Abstract
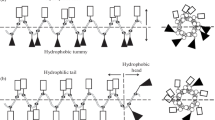
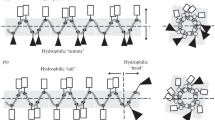
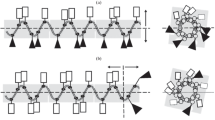
According to the mechanisms of antimicrobial peptides presented in current research literatures, four cationic peptides rich in arginine residues were designed and synthesized in this study. Their antimicrobial activity to four microorganisms and cytotoxicity to human dermal fibroblasts (HDFs) were evaluated. Among these peptides, PEP-1, PEP-2 and PEP-4 could inhibit and kill these microorganisms at certain concentrations. While PEP-3 only exhibited low inhibition activity against E. coli. PEP-1 rich in arginine residues was more effective against Gram-negative bacteria. PEP-4 with tryptophan and lysine residues in the sequence exhibited enhancement in the antimicrobial activity compared with PEP-3 and presented lowest minimal bactericidal concentration (MBC) to S. aureus and C. albicans in these four peptides. These results indicate that the amount and position of cationic residues in the sequence affects the bactericidal activity and the complement of proline with arginine, tryptophan with arginine and lysine residues would enhance the antimicrobial activity. Moreover, PEP-1, PEP-2 and PEP-4 showed low toxicity at their 1× MBC with no considerable difference with the negative control group in the HDFs cytotoxicity test. This study provides us with a better understanding on the structure-activity relationship, which will be useful for new antimicrobial peptide designs and optimizations.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Arfan G et al (2019) Designing an ultra-short antibacterial peptide with potent activity against Mupirocin-resistant MRSA. Chem Biol Drug Des 93:4–11. https://doi.org/10.1111/cbdd.13377
Bandekar J (1992) Amide modes and protein conformation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1120:123–143
Bell G, Gouyon P-H (2003) Arming the enemy: the evolution of resistance to self-proteins. Microbiology 149:1367–1375. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.26265-0
Brogden KA (2005) Antimicrobial peptides: pore formers or metabolic inhibitors in bacteria? Nat Rev Microbiol 3:238–250. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1098
Chan DI, Prenner EJ, Vogel HJ (2006) Tryptophan-and arginine-rich antimicrobial peptides: structures and mechanisms of action. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1758:1184–1202
Chan E et al (2018) Electrospun polythiophene phenylenes for tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules 19, acs.biomac.8b00341
Chia BCS, Bowie JH, Carver JA, Mulhern TD (1999) The solution structure of uperin 3.6, an antibiotic peptide from the granular dorsal glands of the Australian toadlet, Uperoleia mjobergii. J Pept Res 54:137–145. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1399-3011.1999.00095.x
Cutrona KJ, Kaufman BA, Figueroa DM, Elmore DE (2015) Role of arginine and lysine in the antimicrobial mechanism of histone-derived antimicrobial peptides. FEBS Lett 589:3915–3920
Dougherty DA (1996) Cation-π interactions in chemistry and biology: a new view of benzene, Phe, Tyr, and Trp. Science 271:163–168
Findlay B, Zhanel GG, Schweizer F (2010) Cationic amphiphiles, a new generation of antimicrobials inspired by the natural antimicrobial peptide scaffold. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54:4049–4058. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.00530-10
Friedrich C, Scott MG, Karunaratne N, Yan H, Hancock RE (1999) Salt-resistant alpha-helical cationic antimicrobial peptides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 43:1542–1548
Gagnon MC et al (2017) Influence of the length and charge on the activity of α-helical amphipathic antimicrobial peptides. Biochemistry 56:1680–1695
Hancock RE (2001) Cationic peptides: effectors in innate immunity and novel antimicrobials. Lancet Infect Dis 1:156–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(01)00092-5
Hancock R, Patrzykat A (2002) Clinical development of cationic antimicrobial peptides: from natural to novel antibiotics. Curr Drug Targets Infect Disord 2:79–83
Hancock RE, Sahl H-G (2006) Antimicrobial and host-defense peptides as new anti-infective therapeutic strategies. Nat Biotechnol 24:1551
Hansen A, Schäfer I, Knappe D, Seibel P, Hoffmann R (2012) Intracellular toxicity of proline-rich antimicrobial peptides shuttled into mammalian cells by the cell-penetrating peptide penetratin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 00585-00512
Ilker MF, Nüsslein K, Tew GN, Coughlin EB (2004) Tuning the hemolytic and antibacterial activities of amphiphilic polynorbornene derivatives. J Am Chem Soc 126:15870–15875
Jing W, Demcoe AR, Vogel HJ (2003) Conformation of a bactericidal domain of puroindoline a: structure and mechanism of action of a 13-residue antimicrobial peptide. J Bacteriol 185:4938–4947
Justo JA, Bosso JA (2015) Adverse reactions associated with systemic polymyxin therapy. Pharmacotherapy 35:28–33
Kim H, Jang JH, Kim SC, Cho JH (2013) De novo generation of short antimicrobial peptides with enhanced stability and cell specificity. J Antimicrob Chemother 69:121–132
King A et al (2014) High antimicrobial effectiveness with low hemolytic and cytotoxic activity for PEG/quaternary copolyoxetanes. Biomacromolecules 15:456–467
Kumar P, Kizhakkedathu JN, Straus SK (2018) Antimicrobial peptides: diversity, mechanism of action and strategies to improve the activity and biocompatibility in vivo. Biomolecules 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom8010004
Li W et al (2014) Proline-rich antimicrobial peptides: potential therapeutics against antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Amino Acids 46:2287–2294
Lum KY et al (2015) Activity of novel synthetic peptides against Candida albicans. Sci Rep 5:9657. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep09657
Lyu Y, Yang Y, Lyu X, Dong N, Shan A (2016) Antimicrobial activity, improved cell selectivity and mode of action of short PMAP-36-derived peptides against bacteria and Candida. Sci Rep 6:27258. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27258
Mardirossian M et al (2018) Fragments of the non-lytic proline-rich antimicrobial peptide Bac5 kill E. coli cells by inhibiting protein synthesis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 00534-00518
Matejuk A et al (2010) Peptide-based antifungal therapies against emerging infections. Drugs Future 35:197
Matsuzaki K (2009) Control of cell selectivity of antimicrobial peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1788:1687–1692
Mattiuzzo M et al (2007) Role of the Escherichia coli SbmA in the antimicrobial activity of proline-rich peptides. Mol Microbiol 66:151–163
Maupetit J, Derreumaux P, Tufféry P (2010) A fast method for large-scale De Novo peptide and miniprotein structure prediction. J Comput Chem 31:726–738
Minoux H, Chipot C (1999) Cation-π interactions in proteins: can simple models provide an accurate description? J Am Chem Soc 121:10366–10372
Nguyen LT, Haney EF, Vogel HJ (2011) The expanding scope of antimicrobial peptide structures and their modes of action. Trends Biotechnol 29:464–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2011.05.001
Park SC et al (2008) Amphipathic alpha-helical peptide, HP (2-20), and its analogues derived from Helicobacter pylori: pore formation mechanism in various lipid compositions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1778:229–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.09.020
Peng S et al (2018) Mechanism of actions of Oncocin, a proline-rich antimicrobial peptide, in early elongation revealed by single-molecule FRET. Protein Cell 9:890–895. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-017-0495-2
Schibli DJ, Nguyen LT, Kernaghan SD, Rekdal Ø, Vogel HJ (2006) Structure-function analysis of tritrpticin analogs: potential relationships between antimicrobial activities, model membrane interactions, and their micelle-bound NMR structures. Biophys J 91:4413–4426
Scocchi M, Tossi A, Gennaro R (2011) Proline-rich antimicrobial peptides: converging to a non-lytic mechanism of action. Cell Mol Life Sci 68:2317–2330
Shen Y, Maupetit J, Derreumaux P, Tufféry P (2014) Improved PEP-FOLD approach for peptide and miniprotein structure prediction. J Chem Theory Comput 10:4745–4758
Thevenet P et al (2012) PEP-FOLD: an updated de novo structure prediction server for both linear and disulfide bonded cyclic peptides. Nucleic Acids Res 40:W288–W293
Wang G, Li X, Wang Z (2015) APD3: the antimicrobial peptide database as a tool for research and education. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D1087–D1093
Wei Y, Li C, Zhang L, Xu X (2014) Design of novel cell penetrating peptides for the delivery of trehalose into mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1838:1911–1920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2014.02.011
Wiradharma N et al (2011) Synthetic cationic amphiphilic α-helical peptides as antimicrobial agents. Biomaterials 32:2204–2212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.11.054
Xie Y, Fleming E, Chen JL, Elmore DE (2011) Effect of proline position on the antimicrobial mechanism of buforin II. Peptides 32:677–682
Yang C-H et al (2018) An engineered arginine-rich α-helical antimicrobial peptide exhibits broad-spectrum bactericidal activity against pathogenic bacteria and reduces bacterial infections in mice. Sci Rep 8:14602
Yau W-M, Wimley WC, Gawrisch K, White SH (1998) The preference of tryptophan for membrane interfaces. Biochemistry 37:14713–14718
Yeaman MR, Yount NY (2003) Mechanisms of antimicrobial peptide action and resistance. Pharmacol Rev 55:27–55. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.55.1.2
Zhang L, Scott MG, Yan H, Mayer LD, Hancock RE (2000) Interaction of polyphemusin I and structural analogs with bacterial membranes, lipopolysaccharide, and lipid monolayers. Biochemistry 39:14504–14514
Zhang SK et al (2016) Design of an alpha-helical antimicrobial peptide with improved cell-selective and potent anti-biofilm activity. Sci Rep 6:27394. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27394
Funding
This work was supported by the China Scholarship Council [Grant Numbers 201706630077], the Alice T. and William H. Goodwin Jr. Endowment and Wuyi University [Grant Numbers 2020AL009]. We’d like to thank Soochow Ryan nano-medical technology co. LTD for their technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: P.L., X.W. Formal analysis: P.L., X.W. Investigation: P.L. Methodology: P.L., X.Z. Project administration: X.W. Resources: X.W. Writing original draft: P.L., X.Z., X.W.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflcit of interest
The authors declare no competing interests in this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, P., Zeng, X. & Wen, X. Design and Synthesis of New Cationic Antimicrobial Peptides with Low Cytotoxicity. Int J Pept Res Ther 27, 831–840 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-020-10133-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-020-10133-4