Abstract
Purpose
In vivo imaging of programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) during immunotherapy could potentially monitor changing PD-L1 expression and PD-L1 expression heterogeneity within and across tumors. Some protein constructs can be used for same-day positron emission tomography (PET) imaging. Previously, we evaluated the PD-L1-targeting Affibody molecule [18F]AlF-NOTA-ZPD-L1_1 as a PET tracer in a mouse tumor model of human PD-L1 expression. In this study, we evaluated the affinity-matured Affibody molecule ZPD-L1_4, to determine if improved affinity for PD-L1 resulted in increased in vivo targeting of PD-L1.
Procedures
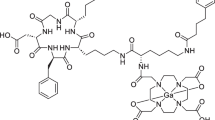
ZPD-L1_4 was conjugated with NOTA and radiolabeled with either [18F]AlF or 68Ga. [18F]AlF-NOTA-ZPD-L1_4 and [68Ga]NOTA-ZPD-L1_4 were evaluated in immunocompromised mice with LOX (PD-L1+) and SUDHL6 (PD-L1-) tumors with PET and ex vivo biodistribution measurements. In addition, whole-body PET studies were performed in rhesus monkeys to predict human biodistribution in a model with tracer binding to endogenous PD-L1, and to calculate absorbed radiation doses.
Results
Ex vivo biodistribution measurements showed that both tracers had > 25 fold higher accumulation in LOX tumors than SUDHL6 ([18F]AlF-NOTA-ZPD-L1_4: LOX: 8.7 ± 0.7 %ID/g (N = 4) SUDHL6: 0.2 ± 0.01 %ID/g (N = 6), [68Ga]NOTA-ZPD-L1_4: LOX: 15.8 ± 1.0 %ID/g (N = 6) SUDHL6: 0.6 ± 0.1 %ID/g (N = 6)), considerably higher than ZPD-L1_1. In rhesus monkeys, both PET tracers showed fast clearance through kidneys and low background signal in the liver ([18F]AlF-NOTA-ZPD-L1_4: 1.26 ± 0.13 SUV, [68Ga]NOTA-ZPD-L1_4: 1.11 ± 0.06 SUV). PD-L1-expressing lymph nodes were visible in PET images, indicating in vivo PD-L1 targeting. Dosimetry estimates suggest that both PET tracers can be used for repeated clinical studies, although high kidney accumulation may limit allowable radioactive doses.
Conclusions
[18F]AlF-NOTA-ZPD-L1_4 and [68Ga]NOTA-ZPD-L1_4 are promising candidates for same-day clinical PD-L1 PET imaging, warranting clinical evaluation. The ability to use either [18F] or [68Ga] may expand access to clinical sites.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Topalian SL, Drake CG, Pardoll DM (2015) Immune checkpoint blockade: a common denominator approach to cancer therapy. Cancer Cell 27(4):450–461
Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR, Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Carvajal RD, Sosman JA, Atkins MB (2012) and others. Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti–PD-1 antibody in Cancer. N Engl J Med 366(26):2443–2454
Brahmer JR, Tykodi SS, Chow LQ, Hwu WJ, Topalian SL, Hwu P, Drake CG, Camacho LH, Kauh J, Odunsi K et al (2012) Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with advanced cancer. N Engl J Med 366(26):2455–2465
Garon EB, Rizvi NA, Hui R, Leighl N, Balmanoukian AS, Eder JP, Patnaik A, Aggarwal C, Gubens M, Horn L (2015) and others. Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 372(21):2018–2028
Langer CJ, Gadgeel SM, Borghaei H, Papadimitrakopoulou VA, Patnaik A, Powell SF, Gentzler RD, Martins RG, Stevenson JP, Jalal SI (2016) and others. Carboplatin and pemetrexed with or without pembrolizumab for advanced, non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer: a randomised, phase 2 cohort of the open-label KEYNOTE-021 study. Lancet Oncol 17(11):1497–1508
Le DT, Durham JN, Smith KN, Wang H, Bartlett BR, Aulakh LK, Lu S, Kemberling H, Wilt C, Luber BS et al (2015) Mismatch repair deficiency predicts response of solid tumors to PD-1 blockade. Science 357(6349):409–413
Seiwert TY, Burtness B, Mehra R, Weiss J, Berger R, Eder JP, Heath K, McClanahan T, Lunceford J, Gause C et al (2016) Safety and clinical activity of pembrolizumab for treatment of recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-012): an open-label, multicentre, phase 1b trial. Lancet Oncol 17(7):956–965
Vokes EE, Ready N, Felip E, Horn L, Burgio MA, Antonia SJ, Aren Frontera O, Gettinger S, Holgado E, Spigel D et al (2018) Nivolumab versus docetaxel in previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 017 and CheckMate 057): 3-year update and outcomes in patients with liver metastases. Ann Oncol 29(4):959–965
Akin Telli T, Bregni G, Camera S, Deleporte A, Hendlisz A, Sclafani F (2020) PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors in oesophago-gastric cancers. Cancer Lett 469:142–150
Wang Y, Li G (2019) PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in cervical cancer: current studies and perspectives. Front Med 13(4):438–450
Abou Alaiwi S, Xie W, Nassar AH, Dudani S, Martini D, Bakouny Z, Steinharter JA, Nuzzo PV, Flippot R, Martinez-Chanza N et al (2020) Safety and efficacy of restarting immune checkpoint inhibitors after clinically significant immune-related adverse events in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Immunother Cancer 8(1)
Balar AV, Castellano D, O'Donnell PH, Grivas P, Vuky J, Powles T, Plimack ER, Hahn NM, de Wit R, Pang L (2017) and others. First-line pembrolizumab in cisplatin-ineligible patients with locally advanced and unresectable or metastatic urothelial cancer (KEYNOTE-052): a multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol 18(11):1483–1492
Ding W, LaPlant BR, Call TG, Parikh SA, Leis JF, He R, Shanafelt TD, Sinha S, Le-Rademacher J, Feldman AL (2017) and others. Pembrolizumab in patients with CLL and Richter transformation or with relapsed CLL. Blood 129(26):3419–3427
Reck M, Rodriguez-Abreu D, Robinson AG, Hui R, Csoszi T, Fulop A, Gottfried M, Peled N, Tafreshi A, Cuffe S et al (2016) Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 375(19):1823–1833
Yi M, Jiao D, Xu H, Liu Q, Zhao W, Han X, Wu K (2018) Biomarkers for predicting efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. Mol Cancer 17(1):129
Herbst RS, Soria J-C, Kowanetz M, Fine GD, Hamid O, Gordon MS, Sosman JA, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Gettinger SN (2014) and others. Predictive correlates of response to the anti-PD-L1 antibody MPDL3280A in cancer patients. Nature 515(7528):563–567
Hersom M, Jorgensen JT (2018) Companion and complementary diagnostics-focus on PD-L1 expression assays for PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. Ther Drug Monit 40(1):9–16
Patel SP, Kurzrock R (2015) PD-L1 Expression as a predictive biomarker in cancer immunotherapy. Mol Cancer Ther 14(4):847–856
McLaughlin J, Han G, Schalper KA et al (2016) Quantitative assessment of the heterogeneity of PD-L1 expression in non–small-cell lung cancer. JAMA Oncol 2(1):46–54
Mansfield AS, Murphy SJ, Peikert T, Yi ES, Vasmatzis G, Wigle DA, Aubry MC (2016) Heterogeneity of programmed cell death ligand 1 expression in multifocal lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 22(9):2177–2182
Dill EA, Gru AA, Atkins KA, Friedman LA, Moore ME, Bullock TN, Cross JV, Dillon PM, Mills AM (2017) PD-L1 Expression and intratumoral heterogeneity across breast cancer subtypes and stages: an assessment of 245 primary and 40 metastatic tumors. Am J Surg Pathol 41(3):334–342
Madore J, Vilain RE, Menzies AM, Kakavand H, Wilmott JS, Hyman J, Yearley JH, Kefford RF, Thompson JF, Long GV et al (2015) PD-L1 expression in melanoma shows marked heterogeneity within and between patients: implications for anti-PD-1/PD-L1 clinical trials. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 28(3):245–253
Ilie M, Long-Mira E, Bence C, Butori C, Lassalle S, Bouhlel L, Fazzalari L, Zahaf K, Lalvée S, Washetine K et al (2016) Comparative study of the PD-L1 status between surgically resected specimens and matched biopsies of NSCLC patients reveal major discordances: a potential issue for anti-PD-L1 therapeutic strategies. Ann Oncol 27(1):147–153
Messenheimer DJ, Jensen SM, Afentoulis ME, Wegmann KW, Feng Z, Friedman DJ, Gough MJ, Urba WJ, Fox BA (2017) Timing of PD-1 blockade is critical to effective combination immunotherapy with anti-OX40. Clin Cancer Res 23(20):6165–6177
Hettich M, Braun F, Bartholom Ã, Schirmbeck R, Niedermann G (2016) High-resolution PET imaging with therapeutic antibody-based PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint tracers. Theranostics 6(10):1629–1640
Lesniak WG, Chatterjee S, Gabrielson M, Lisok A, Wharram B, Pomper MG, Nimmagadda S (2016) PD-L1 detection in tumors using [64Cu] atezolizumab with PET. Bioconjug Chem 27(9):2103–2110
Ehlerding EB, Lee HJ, Barnhart TE, Jiang D, Kang L, McNeel DG, Engle JW, Cai W (2019) Noninvasive imaging and quantification of radiotherapy-induced PD-L1 upregulation with (89)Zr-Df-atezolizumab. Bioconjug Chem 30(5):1434–1441
England CG, Ehlerding EB, Hernandez R, Rekoske BT, Graves SA, Sun H, Liu G, McNeel DG, Barnhart TE, Cai W (2017) Preclinical pharmacokinetics and biodistribution studies of 89Zr-labeled pembrolizumab. J Nucl Med 58(1):162–168
Kikuchi M, Clump DA, Srivastava RM, Sun L, Zeng D, Diaz-Perez JA, Anderson CJ, Edwards WB, Ferris RL (2017) Preclinical immunoPET/CT imaging using Zr-89-labeled anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody for assessing radiation-induced PD-L1 upregulation in head and neck cancer and melanoma. Oncoimmunology 6(7):e1329071
Natarajan A, Mayer AT, Reeves RE, Nagamine CM, Gambhir SS (2017) Development of novel ImmunoPET tracers to image human PD-1 checkpoint expression on tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in a humanized mouse model. Mol Imaging Biol 19(6):903–914
Natarajan A, Mayer AT, Xu L, Reeves RE, Gano J, Gambhir SS (2015) Novel radiotracer for ImmunoPET imaging of PD-1 checkpoint expression on tumor infiltrating lymphocytes. Bioconjug Chem 26(10):2062–2069
Natarajan A, Patel CB, Habte F, Gambhir SS (2018) Dosimetry prediction for clinical translation of (64)Cu-pembrolizumab immunoPET targeting human PD-1 expression. Sci Rep 8(1):633
Truillet C, Oh HLJ, Yeo SP, Lee CY, Huynh LT, Wei J, Parker MFL, Blakely C, Sevillano N, Wang YH (2018) and others. Imaging PD-L1 expression with ImmunoPET. Bioconjug Chem 29(1):96–103
Bensch F, van der Veen EL, Lub-de Hooge MN, Jorritsma-Smit A, Boellaard R, Kok IC, Oosting SF, Schroder CP, Hiltermann TJN, van der Wekken AJ et al (2018) (89)Zr-atezolizumab imaging as a non-invasive approach to assess clinical response to PD-L1 blockade in cancer. Nat Med 24(12):1852–1858
Jagoda EM, Vasalatiy O, Basuli F, Opina ACL, Williams MR, Wong K, Lane KC, Adler S, Ton AT, Szajek LP et al (2019) Immuno-PET imaging of the programmed cell death-1 ligand (PD-L1) using a zirconium-89 labeled therapeutic antibody, avelumab. Mol Imaging 18:1536012119829986
Vento J, Mulgaonkar A, Woolford L, Nham K, Christie A, Bagrodia A, de Leon AD, Hannan R, Bowman I, McKay RM et al (2019) PD-L1 detection using (89)Zr-atezolizumab immuno-PET in renal cell carcinoma tumorgrafts from a patient with favorable nivolumab response. J Immunother Cancer 7(1):144
Niemeijer AN, Leung D, Huisman MC, Bahce I, Hoekstra OS, van Dongen G, Boellaard R, Du S, Hayes W, Smith R et al (2018) Whole body PD-1 and PD-L1 positron emission tomography in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat Commun 9(1):4664
Cao Y, Jusko WJ (2014) Survey of monoclonal antibody disposition in man utilizing a minimal physiologically-based pharmacokinetic model. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 41(6):571–580
Mould DR, Sweeney KR (2007) The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of monoclonal antibodies--mechanistic modeling applied to drug development. Curr Opin Drug Discov Dev 10(1):84–96
Wester HJ, Kessler H (2005) Molecular targeting with peptides or peptide-polymer conjugates: just a question of size? J Nucl Med 46(12):1940–1945
Maute RL, Gordon SR, Mayer AT, McCracken MN, Natarajan A, Ring NG, Kimura R, Tsai JM, Manglik A, Kruse AC (2015) and others. Engineering high-affinity PD-1 variants for optimized immunotherapy and immuno-PET imaging. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112(47):E6506–E6514
Chatterjee S, Lesniak WG, Miller MS, Lisok A, Sikorska E, Wharram B, Kumar D, Gabrielson M, Pomper MG, Gabelli SB et al (2017) Rapid PD-L1 detection in tumors with PET using a highly specific peptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 483(1):258–263
Donnelly DJ, Smith RA, Morin P, Lipovšek D, Gokemeijer Jochem, Cohen D, Lafont V, Tran T, Cole EL, Wright M et al (2018) Synthesis and biological evaluation of a novel 18F-labeled Adnectin as a PET Radioligand for Imaging PD-L1 expression. J Nucl Med 59:529–535
Ingram JR, Dougan M, Rashidian M, Knoll M, Keliher EJ, Garrett S, Garforth S, Blomberg OS, Espinosa C, Bhan A (2017) and others. PD-L1 is an activation-independent marker of brown adipocytes. Nat Commun 8(647):1–10
Mayer AT, Natarajan A, Gordon SR, Maute RL, McCracken MN, Ring AM, Weissman IL, Gambhir SS (2017) Practical immuno-PET radiotracer design considerations for human immune checkpoint imaging. J Nucl Med 58(4):538–546
González Trotter DE, Meng X, McQuade P, Rubins D, Klimas M, Zeng Z, Connolly BM, Miller PJ, O’Malley SS, Lin S-A (2017) and others. In vivo imaging of the programmed death ligand 1 by 18F PET. J Nucl Med 58(11):1852–1857
De Silva RA, Kumar D, Lisok A, Chatterjee S, Wharram B, Venkateswara Rao K, Mease R, Dannals RF, Pomper MG, Nimmagadda S (2018) Peptide-based (68)Ga-PET radiotracer for imaging PD-L1 expression in cancer. Mol Pharm 15(9):3946–3952
Li D, Cheng S, Zou S, Zhu D, Zhu T, Wang P, Zhu X (2018) Immuno-PET imaging of (89)Zr labeled anti-PD-L1 domain antibody. Mol Pharm 15(4):1674–1681
Kuan H, Hanyu M, Masayuki H, Xie L, Zhang Y, Nagatsu K, Kotaro N, Suzuki H, Hisashi S, Zhang MR (2019) Developing native peptide-based radiotracers for PD-L1 PET imaging and improving imaging contrast by pegylation. Chem Commun (Camb) 55(29):4162–4165
Lesniak WG, Mease RC, Chatterjee S, Kumar D, Lisok A, Wharram B, Kalagadda VR, Emens LA, Pomper MG, Nimmagadda S (2019) Development of [(18)F]FPy-WL12 as a PD-L1 specific PET imaging peptide. Mol Imaging 18:1536012119852189
Wissler HL, Ehlerding EB, Lyu Z, Zhao Y, Zhang S, Eshraghi A, Buuh ZY, McGuth JC, Guan Y, Engle JW (2019) and others. Site-specific immuno-PET tracer to image PD-L1. Mol Pharm 16(5):2028–2036
Li D, Zou S, Cheng S, Song S, Wang P, Zhu X (2019) Monitoring the Response of PD-L1 Expression to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Nonsmall-Cell Lung Cancer Xenografts by Immuno-PET Imaging. Mol Pharm 16(8):3469–3476
Jiang J, Zhang M, Li G, Liu T, Wan Y, Liu Z, Zhu H, Yang Z (2020) Evaluation of (64)Cu radiolabeled anti-hPD-L1 Nb6 for positron emission tomography imaging in lung cancer tumor mice model. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 30(4):126915
Lv G, Sun X, Qiu L, Sun Y, Li K, Liu Q, Zhao Q, Qin S, Lin J (2020) PET Imaging of Tumor PD-L1 Expression with a Highly Specific Nonblocking Single-Domain Antibody. J Nucl Med 61(1):117–122
Xing Y, Chand G, Liu C, Cook GJR, O'Doherty J, Zhao L, Wong NCL, Meszaros LK, Ting HH, Zhao J (2019) Early Phase I Study of a (99 m)Tc-Labeled Anti-Programmed Death Ligand-1 (PD-L1) Single-Domain Antibody in SPECT/CT Assessment of PD-L1 Expression in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J Nucl Med 60(9):1213–1220
Conti M, Eriksson L (2016) Physics of pure and non-pure positron emitters for PET: a review and a discussion. EJNMMI Phys 3(1):8
Cleeren F, Lecina J, Ahamed M, Raes G, Devoogdt N, Caveliers V, McQuade P, Rubins DJ, Li W, Verbruggen A (2017) Al18F-labeling of heat-sensitive biomolecules for positron emission tomography imaging. Theranostics 7(11):2924
Connolly BM, Vanko A, McQuade P, Guenther I, Meng X, Rubins D, Waterhouse R, Hargreaves R, Sur C, Hostetler E (2012) Ex vivo imaging of pancreatic beta cells using a radiolabeled GLP-1 receptor agonist. Mol Imaging Biol 14(1):79–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-011-0481-7.2012(14):79-87
Cloutier RJ, Smith SA, Watson EE, Snyder WS, Warner GG (1973) Dose to the fetus from radionuclides in the bladder. Health Phys 25(2):147–161
Skrable KW, Chabot G, Harris J, French C (1975) Dosimetric Model for the Gastrointestinal Tract. Health Phys 28(4):411–427
Stabin MG, Sparks RB, Crowe E (2005) OLINDA/EXM: The second-generation personal computer software for internal dose assessment in nuclear medicine. J Nucl Med 46(6):1023–1027
Bélanger MJ, Krause SM, Ryan C, Sanabria-Bohorquez S, Li W, Hamill TG, Burns HD (2008) Biodistribution and radiation dosimetry of [18F]F-PEB in nonhuman primates. Nucl Med Commun 29(10):915–919
Fujimoto D, Uehara K, Sato Y, Sakanoue I, Ito M, Teraoka S, Nagata K, Nakagawa A, Kosaka Y, Otsuka K et al (2017) Alteration of PD-L1 expression and its prognostic impact after concurrent chemoradiation therapy in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Sci Rep 7(1):11373
Rojko L, Reiniger L, Teglasi V, Fabian K, Pipek O, Vagvolgyi A, Agocs L, Fillinger J, Kajdacsi Z, Timar J (2018) and others. Chemotherapy treatment is associated with altered PD-L1 expression in lung cancer patients. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 144(7):1219–1226
Takahashi T, Tateishi A, Bychkov A, Fukuoka J (2019) Remarkable alteration of PD-L1 expression after immune checkpoint therapy in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: two autopsy case reports. Int J Mol Sci 20(10):2578
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 84 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rubins, D.J., Meng, X., McQuade, P. et al. In Vivo Evaluation and Dosimetry Estimate for a High Affinity Affibody PET Tracer Targeting PD-L1. Mol Imaging Biol 23, 241–249 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-020-01544-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-020-01544-2