Abstract
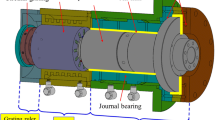
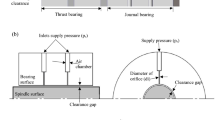
Air bearing spindles (ABS) can meet high accuracy demands for the precise rotation motion, which adopt air bearings to support spindle shaft, and the spindle shaft directly connects the motor rotor. The unbalanced electromagnetic force caused by motor rotor eccentricity (MRE) and air pressure fluctuation (APF) are two important influential factors to the dynamic performance of the spindle system and machining surface quality. This paper addresses the problems of measuring the MRE and APF in an ABS through testing machining surface topography. A permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) was modelled by finite element simulation (FES). Through FES it found that the MRE between the motor rotor and stator hole produced a radial magnetic force (RMF), which could cause ABS to periodically vibrate in the axial direction. Besides, the change of the air supply caused the stiffness variation of ABS and result in the tilt error motions of the spindle shaft. A theoretical model of machining surface topography considering MRE and APF was then proposed for the first time, which revealed that the MRE and APF resulted in the periodic fluctuations of the machining surface topography. The overall surface topography then became grooved surfaces. The above findings were finally validated by measurement results of ultraprecision diamond turning experiments.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABS:
-
Air bearing spindles
- PMSM:
-
Permanent magnet synchronous motor
- MRE:
-
Motor rotor eccentricity
- RMF:
-
Radial magnetic force
- APF:
-
Air pressure variation
- FES:
-
Finite element simulation
- M :
-
Centroid
- n :
-
Rotational speed
- t :
-
Turning time
- f :
-
Feed rate
- ω :
-
The vibration frequency
- ∆L :
-
Amplitude of the vibration
- k :
-
Coefficient
- P s :
-
Air supply pressure
- P a :
-
Atmospheric pressure, 0.1 MPa
- T :
-
Temperature
- d 1 :
-
Orifice diameter
- h 2 :
-
Air gap
- Q 1 :
-
Flow rate
- V :
-
Volume
References
Uriarte, L., Herrero, A., Zatarain, M., Santiso, G., Lacalle, L. N., Lamikiz, A., & Albizuri, J. (2007). Error budget and stiffness chain assessment in a micromilling machine equipped with tools less than 0.3 mm in diameter. Precision Engineering, 31(1), 1–12.
Zhang, S. J., & To, S. (2016). Spindle vibration influencing form error in ultraprecision diamond machining. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part C-Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 231(17), 1989–1996.
Kolar, P., Sulitka, M., & Janota, M. (2011). Simulation of dynamic properties of a spindle and tool system coupled with a machine tool frame. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 54(1), 11–20.
Sung, S. J., Jang, G. H., Jang, J. W., & Lee, H. L. (2013). Vibration and noise in a HDD spindle motor arising from the axial UMF ripple. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 49(6), 2489–2494.
Kim, D. J., Kim, H. J., Hong, J. P., & Park, C. J. (2014). Estimation of acoustic noise and vibration in an induction machine considering rotor eccentricity. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 50(50), 857–860.
Xu, X. B., Liu, J. H., & Chen, S. (2019). Internal model control for reduction of bias and harmonic currents in hybrid magnetic bearing. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 115, 70–81.
Fu, L., Zuo, S. G., Deng, W. Z., & Wu, S. L. (2016). Modeling and analysis of electromagnetic force, vibration, and noise in permanent-magnet synchronous motor considering current harmonics. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 63(12), 7455–7466.
Mystkowski, A., Kierdelewicz, A., Jastrzebski, R. P., Dragasius, E., & Eidukynas, D. (2018). Flux measurement and conditioning system for heteropolar active magnetic bearing using Kapton-foil Hall sensors. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 115, 394–404.
Kim, J. Y., Sung, S. J., & Jang, G. H. (2012). Characterization and experimental verification of the axial unbalanced magnetic force in brushless DC motors. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 48(11), 3001–3004.
Li, Y., Lu, Q., Zhu, Z. Q., Wu, L. J., Li, G. J., & Wu, D. (2015). Analytical synthesis of air-gap field distribution in permanent magnet machines with rotor eccentricity by superposition method. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 51(11), 1–4.
Li, J., & Cho, Y. (2010). Dynamic reduction of unbalanced magnetic force and vibration in switched reluctance motor by the parallel paths in windings. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, 81(2), 407–419.
Wu, Q. H., Sun, Y. Z., Chen, W. Q., Chen, G. D., Bai, Q. S., & Zhang, Q. C. (2018). Effect of motor rotor eccentricity on aerostatic spindle vibration in machining processes. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 232(7), 1331–1342.
Zhang, S. J., To, S., Cheung, C. F., & Wang, H. T. (2012). Dynamic characteristics of an aerostatic bearing spindle and its influence on surface topography in ultra-precision diamond turning. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 62(1), 1–12.
Chen, W. Q., Liang, Y. C., Sun, Y. Z., Bai, Q. S., & An, C. H. (2014). A novel dynamic modeling method for aerostatic spindle based on pressure distribution. Journal of Vibration and Control, 21(16), 3339–3347.
Liang, Y. C., Chen, W. Q., Bai, Q. S., Sun, Y. Z., Chen, G. D., Zhang, Q., & Sun, Y. (2013). Design and dynamic optimization of an ultraprecision diamond flycutting machine tool for large KDP crystal machining. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 69(1–4), 237–244.
Chen, G. D., Sun, Y. Z., Zhang, F. H., An, C. H., Chen, W. Q., & Su, H. (2017). Influence of ultra-precision flycutting spindle error on surface frequency domain error formation. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 88(9), 3233–3241.
Chen, G. D., Sun, Y. Z., An, C. H., Zhang, F. H., Sun, Z. J., & Chen, W. Q. (2016). Measurement and analysis for frequency domain error of ultra-precision spindle in a flycutting machine tool. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954405416673102.
Xi, S. T., Cao, H. R., & Chen, X. F. (2019). Dynamic modeling of spindle bearing system and vibration response investigation. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 114, 486–511.
Nakao, Y., Suzuki, K., Yamada, K., & Nagasaka, K. (2014). Feasibility study on design of spindle supported by high-stiffness water hydrostatic thrust bearing. International Journal of Automation Technology, 8, 530–538.
Chen, W. Q., Liang, Y. C., Sun, Y. Z., An, C. H., & Chen, G. D. (2014). Investigation of the influence of constant pressure oil source fluctuations on ultra-precision machining. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture, 229(2), 372–376.
Khanfir, H., Bonis, M., & Revel, P. (2005). Improving waviness in ultra precision turning by optimizing the dynamic behavior of a spindle with magnetic bearings. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 45(7), 841–848.
Feng, H. H., Xu, C. D., & Wan, J. (2014). Mathematical model and analysis of the water-lubricated hydrostatic journal bearings considering the translational and tilting motions. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2014, 353769.
Liu, J., & Chen, X. (2014). Dynamic design for motorized spindles based on an integrated model. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 71(9), 1961–1974.
Zhang, S., Li, Z., Xiong, Z. W., & Suet, T. (2019). A theoretical and experimental study of forced spindle vibration under unbalanced magnetic forces in ultra-precision machining. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 103(9–12), 4689–4694.
He, C., & Zong, W. J. (2019). Influencing factors and theoretical models for the surface topography in diamond turning process: A review. Micromachines, 10(5), 288.
Ning, J., & Liang, S. (2019). Predictive modeling of machining temperatures with force–temperature correlation using cutting mechanics and constitutive relation. Materials, 12(2), 284.
Ning, J., Nguyen, V., Huang, Y., Hartwig, K., Liang, S. (2019). Constitutive modeling of ultra-fine-grained titanium flow stress for machining temperature prediction. Bio-Design and Manufacturing, 2, 153–160.
Ning, J., Nguyen, V., & Liang, S. Y. (2019). Analytical modeling of machining forces of ultra-fine-grained titanium. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 101, 627–636.
Valavi, M., Nysveen, A., Nilssen, R., Lorenz, R., & Rølvåg, T. (2014). Influence of pole and slot combinations on magnetic forces and vibration in low-speed PM wind generators. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 50(5), 1–11.
Chen, X., Yuan, S. H., & Peng, Z. X. (2015). Nonlinear vibration for PMSM used in HEV considering mechanical and magnetic coupling effects. Nonlinear Dynamics, 80(1–2), 541–552.
Wang, Y. (1999). Gas lubricated theory and design manual of gas bearings (pp. 154–167). Beijing: Machinery Industry Press.
Wu, Q. H., Sun, Y. Z., Chen, W. Q., Wang, Q., & Chen, G. D. (2019). Theoretical prediction and experimental verification of the unbalanced magnetic force in air bearing motor spindles. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture, 233(3), 2330–2344.
Wu, Q. H., Sun, Y. Z., Chen, W. Q., Liu, H. T., & Luo, X. C. (2019). An mechatronics coupling design approach for aerostatic bearing spindles. International Journal Precision Engineering and Manufacturing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-019-00098-w.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support of the International Science & Technology Cooperation Program of China (No. 2015DFA70630), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51505107 and 51705462), and Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. LQ20E050021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y., Wu, Q., Chen, W. et al. Influence of Unbalanced Electromagnetic Force and Air Supply Pressure Fluctuation in Air Bearing Spindles on Machining Surface Topography. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 22, 1–12 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-020-00428-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-020-00428-3