Abstract
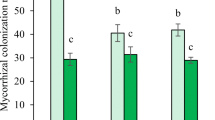
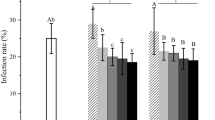
Environmental risks of silver (Ag) nanoparticles (NPs) have aroused considerable concern, however, their ecotoxicity in soil-plant systems has yet not been well elaborated, particularly in agroecosystems with various fertility levels and soil biota. The aims of the present study were to determine AgNPs impacts on maize as influenced by mycorrhizal inoculation and P fertilization. A greenhouse pot experiment was conducted determine the effects of mycorrhizal inoculation with Rhizophagus intraradices and P fertilization (0, 20, and 50 P mg/kg soil, as Ca(H2PO4)2) on plant growth, Ag accumulation and physiological responses of maize exposed to AgNPs (1 mg/kg), or an equivalent Ag+. Overall, AgNPs and Ag+ did not significantly affect plant biomass and acquisition of mineral nutrients, activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and peroxidase (POD), chlorophyll contents and photosystem (PS) II photochemical efficiency. In most cases, AgNPs and Ag+ caused similar Ag accumulation in plant tissues. P fertilization significantly increased Ag bioavailability and plant Ag accumulation, but only promoted the growth and P uptake of nonmycorrhizal plants. AM inoculation produced positive impacts on plant biomass, nutritional and physiological responses, but slightly affected extractable Ag in soil and Ag accumulation in plants. Mycorrhizal responses in plant growth and P uptake were more pronounced in the treatments without P but with Ag. By and large, AgNPs exhibited similar phytoavailability, phytoaccumulation and low phytotoxicity compared to Ag+, but higher fungitoxicity (i.e., lower root colonization). In conclusion, both AM inoculation and P fertilization can improve plant performance in the soil exposed to Ag, but P increases environmental risk of Ag. Our results indicate a beneficial role of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi but a dual role of P in soil-plant systems exposed to AgNPs or Ag+.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd-Alla MH, Nafady NA, Khalaf DM (2016) Assessment of silver nanoparticles contamination on faba bean-Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae-Glomus aggregatum symbiosis: implications for induction of autophagy process in root nodule. Agric Ecosyst Environ 218:163–177
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Anjum NA, Gill SS, Duarte AC, Pereira E, Ahmad I (2013) Silver nanoparticles in soil–plant systems. J Nanopart Res 15:1–26
Bell RA, Kramer JR (1999) Structural chemistry and geochemistry of silver-sulfur compounds: critical review. Environ Toxicol Chem 18:9–22
Bolan NS (1991) A critical review on the role of mycorrhizal fungi in the uptake of phosphorus by plants. Plant Soil 134:189–207
Bundschuh M, Filser J, Lüderwald S, McKee MS, Metreveli G, Schaumann GE, Schulz R, Wagner S (2018) Nanoparticles in the environment: where do we come from, where do we go to? Environ Sci Europe 30:6
Calder AJ, Dimkpa CO, Mclean JE, Britt DW, Johnson W, Anderson AJ (2012) Soil components mitigate the antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles towards a beneficial soil bacterium, Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6. Sci Total Environ 429:215–222
Cao J, Feng Y, He S, Lin X (2017) Silver nanoparticles deteriorate the mutual interaction between maize (Zea mays L.) and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: a soil microcosm study. Appl Soil Ecol 119:307–316
Cao J, Feng Y, Lin X, Wang J (2020) A beneficial role of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in influencing the effects of silver nanoparticles on plant-microbe systems in a soil matrix. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:11782–11796
Colman BP, Arnaout CL, Anciaux S, Gunsch CK, Hochella MF, Kim B, Lowry GV, McGill BM, Reinsch BC, Richardson CJ, Unrine JM, Wright JP, Yin L, Bernhardt ES (2013) Low concentrations of silver nanoparticles in biosolids cause adverse ecosystem responses under realistic field scenario. PLoS ONE 8:e57189
Falco WF, Queiroz AM, Fernandes J, Botero ER, Falcão EA, Guimarães FEG, M’Peko JC, Oliveira SL, Colbeck I, Caires ARL (2015) Interaction between chlorophyll and silver nanoparticles: A close analysis of chlorophyll fluorescence quenching. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 299:203–209
Feng Y, Cui X, He S, Dong G, Chen M, Wang J, Lin X (2013) The role of metal nanoparticles in influencing arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi effects on plant growth. Environ Sci Technol 47:9496–9504
Force L, Critchley C, van Rensen JJ (2003) New fluorescence parameters for monitoring photosynthesis in plants. Photosynth Res 78:17
Giannopolitis CN, Ries SK (1977) Superoxide dismutases I. Occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol 59:309–314
Gottschalk F, Sonderer T, Scholz RW, Nowack B (2009) Modeled environmental concentrations of engineered nanomaterials (TiO2, ZnO, Ag, CNT, fullerenes) for different regions. Environ Sci Technol 43:9216–9222
Grün AL, Straskraba S, Schulz S, Schloter M, Emmerling C (2018) Long-term effects of environmentally relevant concentrations of silver nanoparticles on microbial biomass, enzyme activity, and functional genes involved in the nitrogen cycle of loamy soil. J Environ Sci 69:12–22
Homaee MB, Ehsanpour AA (2016) Silver nanoparticles and silver ions: Oxidative stress responses and toxicity in potato (Solanum tuberosum L) grown in vitro. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 57:544–553
Jiang HS, Li M, Chang FY, Li W, Yin LY (2012) Physiological analysis of silver nanoparticles and AgNO3 toxicity to Spirodela polyrhiza. Environ Toxicol Chem 31:1880–1886
Jing X, Su Z, Xing H, Wang F, Shi Z, Liu X (2016) Biological effects of ZnO nanoparticles as influenced by arbuscular mycorrhizal inoculation and phosphorus fertilization. Environ Sci 37:3208–3215
Judy JD, Kirby JK, Creamer C, McLaughlin MJ, Fiebiger C, Wright C, Cavagnaro TR, Bertsch PM (2015) Effects of silver sulfide nanomaterials on mycorrhizal colonization of tomato plants and soil microbial communities in biosolid-amended soil. Environ Pollut 206:256–263
Kalaji HM, Bąba W, Gediga K, Goltsev V, Samborska IA, Cetner MD, Dimitrova S, Piszcz U, Bielecki K, Karmowska K, Dankov K, Kompała-Bąba A (2018) Chlorophyll fluorescence as a tool for nutrient status identification in rapeseed plants. Photosynth Res 136:329–343
Kalaji HM, Oukarroum A, Alexandrov V, Kouzmanova M, Brestic M, Zivcak M, Samborska IA, Cetner MD, Allakhverdiev SI, Goltsev V (2014) Identification of nutrient deficiency in maize and tomato plants by in vivo chlorophyll a fluorescence measurements. Plant Physiol Biochem 81:16–25
Lee WM, Kwak JI, An YJ (2012) Effect of silver nanoparticles in crop plants Phaseolus radiatus and Sorghum bicolor: Media effect on phytotoxicity. Chemosphere 86:491–499
Li M, Wang P, Dang F, Zhou DM (2017) The transformation and fate of silver nanoparticles in paddy soil: effects of soil organic matter and redox conditions. Environ Sci Nano 4:919–928
Lodeiro C, Capelo JL, Oliveira E, Lodeiro JF (2019) New toxic emerging contaminants: beyond the toxicological effects. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:1–4
Ma X, Geiser-Lee J, Deng Y, Kolmakov A (2010) Interactions between engineered nanoparticles (ENPs) and plants: phytotoxicity, uptake and accumulation. Sci Total Environ 408:3053–3061
Mcgillicuddy E, Murray I, Kavanagh S, Morrison L, Fogarty A, Cormican M, Dockery P, Prendergast M, Rowan N, Morris D (2017) Silver nanoparticles in the environment: sources, detection and ecotoxicology. Sci Total Environ 575:231–246
Miransari M (2010) Contribution of arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis to plant growth under different types of soil stress. Plant Biol 12:563–569
Mishra S, Singh HB (2015) Biosynthesized silver nanoparticles as a nanoweapon against phytopathogens: exploring their scope and potential in agriculture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:1097–1107
Noori A, White JC, Newman LA (2017) Mycorrhizal fungi influence on silver uptake and membrane protein gene expression following silver nanoparticle exposure. J Nanopart Res 19:66
Pallavi, Mehta CM, Srivastava R, Arora S, Sharma AK (2016) Impact assessment of silver nanoparticles on plant growth and soil bacterial diversity. 3 Biotech 6:254
Peyrot C, Wilkinson KJ, Desrosiers M, Sauvé S (2014) Effects of silver nanoparticles on soil enzyme activities with and without added organic matter. Environ Toxicol Chem 33:115–125
Pütter J, Becker R (1983) Peroxidase. In: Bergmeyer HU (Ed) Methods of Enzymatic Analysis. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, p 286
Queiroz AM, Mezacasa AV, Graciano DE, Falco WF, M’Peko JC, Guimarães FEG, Lawson T, Colbeck I, Oliveira SL, Caires ARL (2016) Quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence induced by silver nanoparticles. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 168:73–77
Rahmatpour S, Shirvani M, Mosaddeghi MR, Nourbakhsh F, Bazarganipour M (2017) Dose–response effects of silver nanoparticles and silver nitrate on microbial and enzyme activities in calcareous soils. Geoderma 285:313–322
Rai M, Yadav A, Gade A (2009) Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol Adv 27:76–83
Rajput VD, Minkina T, Sushkova S, Tsitsuashvili V, Mandzhieva S, Gorovtsov A, Nevidomskyaya D, Gromakova N (2018) Effect of nanoparticles on crops and soil microbial communities. J Soils Sediments 18:2179–2187
Rozpadek P, Wezowicz K, Stojakowska A, Malarz J, Surowka E, Sobczyk L, Anielska T, Wazny R, Miszalski Z, Turnau K (2014) Mycorrhizal fungi modulate phytochemical production and antioxidant activity of Cichorium intybus L. (Asteraceae) under metal toxicity. Chemosphere 112:217–224
Schlich K, Hund-Rinke K (2015) Influence of soil properties on the effect of silver nanomaterials on microbial activity in five soils. Environ Pollut 196:321–330
Shi Z, Zhang J, Lu S, Li Y, Wang F (2020) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi improve the performance of sweet sorghum grown in a Mo-contaminated soil. J Fungi 6:44
Sillen WMA, Thijs S, Abbamondi GR, Janssen J, Weyens N, White JC, Vangronsveld J (2015) Effects of silver nanoparticles on soil microorganisms and maize biomass are linked in the rhizosphere. Soil Biol Biochem 91:14–22
Simbine EO, Rodrigues LDC, Lapa-Guimarães J, Kamimura ES, Corassin CH, Oliveira CAFD (2019) Application of silver nanoparticles in food packages: A review. Food Sci Technol Int 39:793–802
Singh SK, Reddy VR, Fleisher DH, Timlin DJ (2017) Relationship between photosynthetic pigments and chlorophyll fluorescence in soybean under varying phosphorus nutrition at ambient and elevated CO2. Photosynthetica 55:421–433
Smith SE, Christophersen HM, Pope S, Smith FA (2010) Arsenic uptake and toxicity in plants: integrating mycorrhizal influences. Plant Soil 327:1–21
Smith SE, Jakobsen I, Grønlund M, Smith FA (2011) Roles of arbuscular mycorrhizas in plant phosphorus nutrition: interactions between pathways of phosphorus uptake in arbuscular mycorrhizal roots have important implications for understanding and manipulating plant phosphorus acquisition. Plant Physiol 156:1050–1057
Smith SE, Read DJ (2008) Mycorrhizal symbiosis, 3rd ed. Academic Press, San Diego
Stewart LI, Hamel C, Hogue R, Moutoglis P (2005) Response of strawberry to inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi under very high soil phosphorus conditions. Mycorrhiza 15:612–619
Strasser RJ, Tsimilli-Michael M, Qiang S, Goltsev V (2010) Simultaneous in vivo recording of prompt and delayed fluorescence and 820-nm reflection changes during drying and after rehydration of the resurrection plant Haberlea rhodopensis. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics 1797:1313–1326
Stuart EJ, Compton RG (2015) Nanoparticles-emerging contaminants. In: Moretto L, Kalcher K (eds) Environmental analysis by electrochemical sensors and biosensors nanostructure science and technology. Springer, New York, NY
Subramanian KS, Bharathi C, Jegan A (2008) Response of maize to mycorrhizal colonization at varying levels of zinc and phosphorus. Biol Fertil Soils 45:133–144
Trouvelot E, Kough JL, Gianinazzi-Pearson V (1986) Mesure du taux de mycorhization VA d’un système radiculaire. Recherche et méthodes d’estimation ayant une signification fonctionnelle. In: Gianinazzi-Pearson V, Gianinazzi S (eds) The Mycorrhizae: Physiology and Genetic. INRA Press, Paris
Vierheilig H, Coughlan AP, Wyss U, Piché Y (1998) Ink and vinegar, a simple staining technique for arbuscular-mycorrhizal fungi. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:5004–5007
Wang F (2017) Occurrence of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in mining-impacted sites and their contribution to ecological restoration: Mechanisms and applications. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 47:1901–1957
Wang F, Adams CA, Yang W, Sun Y, Shi Z (2020) Benefits of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in reducing organic contaminant residues in crops: Implications for cleaner agricultural production. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 50:1580–1612
Wang F, Jin X, Adams CA, Shi Z, Sun Y (2018) Decreased ZnO nanoparticles phytotoxicity to maize by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and organic phosphorus. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:23736–23747
Wang F, Liu X, Shi Z, Tong R, Adams CA, Shi X (2016) Arbuscular mycorrhizae alleviate negative effects of zinc oxide nanoparticle and zinc accumulation in maize plants–A soil microcosm experiment. Chemosphere 147:88–97
Wang F, Sun Y, Shi Z (2019) Arbuscular mycorrhiza enhances biomass production and salt tolerance of sweet sorghum. Microorganisms 7:289
Watts-Williams SJ, Turney TW, Patti AF, Cavagnaro TR (2014) Uptake of zinc and phosphorus by plants is affected by zinc fertiliser material and arbuscular mycorrhizas. Plant Soil 376:165–175
Whiteley CM, Valle MD, Jones KC, Sweetman AJ (2013) Challenges in assessing release, exposure and fate of silver nanoparticles within the UK environment. Environ Sci Proc Imp 15:2050–2058
Xiu ZM, Ma J, Alvarez PJJ (2011) Differential effect of common ligands and molecular oxygen on antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles versus silver ions. Environ Sci Technol 45:9003–9008
Yan A, Chen Z (2019) Impacts of silver nanoparticles on plants: a focus on the phytotoxicity and underlying mechanism. Int J Mol Sci 20:1003
Yu SJ, Yin YG, Liu JF (2013) Silver nanoparticles in the environment. Environ Sci Proc Imp 15:78–92
Zhai Y, Hunting ER, Marja W, Peijnenburg WJGM, Vijver MG (2016) Silver nanoparticles, ions, and shape governing soil microbial functional diversity: nano shapes micro. Front Microbiol 7:1123
Zhang Y, Liang Y, Zhao X, Jin X, Hou L, Shi Y, Ahammed GJ (2019) Silicon compensates phosphorus deficit-induced growth inhibition by improving photosynthetic capacity, antioxidant potential, and nutrient homeostasis in tomato. Agronomy 9:733
Zhang Y, Zhang S, Wang R, Cai J, Zhang Y, Li H, Huang S, Jiang Y (2016) Impacts of fertilization practices on pH and the pH buffering capacity of calcareous soil. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 62:432–439
Zhang Z, Lynch JP, Zhang B, Wang Q (2017) NPK deficiency modulates oxidative stress in plants. In: Hossain MA, Kamiya T, Burritt DJ, Tran LSP, Fujiwara T (eds) Plant Macronutrient Use Efficiency Molecular and Genomic Perspectives in Crop Plants. Academic Press, Cambridge, MA, USA
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41471395), Shandong Provincial Key Research and Development Program (2019GSF109008), Qingdao Special Funds for the Science and Technology Program of Public Wellbeing (20-3-4-29-nsh), Scientific and Technological Research Projects of Henan Province (192102110128), the Program for Science & Technology Innovation Talents in Universities of Henan Province (18HASTIT013), and the Doctoral Foundation of QUST (0100229003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Li, K. & Shi, Z. Phosphorus fertilization and mycorrhizal colonization change silver nanoparticle impacts on maize. Ecotoxicology 30, 118–129 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02298-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02298-x