of BaFe12O19 fabricated under mild conditions. J. Phys. Condens. Mater. 15, L335–L339 (2003)
Kong, L.B., Li, Z.W., Lin, G.Q., Gan, Y.B.: Electrical and magnetic properties of magnesium ferrite ceramics doped with Bi2O3. J. Acta Materialia. 55, 6561–6572 (2007)
Che, S., Wang, J., Chen, Q.: Soft magnetic nanoparticles of BaFe12O19 fabricated under mild conditions. J. Phys. Condens. Mater. 15, 335–339 (2003)
Iqbal, M.J., Ashiq, M.N.: Physical and electrical properties of Zr-Cu substituted strontium hexaferrite nanoparticles synthesized by coprecipitation method. Chem. Eng. J. 136, 383–389 (2008)
Mallick, K.K., Shepherd, P., Roger, J.: Green dielectric properties of M-type barium hexaferrite prepared by co-precipitation. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 27, 2045–2052 (2007)
Jia, L., Luo, J., Zhang, H., Xue, G., Jing, Y.: High-frequency properties of Si-doped Z-type hexaferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 489, 162–166 (2010)
Watawe, S.C., Sarwede, B.D., Bellad, S.S., Sutar, B.D., Chougule, B.K.: Microstructure, frequency and temperature-dependent dielectric properties of cobalt-substituted lithium ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 214, 55–60 (2000)
Bellad, S.S., Chougule, B.K.: Composition and frequency dependent dielectric properties of Li-Mg-Ti ferrites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 66, 58–65 (2000)
Singh, A.K., Goel, T.C., Mendiratta, R.G., Thakur, O.P., Prakash, C.: Dielectric properties of Mn-substituted Ni-Zn ferrites. J. Appl. Phys. 91, 6626 (2002)
Rezlescu, N., Rezlescu, E.: Dielectric properties of copper containing ferrites. J. Phys. Status Solid. 23, 575 (1974)
Kolekar, C.B., Vasambekar, P.N., Kulkarni, S.G., Vaingankar, A.S.: Effect of Gd3+ substitution on dielectric behaviour of copper cadmium ferrites. J. Mater. Sci. 30, 5784–5788 (1995)
Iqbal, M.J., Khan, R.A., Mizukami, S., Miyazaki, T.: Tailoring of structural, electrical and magnetic properties of BaCo2 W-type hexaferrites by doping with Zr-Mn binary mixtures for useful applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 2137–2144 (2011)
Gul, I.H., Maqsood, A.: Influence of Zn-Zr ions on physical and magnetic properties of co-precipitated cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 316, 13–18 (2007)
Almeida, R.M., Paraguassu, W., Pires, D.S., Corrêa, R.R., de Paschoal, C.W.A.: Impedance spectroscopy analysis of BaFe12O19 M-type hexaferrite obtained by ceramic method. Ceram. Int. 2443–2447 (2009)
Chowdari, B.V.R., Krishnnan, R.G.: AC conductivity analysis of glassy silver iodomolybdate system. J. Solid State Ion. 23, 225–233 (1987)
Kao, K.C.: Dielectric phenomena in solids, vol. 2, pp. 51–43. Elsevier Academic Press, San Diego (2004)
Mazen, S.A., Zaki, H.M.: AC conductivity of Li-Ge ferrite. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 28, 609–613 (1995)
Junior, G.F.M.P., Rodrigues, H.O., Almeida, J.S., Sancho, E.O., Goes, J.C., Costa, M.M., Denardin, J.C., Sombra, A.S.B.: Study of the dielectric and magnetic properties of Co2Y, Y-type hexaferrite. (Ba2Co2Fe12O22) added with PbO and Bi2O3 in the RF frequency range. J. Alloys Compd. 493, 326–334 (2010)
Mazen, S.A., Zaki, H.M.: AC conductivity of Li-Ge ferrite. J. Phys. 28, 609–613 (1995)
Cho, H., Kim, S.: M-Hexaferrites with planar magnetic anisotropy and their application to high-frequency microwave absorbers. IEEE Trans. Magn. 35, 3151–3153 (1999)
Nedkov, I., Petkov, A., Karpov, A.: Microwave absorption in Scand Co-Ti-substituted Ba hexaferrite powders. IEEE Trans. Magn. 26, 1483–1487 (1990)
Asghar, G., Anis-ur-Rehman, M.: Structral, dielectric and magnetic properties of Cr-Zn doped strontium hexa-ferrtie for high frequency applications. J. Alloys Compd. 528, 85–90 (2012)
Acknowledgments
Higher Education Commission (HEC), Applied Thermal Physics Laboratory (ATPL), COMSATS University Islamabad (CUI), Higher Education Commission (HEC) Islamabad, and Punjab Higher Education Commission (PHEC) Lahore, Pakistan, are acknowledged for technical and financial support to complete this work. Best wishes to all my colleagues for their moral support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmood, W., Haq, A., Rasheed, S. et al. Correlation of Structural Properties and Dielectric Spectroscopy in Pb-Doped Barium Hexaferrites. J Supercond Nov Magn 34, 1765–1773 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05722-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05722-9