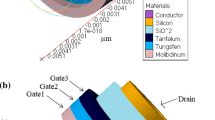
Abstract
In this work, drain current ID for 7-nm gate length dual-material (DM) cylindrical gate all around (CGAA) silicon nanowire (SiNW) has been studied and simulation results are reported using Silvaco ATLAS 3D TCAD. In this device, we consider the non-equilibrium Green’s function (NEGF) approach and self-consistent solution of Schrödinger's equation with Poisson’s equation. The splitting of conduction in multiple sub-bands has been considered and there is no doping in the channel region. The effect of DM gate engineering (variation of screen gate and control gate length having different work function) for SiNW channel with 2-nm radius and gate oxide (SiO2) thickness of 0.8 nm on ID have been studied. It was found that DM gate engineering reduces drain-induced barrier lowering (DIBL) but it also slightly increases sub-threshold slope (SS). This work has obtained small DIBL (~54 mV/V), small SS (~68 mV/dec), and higher IOn/IOff (~4 × 108) ratio as compared to literature concerning the inversion mode devices. The smallest DIBL is obtained when control gate length is the highest, and vice versa. With increase in control gate length, there is also increase in both IOn and IOff but IOn/IOff ratio decreases.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
A. Baidya, T. R. Lenka, and S. Baishya, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 71, 413 (2017).
J. Robertson and R. M. Wallace, Mater. Sci. Eng. R 88, 1 (2015).
F. Adamu-Lema, X. Wang, S. M. Amoroso, C. Riddet, B. Cheng, L. Shifren, R. Aitken, S. Sinha, G. Yeric, and A. Asenov, IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 61, 3372 (2014).
U. K. Das, G. Eneman, R. S. R. Velampati, Y. S. Chauhan, K. B. Jinesh, and T. K. Bhattacharyya, J. Electron Dev. Soc. 6, 1129 (2018).
U. K. Das, M. G. Bardon, D. Jang, G. Eneman, P. Schuddinck, D. Yakimets, P. Raghavan, and G. Groeseneken, IEEE Electron Dev. Lett. 38, 9 (2017).
A. Kundu, A. Dasgupta, R. Das, S. Chakraborty, A. Dutta, and C. K. Sarkar, Superlatt. Microstruct. 94, 60 (2016).
B. Jena, K. P. Pradhan, D. Dash, G. P. Mishra, P. K. Sahu, and S. K. Mohapatra, Adv. Nat. Sci.: Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 6, 035010 (2015).
B. Jena, K. P. Pradhan, P. K. Sahu, S. Dash, G. P. Mishra, and S. K. Mohapatra, Electron. Energet. 28, 637 (2015).
H. Wong and H. Iwai, Microelectron. Eng. 83, 1867 (2006).
Silvaco T-CAD, Version: ATLAS 5.19.20.R (2020).
J. Robertson and B. Falabretti, J. Appl. Phys. 100, 014111 (2006).
K. Han, X. Wang, H. Yang, and W. Wang, J. Semicond. 36, 036004 (2015).
K. Kita and A. Toriumi, Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 132902 (2009).
R. K. Baruah and R. P. Paily, IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 61, 123 (2014).
R. K. Sharma, R. Gupta, M. Gupta, and R. S. Gupta, IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 56, 1284 (2009).
P. Kasturi, M. Saxena, M. Gupta, and R. S. Gupta, IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 55, 372 (2008).
S. Rewari, V. Nath, S. Haldar, S. S. Deswal, and R. S. Gupta, Microsyst. Technol. 25, 1537 (2017).
Y.-B. Liao, M.-H. Chiang, N. Damrongplasit, W.-C. Hsu, and T.-J. K. Liu, IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 61, 2371 (2014).
P. Zheng, Yi. B. Liao, N. Damrongplasit, M. H. Chiang, and T. J. K. Liu, IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 61, 3949 (2014).
D. Nagy, G. Indalecio, A. J. G. Loureiro, M. A. Elmessary, K. Kalna, and N. Seoane, IEEE J. Electron Dev. Soc. 6, 332 (2018).
C. W. Lee, I. Ferain, A. Afzalian, R. Yan, N. D. Akhavan, P. Razavi, and J. P. Colinge, Solid-State Electron. 54, 97 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanjay, Prasad, B. & Vohra, A. Dual Material Gate Engineering to Reduce DIBL in Cylindrical Gate All Around Si Nanowire MOSFET for 7-nm Gate Length. Semiconductors 54, 1490–1495 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063782620110111
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063782620110111