Abstract
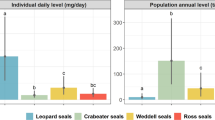
Large animals such as sea birds and marine mammals can transport limiting nutrients between different regions of the ocean, thereby stimulating and enhancing productivity. In Antarctica this process is influenced by formation and breakup of sea ice and its influence on the feeding behaviour of predators and their prey. We used analyses of bioactive metals (for example, Fe, Co, Mn), macronutrients (for example, N) and stable isotopes (δ13C and δ15N) in the excreta of Adélie (Pygoscelis adeliae) and emperor penguins (Aptenodytes forsteri) as well as Weddell seals (Leptonychotes weddellii) from multiple sites, among multiple years (2012–2014) to resolve how changes in sea ice dynamics, as indicated by MODIS satellite images, were coincident with prey switching and likely changes in nutrient fluxes between the offshore pelagic and coastal zones. We also sampled excreta of the south polar skua (Stercorarius maccormicki), which preys on penguins and scavenges the remains of both penguins and seals. We found strong coincidence of isotopic evidence for prey switching, between euphausiids (Euphausia superba and E. crystallorophias) and pelagic/cryopelagic fishes (for example, Pleuragramma antarcticum) in penguins, and between pelagic/cryopelagic fishes and Antarctic toothfish (Dissostichus mawsoni) in Weddell seals, with changes in sea ice cover among years. Further, prey switching was strongly linked to changes in the concentrations of nutrients (Fe and N) deposited in coastal environments by both penguins and seals. Our findings have important implications for understanding how the roles of large animals in supporting coastal productivity may shift with environmental conditions in polar ecosystems.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainley DG, Ballard G, Dugger KM. 2006. Competition among penguins and cetaceans reveals trophic cascades in the western Ross Sea, Antarctica. Ecology 87:2080–93.
Ainley DG, Ballard G, Emslie SD, Fraser WR, Wilson PR, Woehler EJ. 2003. Adélie penguins and environmental change. Science 80(300):429–30.
Ainley DG, Ballard G, Jones RM, Jongsomjit D, Pierce SD, Smith WO Jr, Veloz S. 2015. Trophic cascades in the western Ross Sea, Antarctica: revisited. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 534:1–16.
Ainley DG, Russell J, Jenouvrier S, Woehler E, Lyver P, Fraser WR, Kooyman GL. 2010. Antarctic penguin response to habitat change as Earth’s troposphere reaches 2°C above preindustrial levels. Ecol Monogr 80:49–66.
Ainley DG, Siniff DB. 2009. The importance of antarctic toothfish as prey of Weddell seals in the Ross Sea. Antarct Sci 21:317–27.
Ainley DG, Wilson PR, Barton KJ, Ballard G, Nur N, Karl B. 1998. Diet and foraging effort of Adélie penguins in relation to pack-ice conditions in the southern Ross Sea. Polar Biol 20:311–19.
Arkhipkin AI. 2013. Squid as nutrient vectors linking Southwest Atlantic marine ecosystems. Deep Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 95:7–20.
Barbraud C, Weimerskirch H. 2001. Emperor penguins and climate change. Nature 411:183–6.
Brault EK, Koch PL, Costa DP, McCarthy MD, Hückstädt LA, Goetz KT, McMahon KW, Goebel ME, Karlsson O, Teilmann J, Harkonen T, Harding KC. 2019. Trophic position and foraging ecology of Ross, Weddell, and crabeater seals revealed by compound-specific isotope analysis. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 611:1–18.
Brimble SK, Foster KL, Mallory ML, Macdonald RW, Smol JP, Biais JM. 2009. High arctic ponds receiving biotransported nutrients from a nearby seabird colony are also subject to potentially toxic loadings of arsenic, cadmium, and zinc. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:2426–33.
Burns JM, Kooyman GL. 2001. Habitat use by Weddell seals and emperor penguins foraging in the Ross Sea, Antarctica. Am Zool 41:90–8.
Burns JM, Trumble SJ, Castellini MA, Testa JW. 1998. The diet of Weddell seals in McMurdo Sound, Antarctica as determined from scat collections and stable isotope analysis. Polar Biol 19:272–82.
Cherel Y. 2008. Isotopic niches of emperor and Adélie penguins in Adélie Land, Antarctica. Mar Biol 154:813–21.
Cherel Y, Hobson KA. 2007. Geographic variation in carbon stable isotope signatures of marine predators: a tool to investigate their foraging areas in the Southern Ocean. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 329:281–7.
Cherel Y, Koubbi P, Giraldo C, Penot F, Tavernier E, Moteki M, Ozouf-Costaz C, Causse R, Chartier A, Hosie G. 2011. Isotopic niches of fishes in coastal, neritic and oceanic waters off Adélie land, Antarctica. Polar Sci 5:286–97.
Clarke A, Murphy EJ, Meredith MP, King JC, Peck LS, Barnes DKA, Smith RC. 2007. Climate change and the marine ecosystem of the western Antarctic Peninsula. Philos Trans R Soc B Biol Sci 362:149–66.
Daneri GA, Negri A, Coria NR, Negrete J, Libertelli MM, Corbalán A. 2018. Fish prey of Weddell seals, Leptonychotes weddellii, at Hope Bay, Antarctic Peninsula, during the late summer. Polar Biol 41:1027–31.
Doney SC, Ruckelshaus M, Emmett Duffy J, Barry JP, Chan F, English CA, Galindo HM, Grebmeier JM, Hollowed AB, Knowlton N, Polovina J, Rabalais NN, Sydeman WJ, Talley LD. 2012. Climate change impacts on marine ecosystems. Annu Rev Mar Sci 4:11–37.
Doughty CE, Roman J, Faurby S, Wolf A, Haque A, Bakker ES, Malhi Y, Dunning JB, Svenning JC. 2015. Global nutrient transport in a world of giants. Proc Natl Acad Sci 113:868–73.
Dugger KM, Ballard G, Ainley DG, Lyver POB, Schine C. 2014. Adélie penguins coping with environmental change: results from a natural experiment at the edge of their breeding range. Front Ecol Evol 2:1–12.
Emslie SD, McKenzie A, Patterson WP. 2018. The rise and fall of an ancient Adélie penguin ‘supercolony’ at Cape Adare, Antarctica. R Soc Open Sci 5:172032.
Emslie SD, Patterson WP. 2007. Isotopic record of penguin diet. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:11666–9.
Fitzwater SE, Johnson KS, Gordon RM, Coale KH, Smith WO. 2000. Trace metal concentrations in the Ross Sea and their relationship with nutrients and phytoplankton growth. Deep Res II 47:3159–79.
Flores H, Atkinson A, Kawaguchi S, Krafft B, Milinevsky G, Nichol S, Werner T. 2012. Impact of climate change on Antarctic krill. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 458:1–19.
Fry B. 2006. Stable isotope ecology. New York: Springer.
Gillies CL, Stark JS, Smith SDA. 2012. Research article: small-scale spatial variation of δ13C and δ15N isotopes in Antarctic carbon sources and consumers. Polar Biol 35:813–27.
Giraldo C, Cherel Y, Vallet C, Mayzaud P, Tavernier E, Moteki M, Hosie G, Koubbi P. 2011. Ontogenic changes in the feeding ecology of the early life stages of the Antarctic silverfish (Pleuragramma antarcticum) documented by stable isotopes and diet analysis in the Dumont d’Urville Sea (East Antarctica). Polar Sci 5:252–63.
Goetz KT, Burns JM, Hückstädt LA, Shero MR, Costa DP. 2017. Temporal variation in isotopic composition and diet of Weddell seals in the western Ross Sea. Deep Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 140:36–44.
Goutte A, Charrassin JB, Cherel Y, Carravieri A, De Grissac S, Massé G. 2014. Importance of ice algal production for top predators: new insights using sea-ice biomarkers. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 513:269–75.
Goutte A, Cherel Y, Churlaud C, Ponthus JP, Massé G, Bustamante P. 2015. Trace elements in Antarctic fish species and the influence of foraging habitats and dietary habits on mercury levels. Sci Total Environ 538:743–9.
Graham NAJ, Wilson SK, Carr P, Hoey AS, Jennings S, MacNeil MA. 2018. Seabirds enhance coral reef productivity and functioning in the absence of invasive rats. Nature 559:250–3.
Grubbs FE. 1950. Sample criteria for testing outlying observations. Ann Math Statist 21:27–58.
Huang T, Sun L, Wang Y, Chu Z, Qin X, Yang L. 2014. Transport of nutrients and contaminants from ocean to island by emperor penguins from Amanda Bay, East Antarctic. Sci Total Environ 468–469:578–83.
IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change). 2019. Special report: the ocean and cryosphere in a changing climate. IPCC Summ Policymalers TBD:TBD. https://www.ipcc.ch/report/srocc/.
Jack L, Wing SR. 2011. Individual variability in trophic position and diet of a marine omnivore is linked to kelp bed habitat. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 443:129–39.
Jack L, Wing SR, McLeod RJ. 2009. Prey base shifts in red rock lobster Jasus edwardsii in response to habitat conversion in Fiordland marine reserves. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 381:213–22.
Jarman SN, McInnes JC, Faux C, Polanowski AM, Marthick J, Deagle BE, Southwell C, Emmerson L. 2013. Adélie penguin population diet monitoring by analysis of food DNA in scats. PLoS One 8:e82227.
Jo H-S, Yeon I, Lim C, Hanchet SM, Lee D-W, Kang C-K. 2013. Fatty acid and stable isotope analyses to infer diet of Antarctic toothfish caught in the southern Ross Sea. CCAMLR Sci 20:21–36.
Kennedy H, Thomas DN, Kattner G, Hass C, Dieckmann GS. 2002. Particulate organic matter in Antarctic summer sea ice: concentration and stable isotope composition. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 238:1–13.
Kim SL, Conlan K, Malone DP, Lewis CV. 2005. Possible food caching and defence in the Weddell seal: observations from McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. Antarct Sci 17:71–2.
Kokubun N, Choy E-J, Kim J-H, Takahashi A. 2015. Isotopic values of Antarctic krill in relation to foraging habitat of penguins. Ornithol Sci 14:13–20.
Kooyman GL, Ponganis PJ. 2017. Rise and fall of Ross Sea emperor penguin colony populations: 2000 to 2012. Antarct Sci 29:207–8.
Koshino Y, Kudo H, Kaeriyama M. 2013. Stable isotope evidence indicates the incorporation into Japanese catchments of marine-derived nutrients transported by spawning Pacific Salmon. Freshw Biol 58:1864–77.
LaRue MA, Rotella JJ, Garrott RA, Siniff DB, Ainley DG, Stauffer GE, Porter CC, Morin PJ. 2011. Satellite imagery can be used to detect variation in abundance of Weddell seals (Leptonychotes weddellii) in Erebus Bay, Antarctica. Polar Biology 34:1727–37.
Lavery TJ, Roudnew B, Gill P, Seymour J, Seuront L, Johnson G, Mitchell JG, Smetacek V. 2010. Iron defecation by sperm whales stimulates carbon export in the Southern Ocean. Proc R Soc B 277:3527–31.
Lavery TJ, Roudnew B, Seymour J, Mitchell JG, Smetacek V, Nicol S. 2014. Whales sustain fisheries: blue whales stimulate primary production in the Southern Ocean. Mar Mammal Sci 30(3):888–904.
Loreau M, Holt RD. 2004. Spatial flows and the regulation of ecosystems. Am Nat 132:652–61.
Loreau M, Mouquet N, Holt RD. 2003. Meta-ecosystems: a theoretical framework for a spatial ecosystem ecology. Ecol Lett 6:673–9.
Lorenzini S, Baroni C, Baneschi I, Salvatore MC, Fallick AE, Hall BL. 2014. Adélie penguin dietary remains reveal Holocene environmental changes in the western Ross Sea (Antarctica). Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 395:21–8.
Lyver POB, Barron M, Barton KJ, Ainley DG, Pollard A, Gordon S, McNeill S, Ballard G, Wilson PR. 2014. Trends in the breeding population of Adélie penguins in the Ross Sea, 1981–2012: a coincidence of climate and resource extraction effects. PLoS One 9:1–10.
Lyver POB, MacLeod CJ, Ballard G, Karl BJ, Barton KJ, Adams J, Ainley DG, Wilson PR. 2011. Intra-seasonal variation in foraging behavior among Adélie penguins (Pygocelis adeliae) breeding at Cape Hallett, Ross Sea, Antarctica. Polar Biol 34:49–67.
Maldonado MT, Surma S, Pakhomov EA. 2016. Southern Ocean biological iron cycling in the pre-whaling and present ecosystems. Philos Trans R Soc A Math Phys Eng Sci 374:2081.
McCutchan JH Jr, Lewis WM, Kendall C, McGrath CC. 2003. Variation in trophic shift for stable isotope ratios of carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur. Oikos 102:378–90.
McGillicuddy DJ, Sedwick PN, Dinniman MS, Arrigo KR, Bibby TS, Greenan BJW, Hofmann EE, Klinck JM, Smith WO, Mack SL, Marsay CM, Sohst BM, Van Dijken GL. 2015. Iron supply and demand in an Antarctic shelf ecosystem. Geophys Res Lett 42(19):8088–97.
McMullin RM, Wing SR, Reid MR. 2017a. Ice fish otoliths record dynamics of advancing and retreating sea ice in Antarctica. Limnol Oceanogr 62:2662–73.
McMullin RM, Wing SR, Wing LC, Shatova OA. 2017b. Trophic position of Antarctic ice fishes reflects food web structure along a gradient in sea ice persistence. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 564:87–98.
Michelutti N, Keatley BE, Brimble S, Blais JM, Liu H, Douglas MSV, Mallory ML, MacDonald RW, Smol JP. 2009. Seabird-driven shifts in Arctic pond ecosystems. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 276:591–6.
Nicol S, Bowie A, Jarman S, Lannuzel D, Meiners KM, van der Merwe P. 2010. Southern ocean iron fertilization by baleen whales and Antarctic krill. Fish Fish 11:203–9.
Nie Y, Liu X, Sun L, Emslie SD. 2012. Effect of penguin and seal excrement on mercury distribution in sediments from the Ross Sea region, East Antarctica. Sci Total Environ 433:132–40.
Norkko A, Thrush SF, Cummings VJ, Gibbs MM, Andrew NL, Norkko J, Schwarz AM. 2007. Trophic structure of coastal antarctic food webs associated with changes in sea ice and food supply. Ecology 88:2810–20.
Palmer AS, Snape I, Stark JS, Johnstone GJ, Townsend AT. 2006. Baseline metal concentrations in Paramoera walkeri from East Antarctica. Mar Pollut Bull 52:1441–9.
Pinkerton MH, Forman J, Bury SJ, Brown J, Horn P, O’Driscoll RL. 2013. Diet and trophic niche of Antarctic silverfish Pleuragramma antarcticum in the Ross Sea, Antarctica. J Fish Biol 82:141–64.
Polis GA, Anderson WB, Holt RD. 1997. Toward an integration of landscape and food web ecology: the dynamics of spatially subsidized food webs. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 28:289–316.
Ponganis PJ, Stockard TK. 2007. Short note: the Antarctic toothfish: How common a prey for Weddell seals? Antarct Sci 19:441–2.
Ratnarajah L, Melbourne-Thomas J, Marzloff MP, Lannuzel D, Meiners KM, Chever F, Nicol S, Bowie AR. 2016. A preliminary model of iron fertilisation by baleen whales and Antarctic krill in the Southern Ocean: sensitivity of primary productivity estimates to parameter uncertainty. Ecol Model 320:203–12.
Ratnarajah L, Nicol S, Bowie AR. 2018. Pelagic iron recycling in the Southern Ocean: exploring the contribution of marine animals. Front Mar Sci 5:109.
Rau GH, Sullivan CW, Gordon LI. 1991. δ13C and δ15N variations in Weddell Sea particulate organic-matter. Mar Chem 35:355–69.
Roman J, McCarthy JJ. 2010. The whale pump: marine mammals enhance primary productivity in a coastal basin. PLoS One 5:e13255.
Schlosser C, Schmidt K, Aquilina A, Homoky WB, Castrillejo M, Mills RA, Patey MD, Fielding S, Atkinson A, Achterberg EP. 2018. Mechanisms of dissolved and labile particulate iron supply to shelf waters and phytoplankton blooms off South Georgia, Southern Ocean. Biogeosciences 15:4973–93.
Schmidt K, Atkinson A, Steigenberger S, Fielding S, Lindsay MCM, Pond DW, Tarling GA, Klevjer TA, Allen CS, Nicol S, Achterberg EP. 2011. Seabed foraging by Antarctic krill: implications for stock assessment, bentho-pelagic coupling, and the vertical transfer of iron. Limnol Oceanogr 56:1411–28.
Schmidt K, Schlosser C, Atkinson A, Fielding S, Venables HJ, Waluda CM, Achterberg EP. 2016. Zooplankton gut passage mobilizes lithogenic iron for ocean productivity. Curr Biol 26:2667–73.
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW. 2012. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9:671–5.
Sedwick PN, DiTullio GR. 1997. Regulation of algal blooms in Antarctic shelf waters by the release of iron from melting sea ice. Geophys Res Lett 24:2515–18.
Sedwick PN, DiTullio GR, Mackey DJ. 2000. Iron and manganese in the Ross Sea, Antarctica: seasonal iron limitation in Antarctic shelf waters. J Geophys Res 105:11321–36.
Shatova O, Wing SR, Gault-Ringold M, Wing L, Hoffmann LJ. 2016. Seabird guano enhances phytoplankton production in the Southern Ocean. J Exp Mar Bio Ecol 483:74–87.
Shatova OA, Wing SR, Hoffmann LJ, Wing LC, Gault-Ringold M. 2017. Phytoplankton community structure is influenced by seabird guano enrichment in the Southern Ocean. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 191:125–35.
Subalusky AL, Dutton CL, Rosi-Marshall EJ, Post DM. 2015. The hippopotamus conveyor belt: vectors of carbon and nutrients from terrestrial grasslands to aquatic systems in sub-Saharan Africa. Freshw Biol 60:512–25.
Sun LG, Emslie SD, Huang T, Blais JM, Xie ZQ, Liu XD, Yin XB, Wang YH, Huang W, Hodgson DA, Smol JP. 2013. Vertebrate records in polar sediments: biological responses to past climate change and human activities. Earth-Sci Rev 126:147–55.
Thrush SF, Cummings VJ. 2011. Massive icebergs, alteration in primary food resources and change in benthic communities at Cape Evans, Antarctica. Mar Ecol 32:289–99.
Tierney M, Southwell C, Emmerson LM, Hindell MA. 2008. Evaluating and using stable-isotope analysis to infer diet composition and foraging ecology of Adélie penguins Pygoscelis adeliae. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 355:297–307.
Tovar-Sanchez A, Duarte CM, Hernández-León S, Sañudo-Wilhelmy SA. 2007. Krill as a central node for iron cycling in the Southern Ocean. Geophys Res Lett 34:1–4.
Vacchi M, Pisano E, Ghigliotti L, Eds. 2017. Advances in polar ecology the Antarctic silverfish: a keystone species in a changing ecosystem. New York: Springer.
Wada E, Terazaki M, Kabaya Y, Nemoto T. 1987. 15N and 13C abundance in the Antarctic Ocean with emphasis on the biogeochemical structure of the food web. Deep Sea Res 34:829–41.
Wing SR, Gault-Ringold M, Stirling CH, Wing LC, Shatova OA, Frew RD. 2017a. δ56Fe in seabird guano reveals extensive recycling of iron in the Southern Ocean ecosystem. Limnol Oceanogr 62:1671–81.
Wing SR, Jack L, Shatova O, Leichter JJ, Barr D, Frew RD, Gault-Ringold M. 2014. Seabirds and marine mammals redistribute bioavailable iron in the Southern Ocean. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 510:1–13.
Wing SR, Leichter JJ, Wing LC, Stokes D, Genovese SJ, McMullin RM, Shatova OA. 2018. Contribution of sea ice microbial production to Antarctic benthic communities is driven by sea ice dynamics and composition of functional guilds. Glob Change Biol 24:3642–53.
Wing SR, McLeod RJ, Leichter JJ, Frew RD, Lamare MD. 2012. Sea ice microbial production supports Ross Sea benthic communities: influence of a small but stable subsidy. Ecology 93:226–35.
Wing SR, O’Connell-Milne SA, Wing LC, Reid MR. 2020. Trace metals in Antarctic clam shells record the chemical dynamics of changing sea ice conditions. Limnol Oceanogr 65:504–14.
Wing SR, Wing LC, Shatova OA, Van Hale R. 2017b. Marine micronutrient vectors: seabirds, marine mammals and fishes egest high concentrations of bioactive metals in the subantarctic island ecosystem. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 563:13–23.
Zhao L, Castellini MA, Mau TL, Trumble SJ. 2004. Trophic interactions of Antarctic seals as determined by stable isotope signatures. Polar Biol 27:368–73.
Acknowledgements
We thank R. Robbins, S. Rupp, M Lamare, O Shatova, Rebecca McMullin, Simon Trotter and the staff of New Zealand’s Scott Base as well as the United States Antarctic Program at McMurdo Station for their assistance with logistics and fieldwork. We are also grateful to Robert van Hale and Dianne Clark at the Isotrace research group, in the Department of Chemistry, who carried out stable isotope analysis on samples used in the research presented here. Monetary support was provided by grants from Antarctica New Zealand, The Royal Society of New Zealand’s Marsden Fund and the University of Otago Graduate Research School to SRW, with additional support provided by Scripps Institution of Oceanography and the University of California San Diego Academic Senate to DS and JJL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Author Contributions
The authors each contributed substantially to the study’s conception, data analysis and manuscript preparation. SAO and DB were responsible for preparation of field samples and analysis of trace metal and stable isotope data. LCW, DS, SG and JJL collected samples and contributed to analysis of data. SRW was involved in each aspect of the study and was primarily responsible for statistical analysis and initial manuscript preparation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wing, S.R., Wing, L.C., O’Connell-Milne, S.A. et al. Penguins and Seals Transport Limiting Nutrients Between Offshore Pelagic and Coastal Regions of Antarctica Under Changing Sea Ice. Ecosystems 24, 1203–1221 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-020-00578-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-020-00578-5