Abstract
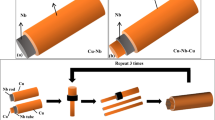
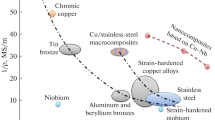
Cu-Nb microcomposite wire was successfully prepared by a groove rolling process. The effects of groove rolling on the diffraction peaks, microstructure, and properties of the Cu-Nb microcomposite were investigated and the microstructure evolutions and strengthening mechanism were discussed. The tensile strength of the Cu-Nb microcomposite wire with a diameter of 2.02 mm was greater than 1 GPa, and its conductivity reached 68% of the International Annealed Copper Standard, demonstrating the Cu-Nb microcomposite wire with high tensile strength and high conductivity after groove rolling. The results show that an appropriate groove rolling method can improve the performance of the Cu-Nb microcomposite wire.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Q.Q. Sun, F. Jiang, L. Deng, H.X. Xiao, L. Li, M. Liang, and T. Peng, Uniaxial fatigue behavior of Cu-Nb micro-composite conductor, part I: Effect of peak stress and stress ratio, Int. J. Fatigue, 91(2016), p. 275.
J. Wang, R.G. Hoagland, J.P. Hirth, and A. Misra, Atomistic simulations of the shear strength and sliding mechanisms of copper-niobium interfaces, Acta Mater., 56(2008), No. 13, p. 3109.
L. Thilly, P.O. Renault, V. Vidal, F. Lecouturier, S. Van Petegem, U. Stuhr, and H. Van Swygenhoven, Plasticity of multiscale nanofifilamentary Cu/Nb composite wires during in situ neutron diffraction: Codeformation and size effect, Appl. Phys. Lett., 88(2006), No. 19, art. No. 191906.
K. Han, V.J. Toplosky, R. Walsh, C. Swenson, B. Lesch, and V.I. Pantsyrnyi, Properties of high strength Cu-Nb conductor for pulsed magnet applications, IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond., 12(2002), No. 1, p. 1176.
K. Kindo, 100 T magnet developed in Osaka, Physica B, 294–295(2001), p. 585.
L. Thilly, S.V. Petegem, P.-O. Renault, F. Lecouturier, V. Vidal, B. Schmitt, and H. Van Swygenhoven, A new criterion for elasto-plastic transition in nanomaterials: Application to size and composite effects on Cu-Nb nanocomposite wires, Acta Mater., 57(2009), No. 11, p. 3157.
X.C. Pan, J. Zhang, Y. Huang, and Y.C. Liu, Construction of metallurgical interface with high strength between immiscible Cu and Nb by direct bonding method, J. Alloys Compd., 723(2017), p. 1053.
P.F. Wang, P.X. Zhang, M. Liang, C.S. Li, and J.S. Li, Heat treatment effect on the microstructure and properties of a high-strength and high-conductivity Cu-Nb-Cu microcomposite, IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond., 29(2019), No. 4, art. No. 6000205.
K. Shimoyama, S. Yokoyama, S. Kaneko, and F. Fujita, Effect of grooved roll profiles on microstructure evolutions of AZ31 sheets in Periodical Straining Rolling process, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 611(2014), p. 58.
L.F. Zeng, R. Gao, Q.F. Fang, X.P. Wang, Z.M. Xie, S. Miao, T. Hao, and T. Zhang, High strength and thermal stability of bulk Cu/Ta nanolamellar multilayers fabricated by cross accumulative roll bonding, Acta Mater., 110(2016), p. 341.
M. Knezevic and A. Bhattacharyya, Characterization of micro-structure in Nb rods processed by rolling: Effect of grooved rolling die geometry on texture uniformity, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 66(2017), p. 44.
R.D. Nyilas and R. Spolenak, Orientation-dependent ductile-to-brittle transitions in nanostructured materials, Acta Mater., 56(2008), No. 19, p. 5627.
S.C.V. Lim and A.D. Rollett, Length scale effects on recrystallization and texture evolution in Cu layers of a roll-bonded Cu-Nb composite, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 520(2009), No. 1–2, p. 189.
B. Zhang, C.L. Yang, Y.X. Sun, X.L. Li, and F. Liu, The micro-structure, mechanical properties and tensile deformation mechanism of rolled AlN/AZ91 composite sheets, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 763(2019), art. No. 138118.
K. Al-Fadhalah, C.N. Tomé, A.J. Beaudoin, I.M. Robertson, J.P. Hirth, and A. Misra, Modeling texture evolution during rolling of a Cu-Nb multilayered system, Philos. Mag., 85(2005), No. 13, p. 1419.
Q. Wu, W.X. Xu, and L.C. Zhang, Microstructure-based modelling of fracture of particulate reinforced metal matrix composites, Composites Part B, 163(2019), p. 384.
K.M. Youssef, M.A. Abaza, R.O. Scattergood, and C.C. Koch, High strength, ductility, and electrical conductivity of in-situ consolidated nanocrystalline Cu-1%Nb, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 711(2018), p. 350.
Z. Fan, S. Xue, J. Wang, K.Y. Yu, H. Wang, and X. Zhang, Unusual size dependent strengthening mechanisms of Cu/amorphous CuNb multilayers, Acta Mater., 120(2016), p. 327.
K. Changela, H. Krishnaswamy, and R.K. Digavalli, Development of combined groove pressing and rolling to produce ultra-fine grained Al alloys and comparison with cryorolling, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 760(2019), p. 7.
X.Q. Shang, H.M. Zhang, Z.S. Cui, M.W. Fu, and J.B. Shao, A multiscale investigation into the effect of grain size on void evolution and ductile fracture: Experiments and crystal plasticity modeling, Int. J. Plast., 125(2020), p. 133.
D.P. Shen, H.B. Zhou, and W.P. Tong, Influence of deformation temperature on the microstructure and thermal stability of HPT-consolidated Cu-1%Nb alloys, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 8(2019), No. 6, p. 6396.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2016YFA0401701) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51601151).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Pf., Liang, M., Xu, Xy. et al. Effect of groove rolling on the microstructure and properties of Cu-Nb microcomposite wires. Int J Miner Metall Mater 28, 279–284 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-020-2073-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-020-2073-5