Abstract
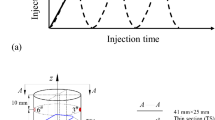
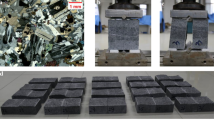
This study designs and introduces an X-ray-compatible thermo-hydro-mechanical coupling triaxial device. The functional parameters of this device included a confining pressure, axial force, injected fluid pressure, and temperature up to 20 MPa, 400 kN, 10 MPa, and 100 °C, respectively. Triaxial stress loading–unloading cycles and permeability experiments for coal specimens were carried out using this device. Following four pre-set cycles, the specimen was scanned to identify internal cracks, and the relationship between stress, strain, permeability, and crack evolution was analysed. The experimental results showed that new cracks were mainly caused by the expansion of initial cracks as the triaxial stress cycles. The crack area fraction (CAF) increased almost linearly with the stress cycle. With the increase in CAF, the permeability of coal had increased under both high and low deviatoric stress. However, the increment of permeability that was driven by the CAF increment had decreased and eventually became stable. During the initial cracking stage, the increase in permeability from the CAF increase under high deviator stress was always greater. This demonstrates that the contribution of new cracks to increasing permeability under different triaxial stresses was significantly different. The outcomes from this study may provide benefits for coalbed methane extraction and dynamic hazard prevention.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barla G, Barla M, Debernardi D (2010) New triaxial apparatus for rocks. Rock Mech Rock Eng 43:225–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-009-0076-7
Chaves V, Beretta G, Balbín JA, Navarro A (2019) Fatigue life and crack growth direction in 7075-T6 aluminium alloy specimens with a circular hole under biaxial loading. Int J Fatigue 125:222–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2019.03.031
Delgado BG, Viana da Fonseca A, Fortunato E, Maia P (2019) Mechanical behavior of inert steel slag ballast for heavy haul rail track: laboratory evaluation. Transp Geotech. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trgeo.2019.100243
Jiang C, Duan M, Yin G et al (2017) Experimental study on seepage properties, AE characteristics and energy dissipation of coal under tiered cyclic loading. Eng Geol 221:114–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.03.005
Jiang Y, Qin C, Kang Z et al (2018) Experimental study of supercritical CO2 fracturing on initiation pressure and fracture propagation in shale under different triaxial stress conditions. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 55:382–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2018.04.022
Jonsson H, Öhman-Mägi C, Alderborn G et al (2019) Crack nucleation and propagation in microcrystalline-cellulose based granules subject to uniaxial and triaxial load. Int J Pharm 559:130–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.12.064
Ju Y, Zhang Q, Zheng J et al (2017) Experimental study on CH4 permeability and its dependence on interior fracture networks of fractured coal under different excavation stress paths. Fuel 202:483–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.04.056
Ju Y, Huang Y, Su S et al (2018) Three-dimensional numerical reconstruction method for irregular structures of granular geomaterials. Geomech Geophys Geoenergy Georesour 4:327–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-018-0089-3
Kamali-Asl A, Kc B, Foroutan M et al (2019) Stress–strain response and seismic signature analysis of phyllite reservoir rocks from Blue Mountain geothermal field. Geothermics 77:204–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2018.09.004
Kelkar S, Lewis K, Karra S et al (2014) A simulator for modeling coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical processes in subsurface geological media. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 70:569–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.06.011
Li F, Yang Y, Fan X et al (2018) Numerical analysis of the hydrofracturing behaviours and mechanisms of heterogeneous reservoir rock using the continuum-based discrete element method considering pre-existing fractures. Geomech Geophys Geoenergy Georesour 4:383–401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-018-0095-5
Li S, Feng XT, Zhang D, Tang H (2019a) Coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical analysis of stimulation and production for fractured geothermal reservoirs. Appl Energy 247:40–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.04.036
Li Y, Long M, Zuo L et al (2019b) Brittleness evaluation of coal based on statistical damage and energy evolution theory. J Pet Sci Eng 172:753–763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2018.08.069
Malecot Y, Zingg L, Briffaut M, Baroth J (2019) Influence of free water on concrete triaxial behavior: the effect of porosity. Cem Concr Res 120:207–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2019.03.010
Ni X, Miao J, Lv R, Lin X (2017) Quantitative 3D spatial characterization and flow simulation of coal macropores based on ΜCT technology. Fuel. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.03.068
Padilla JM, Houston WN, Lawrence CA et al (2006) An automated triaxial testing device for unsaturated soils. Geotech Spec Publ 2006:1775–1786
Peng H, Fan J, Zhang X et al (2020a) Computed tomography analysis on cyclic fatigue and damage properties of rock salt under gas pressure. Int J Fatigue. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2020.105523
Peng K, Zhou J, Zou Q, Song X (2020b) Effect of loading frequency on the deformation behaviours of sandstones subjected to cyclic loads and its underlying mechanism. Int J Fatigue. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2019.105349
Ranjith PG, Perera MSA (2011) A new triaxial apparatus to study the mechanical and fluid flow aspects of carbon dioxide sequestration in geological formations. Fuel 90:2751–2759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2011.04.004
Sampath KHSM, Perera MSA, Li DY et al (2019) Evaluation of the mechanical behaviour of brine + CO2 saturated brown coal under mono-cyclic uni-axial compression. Eng Geol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105312
Stopka KS, McDowell DL (2020) Microstructure-sensitive computational multiaxial fatigue of Al 7075-T6 and duplex Ti–6Al–4V. Int J Fatigue. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2019.105460
Uchida S, Klar A, Yamamoto K (2016) Sand production model in gas hydrate-bearing sediments. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 86:303–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2016.04.009
Wang Y, Li CH, Hu YZ (2018) Use of X-ray computed tomography to investigate the effect of rock blocks on meso-structural changes in soil–rock mixture under triaxial deformation. Constr Build Mater 164:386–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.12.173
Wang T, Zhang T, Ranjith PG et al (2020a) A new approach to the evaluation of rock mass rupture and brittleness under triaxial stress condition. J Pet Sci Eng 184:106482
Wang Y, Feng WK, Li CH (2020b) On anisotropic fracture and energy evolution of marble subjected to triaxial fatigue cyclic-confining pressure unloading conditions. Int J Fatigue. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2020.105524
Xie H, Zhao X, Liu J et al (2012) Influence of different mining layouts on the mechanical properties of coal. Int J Min Sci Technol 22:749–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2012.12.010
Xia T, Zhou F, Liu J et al (2014) A fully coupled hydro-thermo-mechanical model for the spontaneous combustion of underground coal seams. Fuel. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2014.02.023
Xie H, Li C, Zhou T et al (2020) Conceptualization and evaluation of the exploration and utilization of low/medium-temperature geothermal energy: a case study of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. Geomech Geophys Geoenergy Georesour 6:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-019-00140-1
Yang SQ, Ranjith PG, Huang YH et al (2015) Experimental investigation on mechanical damage characteristics of sandstone under triaxial cyclic loading. Geophys J Int 201:662–682. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggv023
Yang Y, Ju Y, Li F et al (2016) The fractal characteristics and energy mechanism of crack propagation in tight reservoir sandstone subjected to triaxial stresses. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 32:415–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2016.04.049
Zhang S, Sheng JJ (2017) Effect of water imbibition on hydration induced fracture and permeability of shale cores. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 45:726–737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2017.06.008
Zhang C, Zhang L (2019) Permeability characteristics of broken coal and rock under cyclic loading and unloading. Nat Resour Res 28:1055–1069. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-018-9436-x
Zhang M, Dou L, Konietzky H et al (2020) Cyclic fatigue characteristics of strong burst-prone coal: experimental insights from energy dissipation, hysteresis and micro-seismicity. Int J Fatigue. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2019.105429
Zhao GF, Russell AR, Zhao X, Khalili N (2014) Strain rate dependency of uniaxial tensile strength in Gosford sandstone by the Distinct Lattice Spring Model with X-ray micro CT. Int J Solids Struct. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2014.01.012
Zhou HW, Zhong JC, Ren WG et al (2018) Characterization of pore-fracture networks and their evolution at various measurement scales in coal samples using X-ray µCT and a fractal method. Int J Coal Geol 189:35–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2018.02.007
Zhou C, Lu Y, Liu Z, Zhang L (2019) An innovative acousto-optic-sensing-based triaxial testing system for rocks. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52:3305–3321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01764-1
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51874053).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no known conflict of interest. To the best of our knowledge, the named authors have no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, J., Song, Z., Liao, Z. et al. Quantification of cracks and the evolution of permeability for reservoir rock under coupled THM: equipment development and experimental research. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-energ. Geo-resour. 6, 63 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-020-00187-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-020-00187-5