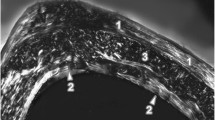
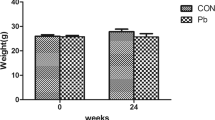
Abstract
Cadmium (Cd) is toxic to the skeletal system resulting in bone loss and pain. We aimed at determining the effect of chronic Cd exposure on bone density and microarchitecture along with changes in the density of a subset of sensory and sympathetic nerve fibers innervating the developing rat femur. Newborn male Wistar rats were injected daily for 49 days with CdCl2 (1 mg/kg i.p.) or saline solution (control group). At the day of sacrifice, levels of Cd in the right femur, liver and kidney were determined by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Additionally, microCT followed by immunohistochemical analyses were performed in the left femur. Results showed Cd accumulation in trabecular bone neared levels seen in liver and kidney. Cd concentration in cortical bone was significantly lower versus trabecular bone. MicroCT analysis revealed that Cd-exposed rats had a significant decrease in trabecular bone parameters at the distal femoral metaphysis; however, most of the cortical bone parameters were not significantly affected. Cd-exposed rats showed a significant loss of TH+ sympathetic nerve fibers, but not of CGRP+ sensory nerve fibers, at the level of bone marrow of the femoral diaphysis as compared to control rats. This study shows that Cd negatively affects bone density and microarchitecture of trabecular bone and decreases the density of sympathetic nerve fibers innervating rat femur. Future studies are warranted to determine the toxigenic mechanisms of Cd on sympathetic nerves and how sympathetic denervation influences bone loss in animals exposed to Cd.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Arvidson B (1980) Regional differences in severity of cadmium-induced lesions in the peripheral nervous system in mice. Acta Neuropathol 49(3):213–224
Axelrod FB, Pearson J (1984) Congenital sensory neuropathies: diagnostic distinction from familial dysautonomia. Am J Dis Child 138(10):947–954
Bhattacharyya MH (2009) Cadmium osteotoxicity in experimental animals: mechanisms and relationship to human exposures. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 238(3):258–265
Boughammoura S, Ben Mimouna S, Chemek M, Ostertag A, Cohen-Solal M, Messaoudi I (2020) Disruption of bone zinc metabolism during postnatal development of rats after early life exposure to cadmium. Int J Mol Sci 21(4):1218
Bouxsein ML, Boyd SK, Christiansen BA, Guldberg RE, Jepsen KJ, Müller R (2010) Guidelines for assessment of bone microstructure in rodents using micro-computed tomography. J Bone Miner Res 25(7):1468–1486
Branca JJV, Morucci G, Pacini A (2018) Cadmium-induced neurotoxicity: still much ado. Neural Regen Res 13(11):1879–1882
Brazill JM, Beeve AT, Craft CS, Ivanusic JJ, Scheller EL (2019) Nerves in bone: evolving concepts in pain and anabolism. J Bone Miner Res 34(8):1393–1406
Brzóska MM, Moniuszko-Jakoniuk J (2004) Low-level lifetime exposure to cadmium decreases skeletal mineralization and enhances bone loss in aged rats. Bone 35(5):1180–1191
Brzóska MM, Majewska K, Kupraszewicz E (2010) Effects of low, moderate and relatively high chronic exposure to cadmium on long bones susceptibility to fractures in male rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 29(3):235–245
Buha A, Jugdaohsingh R, Matovic V, Bulat Z, Antonijevic B, Kerns JG, Powell JJ (2019) Bone mineral health is sensitively related to environmental cadmium exposure-experimental and human data. Environ Res 176:108539
Chen X, Zhu G, Gu S, Jin T, Shao C (2009) Effects of cadmium on osteoblasts and osteoclasts in vitro. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 28(2):232–236
Chen X, Wang G, Li X, Gan C, Zhu G, Jin T, Wang Z (2013) Environmental level of cadmium exposure stimulates osteoclasts formation in male rats. Food Chem Toxicol 60:530–535
Cheng X, Niu Y, Ding Q, Yin X, Huang G, Peng J, Song J (2016) Cadmium exposure and risk of any fracture: a PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 95(10):e2932
Clarke B (2008) Normal bone anatomy and physiology. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3(Suppl 3):S131–S139
Comelekoglu U, Yalin S, Bagis S, Ogenler O, Sahin NO, Yildiz A, Coskun B, Hatungil R, Turac A (2007) Low-exposure cadmium is more toxic on osteoporotic rat femoral bone: Mechanical, biochemical, and histopathological evaluation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 66(2):267–271
Coonse KG, Coonts AJ, Morrison EV, Heggland SJ (2007) Cadmium induces apoptosis in the human osteoblast-like cell line Saos-2. Journal of Toxicology Environmental Health Part A 70(7):575–581
Corry DB, Tuck ML (1999) Obesity, hypertension, and sympathetic nervous system activity. Curr Hypertens Rep 1(2):119–126
Duan P, Bonewald LF (2016) The role of the wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in formation and maintenance of bone and teeth. Intl J Biochem Cell Biol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2016.05.015
Duranova H, Martiniakova M, Omelka R, Grosskopf B, Bobonova I, Toman R (2014) Changes in compact bone microstructure of rats subchronically exposed to cadmium. Acta Vet Scand 56(1):64
Elefteriou F (2018) Impact of the autonomic nervous system on the skeleton. Physiol Rev 98(3):1083–1112
Elefteriou F, Campbell P, Ma Y (2014) Control of bone remodeling by the peripheral sympathetic nervous system. Calcif Tissue Int 94(1):140–151
Engström A, Michaëlsson K, Vahter M, Julin B, Wolk A, Åkesson A (2012) Associations between dietary cadmium exposure and bone mineral density and risk of osteoporosis and fractures among women. Bone 50(6):1372–1378
He JY, Jiang LS, Dai LY (2011) The roles of the sympathetic nervous system in osteoporotic diseases: a review of experimental and clinical studies. Ageing Res Rev 10(2):253–263
He S, Zhuo L, Cao Y, Liu G, Zhao H, Song R, Liu Z (2020) Effect of cadmium on osteoclast differentiation during bone injury in female mice. Environ Toxicol 35(4):487–494
Inaba T, Kobayashi E, Suwazono Y, Uetani M, Oishi M, Nakagawa H, Nogawa K (2005) Estimation of cumulative cadmium intake causing Itai-itai disease. Toxicol Lett 159(2):192–201
Järup L, Åkesson A (2009) Current status of cadmium as an environmental health problem. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 238(3):201–208
Ji YL, Wang H, Liu P, Wang Q, Zhao XF, Meng XH, Xu DX (2010) Pubertal cadmium exposure impairs testicular development and spermatogenesis via disrupting testicular testosterone synthesis in adult mice. Reprod Toxicol 29(2):176–183
Jimenez-Andrade JM, Bloom AP, Mantyh WG, Koewler NJ, Freeman KT, Delong D, Mantyh PW (2009) Capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerve fibers contribute to the generation and maintenance of skeletal fracture pain. Neuroscience 162(4):1244–1254
Kazantzis G (2004) Cadmium, osteoporosis and calcium metabolism. Biometals 17(5):493–498
Kjær I (1998) Neuro-osteology. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 9(2):224–244
Kjellström T (1992) Mechanism and epidemiology of bone effects of cadmium. IARC Sci Publ 118:301–310
Lafuente A, Márquez N, Pérez-Lorenzo M, Pazo D, Esquifino AI (2000) Pubertal and postpubertal cadmium exposure differentially affects the hypothalamic–pituitary–testicular axis function in the rat. Food Chem Toxicol 38(10):913–923
Li J, Bao Q, Chen S, Liu H, Feng J, Qin H, Zong Z (2017) Different bone remodeling levels of trabecular and cortical bone in response to changes in Wnt/β-catenin signaling in mice. J Orthop Res 35(4):812–819
Liu D, Zhao CQ, Li H, Jiang SD, Jiang LS, Dai LY (2008) Effects of spinal cord injury and hindlimb immobilization on sublesional and supralesional bones in young growing rats. Bone 43(1):119–125
Malin Igra A, Vahter M, Raqib R, Kippler M (2019) Early-life cadmium exposure and bone-related biomarkers: a longitudinal study in children. Environ Health Perspect 127(3):037003
Markiewicz-Górka I, Pawlas K, Jaremków A, Januszewska L, Pawłowski P, Pawlas N (2019) Alleviating effect of α-lipoic acid and magnesium on cadmium-induced inflammatory processes, oxidative stress and bone metabolism disorders in wistar rats. Intl J Environ Res Public Health 16(22):4483
Montes S, Alcaraz-Zubeldia M, Ríos C, Muriel P (2002) A method to induce manganese accumulation in the brain of the cirrhotic rat and its evaluation. Brain Res Protoc 9(1):9–15
Ogoshi K, Nanzai Y, Moriyama T (1992) Decrease in bone strength of cadmium-treated young and old rats. Arch Toxicol 66(5):315–320
Ott SM (2018) Cortical or trabecular bone: what’s the difference? Am J Nephrol 47(6):373–375
Panahifar A, Chapman LD, Weber L, Samadi N, Cooper DM (2019) Biodistribution of strontium and barium in the developing and mature skeleton of rats. J Bone Miner Metab 37(3):385–398
Parfitt AM (2002) Misconceptions (2): turnover is always higher in cancellous than in cortical bone. Bone 30(6):807–809
Rodriguez CM, Kirby JL, Hinton BT (2002) The development of the epididymis. In: Robaire B, Hinton BT (eds) The epididymis: from molecules to clinical practice. Kluwer Academic/Plenum, New York, pp 251–267
Sato K, Iwamasa T, Tsuru T, Takeuchi T (1978) An ultrastructural study of chronic cadmium chloride-induced neuropathy. Acta Neuropathol 41(3):185–190
Scimeca M, Feola M, Romano L, Rao C, Gasbarra E, Bonanno E, Brandi M, Tarantino U (2017) Heavy metals accumulation affects bone microarchitecture in osteoporotic patients. Environ Toxicol 32(4):1333–1342
Sheng ZF, Dai RC, Wu XP, Fang LN, Fan HJ, Liao EY (2007) Regionally specific compensation for bone loss in the tibial trabeculae of estrogen-deficient rats. Acta Radiol 48(5):531–539
Sisask G, Bjurholm A, Ahmed M, Kreicbergs A (1996) The development of autonomic innervation in bone and joints of the rat. J Auton Nerv Syst 59(1–2):27–33
Świergosz-Kowalewska R (2001) Cadmium distribution and toxicity in tissues of small rodents. Microsc Res Tech 55(3):208–222
Takeda S, Karsenty G (2008) Molecular bases of the sympathetic regulation of bone mass. Bone 42(5):837–840
Tang L, Chen X, Bao Y, Xu W, Lv Y, Wang Z, Wen X (2016) CT imaging biomarkers of bone damage induced by environmental level of cadmium exposure in male rats. Biol Trace Elem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0447-8
Torres-Sánchez L, Vázquez-Salas RA, Vite A, Galván-Portillo M, Cebrián ME, Macias-Jiménez AP, Montes S (2018) Blood cadmium determinants among males over forty living in Mexico City. Sci Total Environ 637:686–694
Wang B, Du Y (2013) Cadmium and its neurotoxic effects. Oxid Med Cell Long 898034:12
Wirth JJ, Mijal RS (2010) Adverse effects of low level heavy metal exposure on male reproductive function. Syst Biol Reprod Med 56(2):147–167
World Health Organization (2010) Ten chemicals of major public health concern. World Health Organization, 1–4
Wu Q, Magnus JH, Hentz JG (2010) Urinary cadmium, osteopenia, and osteoporosis in the US population. Osteoporos Int 21(8):1449–1454
Wu L, Wei Q, Lv Y, Xue J, Zhang B, Sun Q, Xiao T, Huang R, Wang P, Dai X, Xia H, Li J, Yang X, Liu Q (2019) Wnt/β-catenin pathway is involved in cadmium-induced inhibition of osteoblast differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Sci 20(6):1–17
Funding
This work was supported by Universidad Autónoma Metropolitana-Iztapalapa; financial support number CD.CBS.535.2018. Joel Hernandez receives a Doctorate fellowship From CONACyT Mexico, (622536/570248, CVU/Becario). PhD student from Doctorado en ciencias Biologicas y de la salud, Universidad Autónoma Metropolitana.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Juan M. Jiménez-Andrade, Sergio Montes; Methodology: Mayra A. Graniel-Amador, Joel Hernández-Rodríguez, Sergio Montes; Formal analysis and investigation: Marcela Arteaga-Silva, Héctor F. Torres-Rodríguez Writing - original draft preparation: Mayra A. Graniel-Amador, Juan M. Jiménez-Andrade ; Writing - review and editing: Héctor F. Torres-Rodríguez, Supervision: Sergio Montes.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Graniel-Amador, M.A., Torres-Rodríguez, H.F., Jiménez-Andrade, J.M. et al. Cadmium exposure negatively affects the microarchitecture of trabecular bone and decreases the density of a subset of sympathetic nerve fibers innervating the developing rat femur. Biometals 34, 87–96 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-020-00265-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-020-00265-x