Abstract
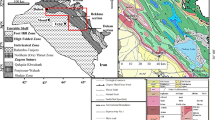
The depositional environment of the Antalo Limestone was previously interpreted from regional field-based studies and microfacies. However, stable oxygen and carbon isotopes are also invaluable proxies of paleo-environmental conditions, depositional, and diagenetic environments. Hence, the analyses of stable oxygen and carbon isotopic composition of this unit were examined from bulk limestone samples and integrated with a detailed petrographic study to interpret depositional environments and diagenetic evolution. The samples were collected from three outcrop sections, which together represent the full thickness of the unit. The microfacies identified from these samples indicate shallow–deep marine depositional as well as meteoric phreatic, marine phreatic, and deep burial diagenetic environments. The limits of variations of the oxygen isotopic ratios range from − 10.46 to − 3.56‰, with − 6.07‰ mean value. The limits of variations of the carbon isotopic ratios range from − 0.02 to 2.56‰, with 1.4‰ mean value. The calculated z values range from 123.08 to129.7 and the paleo-temperatures are estimated to be 32.4–73.52 °C, with an average temperature of 46.5 °C. The carbon isotope ratios indicate marine-water sources. This was confirmed from z values (> 120), indicating that the samples are marine carbonates. The depleted oxygen isotope ratios and high-temperature values, on the other hand, represent deep-burial diagenesis, which indicates the isotopic composition and the temperature conditions of the cement precipitating diagenetic fluids. The compositional fields of the δ18O–δ13C cross plots, also indicate marine carbonates subjected to mixing zone–deep-burial diagenesis. Therefore, both the petrographic and stable oxygen and carbon isotopic evidences are mutually in agreement, indicating related depositional and diagenetic environments.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arkin Y, Beyth M, Dow DB, Levitte D, Haile T, Hailu T (1971) Geological map of-mekele sheet-ND-37-11-Tigre Province. Ministry of Mines, Geological Survey of Ethiopia, Addis Ababa
Ayalew D, Yirgu G (2003) Crustal contribution to the genesis of Ethiopian plateau rhyolitic ignimbrite: basalt and rhyolite geochemical provinciality. J Geol Soc London 160:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1144/0016-764901-169
Ayalew D, Barbey P, Marty B, Reisberg L, Yirgu G, Pik R (2002) Source, genesis, and timing of giant ignimbrite deposits associated with Ethiopian continental flood basalts. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 66:1429–1448
Bathurst RGC (1966) Boring algae, micrite envelopes, and lithification of molluscan biosparites. Geol J 5:15–32
Beccaluva L, Bianchini G, Natali C, Siena F (2009) Continental flood basalts and mantle plumes: a case study of the Northern Ethiopian Plateau. J Petrol 00:1–27. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egp024
Beyth M (1972) Paleozoic-Mesozoic Sedimentary Basin of Mekele Outlier, Northern Ethiopia. AAPG Bull 56:2426–2439. https://doi.org/10.1306/819A422A-16C5-11D7-8645000102C1865D
Beyth M, Avigad D, Wetzel H, Matthews A, Berhe SM (2003) Crustal exhumation and indications for Snowball Earth in the East African Orogen: north Ethiopia and east Eritrea. Precambr Res 123:187–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-9268(03)00067-6
Bishop JW, Osleger DA, Montañez IP, Sumner DY (2014) Meteoric diagenesis and fluid-rock interaction in the Middle Permian Capitan backreef: Yates Formation, Slaughter Canyon, New Mexico. AAPG Bull 98(8):1495–1519. https://doi.org/10.1306/05201311158
Blanford WT (1869) Observations on the geology and zoology of Abyssinia. MacMillan, London
Bosellini A, Russo A, Fantozzi PL, Assefa G, Solomon T (1997) The Mesozoic Succession of the Mekele Outlier (Tigre Province, Ethiopia). Memorie di Sci Geol 49:95–116
Bosence DWJ, Allison PA (1995) A review of marine palaeoenvironmental analysis from fossils. Geol Soc Spec Pub 83:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1144/GSL.SP.1995.083.01.01
Bussert R (2010) Exhumed erosional landforms of the Late Palaeozoic glaciation in northern Ethiopia: indicators of ice-flow direction, palaeolandscape, and regional ice dynamics. Gondwana Res 18:356–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2009.10.009
Bussert R, Schrank E (2007) Palynological evidence for the latest Carboniferous-Early Permian glaciation in Northern Ethiopia. J Afr Earth Sc 49:201–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2007.09.003
Chaves NS, Sial AN (1998) Mixed oceanic and freshwater depositional conditions for beachrocks of Northeast Brazil: evidence from carbon and oxygen isotopes. Int Geol Rev 40:748–754
Choquette PW, James NP (1986) Diagenesis in limestone-3. The deep burial environment. Geosci Canada 14:3–35
Christ N, Immenhauser A, Wood R, Darwich K, Niedermayr A (2015) Petrography and environmental controls on the formation of Phanerozoic marine carbonate hardgrounds. Earth Sci Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.10.002
Copper P (1992) Organisms and carbonate substrates in marine environments. Geosci Can 19:97–112
Corfield RM (1995) An introduction to the techniques, limitations, and landmarks of carbonate oxygen isotope palaeo-thermometry. In: Bosence DWJ, Allison PA (eds) Marine palaeoenvironmental analysis from fossils, vol 83. Geological Society Special Publication, London, pp 27–42
Cuna S, Pop D, Hosu A (2001) Carbon and oxygen isotope ratios in Rona Limestone, Romania. Studia Univ Babeş-Bolyai Geol XLVI:140–151
Dawit E (2010) Adigrat sandstone in Northern and Central Ethiopia: stratigraphy, facies, depositional environments and palynology. Ph.D. Thesis, pp 162. Technische Universität, Berlin
Des Marais DJ (2001) Isotopic evolution of the biogeochemical carbon cycle during the Precambrian. In: Valley JW, Cole DR (eds) Revies in mineralogy and geochemistry: stable isotope geochemistry, vol 43. Mineraogical Sociaty of America, London, pp 555–578
Dickson T (1990) Carbonate mineralogy and chemistry. In: Tucker ME, Wright VP (eds) Carbonate sedimentology, 1st edn. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, pp 284–313
Dickson JAD (2016) Diagenesis of shallow-marine carbonates. Cambridge Earth Sci Series ES 426:173–188
Dow D, Beyth M, Hailu T (1971) Palaeozoic glacial rocks recently discovered in northern Ethiopia. Geol Mag 108:53–60
Dunham RJ (1962) Classification of carbonate rocks according to depositional texture. AAPG Memorandum 1:108–121
Emraninasab BH, Adabi MH, Majidifard M, Ghadimvand NK (2016) Facies interpretation, depositional environment and sequence stratigraphy of the Sartakht Formation in the Bakhshi Section, Located in Kalmard Block, East-Central Iran. Open J Geol 6:314–329
Flügel E (2004) Microfacies of carbonate rocks: analysis, interpretation, and application. Springer-Berlin, Heidelberg
Folk RL (1959) Practical petrographic classifications of limestones. AAPG Bull 43:1–38
Folk RL (1974) The natural history of crystalline calcium carbonate: effect of magnesium content and salinity. J Sediment Petrol 44:40–53
Friedman I, O’Neil JR (1977) Chapter KK. Compilation of stable isotope fractionation factors of geochemical interest. In: Fleischer M (ed) Data of geochemistry, 6th edn. USGS Professional Paper, Washington, pp 1–12
Getaneh W, Valera R (2002) Rare earth element geochemistry of the Antalo Supersequence in the Mekele Outlier (Tigray region, Northern Ethiopia). Chem Geol 182:395–407
Goldring R (1995) Organisms and the substrate; response and effect. In: Bosence DWJ, Allison PA (eds) Marine palaeoenvironmental analysis from fossils, vol 83. Geological Society Special Publications, London, pp 151–180
Hagos M, Koeberl C, Kabeto K, Friedrich K (2010) Geochemical characteristics of the alkaline basalts and the phonolite—trachyte plugs of the Axum area, northern Ethiopia. Aust J Earth Sci 103:153–170
Heckel H (1972) Recognition of ancient shallow marine environment. In: Rigby IJK, Hemblin K (eds) Recognition of ancient sedimentary environments. SEPM Special Publication, Tulsa, pp 226–286
Hodson KR, Crider JG, Huntington KW (2016) Temperature and composition of carbonate cement record early structural control on cementation in a nascent deformation band fault zone: Moab Fault, Utah, USA. Tectonophysics 690:240–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2016.04.032
Hoefs J (2009) Stable isotope geochemistry. Springer, Germany
Hudson JD (1977) Stable isotopes and limestone lithification. J Geol Soc London 133:637–660
Hughes GWG (2004) Middle to Upper Jurassic Saudi Arabian carbonate petroleum reservoirs: biostratigraphy, micropalaeontology, and palaeoenvironments. Geo Arabia 9:79–114
Jones B, Desrochers A (1992) Shallow platform carbonates. In: Walker RG, James NP (eds) Facies models response to sea level change. Geological Association of Canada, St. John’s, pp 277–302
Kabeto K (2010) Geological and geochemical variations in Mid-Tertiary Ethiopian Flood Basalt Province, Maychew, Tigray Region, Ethiopia. Momona Ethiop J Sci 2:4–25
Kazmin V (1973) Geology of Ethiopia (explanatory note to geological map of Ethiopia 1:2,000,000). The Ethiopian Institute of Geological Surveys, Addis Ababa
Kazmin V (1975) Explanation of the geological map of Ethiopia. Geological Survey of Ethiopia, Wageningen
Kazmin BV, Shifferaw A, Balcha T (1978) The Ethiopian basement: stratigraphy and possible manner of evolution. Ethiop Inst Geol Surv 67(2):531–546
Keith ML, Weber JN (1964) Carbon and oxygen isotopic composition of selected limestones and fossils. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 28:1787–1816
Kiessling W, Pandey DK, Schemm-gregory M, Newis H, Aberhan M (2011) Marine benthic invertebrates from the Upper Jurassic of northern Ethiopia and their biogeographic affinities. J Afr Earth Sc 59:195–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2010.10.006
Kobluk D, Risk M (1977) Calcification of exposed filaments of endolithic algae, micrite envelope formation, and sediment production. J Sediment Petrol 47:517–528
Leonard JE, Cameron B, Pilkey OH, Friedman GM (1981) Evaluation of cold-water carbonates as a possible palaeoclimatic indicator. Sed Geol 28:1–28
Longman MW (1980) Carbonate diagenetic textures from near surface diagenetic environments. AAPG Bull 64:461–487
Mabrouk A, Belayouni H, Jarvis I, Moody RTJ (2006) Strontium, δ18O and δ13C as palaeo-indicators of unconformities: Case of the Aleg and Abiod formations (Upper Cretaceous) in the Miskar Field, southeastern Tunisia. Geochem J 40:405–424. https://doi.org/10.2343/geochemj.40.405
Marshall JD (1992) Climatic and oceanographic isotopic signals from the carbonate rock record and their preservation. Geol Mag 129:143–160
Martire L, Clari P, Pavia G (1998) Stratigraphic analysis of the Upper Jurassic (Oxfordian–Kimmeridgian) Antalo Limestone in the Mekele Outlier (Tigrai, northern Ethiopia); preliminary data. In: Crasquin-Soleau E, Barrier S (eds) Epicratonic basins of Peri-Tethyan platforms, vol 4. Memoires du Museum National d’Histoire Naturelle. Peri-Tethys Memoir, Paris, pp 131–144
Mazzullo SJ, Chilingarian GV (1992) Diagenesis and origin of porosity. In: Chilingarian GV, Mazzullo SJ, Rieke HH (eds) Carbonate reservoir characterization: a geologic-engineering analysis, part I: Developments in petroleum science, vol 30. Elsevier Scientific Publishers BV, Amsterdam-London-New York-Tokyo, pp 199–270
McCrea JM (1950) On the isotopic chemistry of carbonates and a paleotemperature scale. J Chem Phys 18:849–857
Melim LA, Swart PK, Maliva RG (1995) Meteoric-Like Fabrics forming in marine waters: implications for the use of petrography to identify diagenetic environments. Geology 23:755–758
Merla G, Minucci R (1938) Missione geologica nel Tigrai, ‘“La Serie dei Terreni”.’ Reale Acca demia d’Italia, Rome
Milliman JD (1974) Marine carbonates: recent sedimentary carbonates part 1. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York
Moore CH (1989) Carbonate Diagenesis and Porosity: developments in sedimentology, vol 46. Elsevier Science BV, Amsterdam
Moore CH (2001) Carbonate reservoirs porosity evaluation and diagenesis in a sequence stratigraphic framework: developments in sedimentology, vol 55. Elsevier BV, Amsterdam, Boston
Nelson CS, Harris GJ, Young HR (1988) Burial-dominated cementation in non-tropical carbonates of the Oligocene Te Kuiti Group, New Zealand. Sed Geol 60:233–250
Nogueira LB, Oliveira VQ, Araújo LP et al (2019) Geochemistry and C and O isotope composition of carbonate rocks from Bemil and Lagoa Seca quarries, Gandarela Formation, Quadrilátero Ferrífero-Brazil. J S Am Earth Sci 92:609–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsames.2019.04.001
Rahimpour-Bonab H, Bone Y (2001) Isotopic signature of the diagenetic fluids and cement in the Tortachilla Limestone, South Australia. Iran Int J Sci 2(1):1–22
Sarfi M, Yazdi-Moghadam M (2016) Stratigraphy of the Upper Jurassic shallow-marine carbonates of the Moghan area (NW Iran), with paleobiogeography implication on Alveosepta jaccardi Stratigraphy of the Upper Jurassic shallow-marine carbonates of the Moghan area (NW Iran), with paleob. Geopersia 6:187–196. https://doi.org/10.22059/jgeope.2016.59089
Schlagintweit F, Tesovic BC (2017) Braciana jelaskai n. gen., n. sp., a new larger benthic foraminifera from the Upper Cretaceous (Santonian?-lower Campanian) of the Dinaric-Hellenic realm. Cretac Res 72:32–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cretres.2016.12.005
Shackleton NJ (1986) Paleogene stable isotope events. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaecol 57:91–102
Sharp Z (2017) Principles of stable isotope geochemistry. Pearson/Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Smith AM, Nelson CS (1996) Stable oxygen and carbon isotope compositional fields for skeletal and diagenetic components in New Zealand Cenozoic nontropical carbonate sediments and limestones: a synthesis and review. NZ J Geol Geophys 39:93–107
Tefera M, Chernet T, Haro W (1996) Explanation of the geological map of Ethiopia: scale 1: 2000,000, vol 3. Ethiopian Institute of Geological Surveys Bull, Addis Ababa
Tucker ME (1993) Carbonate diagenesis and sequence stratigraphy. In: Wright VP (ed) Sedimentology Review/1, 1st edn. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, pp 51–72
Tucker ME, Wright VP (1990) Carbonate Sedimentology. Blackwell Science Ltd., Edinburgh-Cambridge-USA-Australia
Urey HC, Lowenstam HA, Epstein S, McKinney CR (1951) Measurement of paleotemperatures and temperatures of the upper cretaceous of England, Denmark, and the Southeastern United States. Bull Geol Soc Am 62:399–416
Wary JL (1998) Calcareous Algae. In: Haq BU, Boersma A (eds) Introduction to Marine Micropaleontology, 2nd edn. Geological Association of Canada, St. John’s, pp 171–187
Wilson JL (1975) Carbonate facies in geologic history. Springer-Verlag, New York, Heidelberg, Berlin
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the African Union (AU). The authors would like to thank the African Union for funding the research grant. The authors are also grateful to Professor Chris Harris, Head of the Department of Geological Sciences, University of Cape Town, South Africa, for his willingness and cooperation to do isotope analysis in the Stable Isotope Laboratory of the department.
Funding
This study was funded by the African Union.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adefris, D., Nton, M.E., Boboye, O.A. et al. Petrography and stable oxygen and carbon isotopic composition of the Antalo Limestone, Mekelle Basin, Northern Ethiopia: implications for marine environment and deep-burial diagenesis. Carbonates Evaporites 35, 124 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-020-00659-5
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-020-00659-5