Abstract
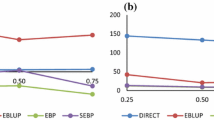
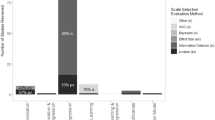
In this paper we present a detailed comparison of the prediction error based model selection criteria in circular random effects models. The study is primarily motivated by the need for an understanding of their performance in real life ecological and environmental applications. Prediction errors are based on posterior predictive distributions and the model selection methods are adjusted for the circular manifold. Plug-in estimators of the circular distance parameters are also considered. A Monte Carlo experiment scheme taking the account of various realistic ecological and biological scenarios is designed. We introduced a coefficient that is based on conditional expectations to examine how the deviation from von Mises (vM) distribution, the standard choice in applications, effects the performances. Our results show that the performances of widely used circular predictive model selection criteria mostly depend on the sample size as well as within-sample-correlation. The approaches and selection strategies are then applied to investigate orientational behaviour of Talitrus saltator under the risk of dehydration and direction of wind with respect to associated atmoshperic variables.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borgioli C, Marchetti GM, Scapini F (1999a) Variation in zonal recovery in four Talitrus saltator populatıons from dıfferent coastlınes: a comparison of orientations in the field and in an experimental arena. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 45:7–85
Borgioli C, Martelli M, Porri F et al (1999b) Orientation in Talitrus saltator (montagu): trends in intrapopulations variability related to environmental and intrinsic factors. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 238:29–47
D’Elia A (2001) A statistical model for orientation mechanism. Stat Methods Appl 10:157–174
Hall DB, Shen J (2015) Marginal projected multivariate linear models for clustered angular data. Aust N Z J Stat 57(2):241–257
Hill T, Chocholek M (2016) Coastal biodiversity and ecosystem service sustainability (CBESS) eddy covariance flux data for Abbotts Hall. NERC Environmental Information Data Centre, Bailrigg. https://doi.org/10.5285/8cfd9a2a-8b68-40c6-94a1-be8e02e869c1
Jammalamadaka RA, SenGupta A (2001) Topics in circular statistics. World Scientific Inc., New York
Lagona F (2016) Regression analysis of correlated circular data based on the multivariate von Mises distribution. Environ Ecol Stat 23(1):89–113
Maity A, Sherman M (2008) On adaptive linear regression. J Appl Stat 35(12):1409–1422
Maruotti A (2016) Analyzing longitudinal circular data by projected normal models: a semi-parametric approach based on finite mixture models. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 23:257–277
Maruotti A, Punzo A, Mastrantonio G et al (2016) A time-dependent extension of the projected normal regression model for longitudinal circular data based on a hidden Markov heterogeneity structure. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 30:1725–1740
Mastrantonio G, Lasinio GJ, Gelfand AE (2016) Spatio-temporal circular models with non-separable covariance structure. Test 25(2):331–350
McMillan GP, Hanson TE, Saunders G et al (2013) A two-component circular regression model for repeated measures auditory localization data. J R Stat Soc Ser C Appl Stat 62(4):515–534
Nunez-Antonio G, Gutierrez-Pena E (2014) A Bayesian model for longitudinal circular data based on the projected normal distribution. Comput Stat Data Anal 71:506–519
Pewsey A (2002) Testing circular symmetry. Can J Stat 30:591–600
Ravindran PK, Ghosh SK (2011) Bayesian analysis of circular data using wrapped distributions. J Stat Theory Pract 5:547–561
Rivest LP, Kato S (2019) A random-effects model for clustered circular data. Can J Stat. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjs.11520
Rossi PE, Allenby GM, McCulloch R (2005) Bayesian statistics and marketing. Wiley, Chichester
Scapini F (1997) Variation in scototaxis and orientation adaptation of Talitrus saltator populations subjected to different ecological constraints. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 44:139–146
Song XKP (2007) Correlated data analysis: modeling analytics, and applications. Springer, Berlin
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank the two anonymous reviewers for their critical reading, comments and suggestions that helped improve and clarify this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Pierre Dutilleul.
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Camli, O., Kalaylioglu, Z. Bayesian predictive model selection in circular random effects models with applications in ecological and environmental studies. Environ Ecol Stat 28, 21–34 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10651-020-00471-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10651-020-00471-3