Abstract
Background
Oxidative damages contributes to age-related macular degeneration (AMD) caused vision blindness, but the molecular mechanisms are still largely unknown.
Objectives
This study managed to investigate this issue by conducting in vitro experiments.
Methods
Oxidative stress were evaluated by L-012 dye, DHE staining and MDA assay. CCK-8 and colony formation assay were conducted to examine cell proliferation. Cell death was evaluated by trypan blue staining and Annexin V-FITC/PI double staining method through flow cytometry (FCM). The binding sites of miR-23a and GLS1 mRNA were predicted by online miRDB database and validated by dual-luciferase reporter gene system. Real-Time qPCR for miR-23a levels and Western Blot for protein expressions.
Results
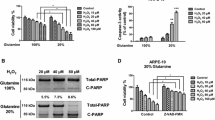
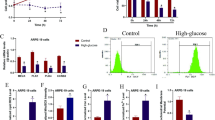
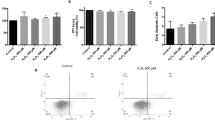
The retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells (ARPE-19) were subjected to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) stimulation to simulate AMD progression in vitro, and we identified a novel miR-23a/glutaminase-1 (GLS1) pathway that regulated H2O2 induced oxidative damages in ARPE-19 cells. Mechanistically, H2O2 induced oxidative stress, inhibited cell proliferation and induced cell death in ARPE-19 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Also, H2O2 stimulation hindered cell invasion, migration and glutamine uptake in ARPE-19 cells. Interestingly, we proved that H2O2 increased miR-23a levels, while downregulated glutaminase-1 (GLS1) in ARPE-19 cells, and miR-23a targeted 3′ untranslated region (3′UTR) of GLS1 mRNA for GLS1 degradation. Finally, our data suggested that silencing miR-23a upregulated GLS1 to reverse the detrimental effects of H2O2 treatment on ARPE-19 cells.
Conclusions
In general, analysis of the data suggested that miR-23a ablation upregulated GLS1 to attenuate H2O2 stimulation induced oxidative damages in ARPE-19 cells in vitro, and this study broadened our knowledge in this field, which might help to provide novel theranostic signatures for AMD.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All the raw data and material involved in this study are available from the corresponding author upon appropriate request.
References
Ansari RE, Craze ML, Althobiti M, Alfarsi L, Ellis IO, Rakha EA, Green AR (2020) Enhanced glutamine uptake influences composition of immune cell infiltrates in breast cancer. Br J Cancer 122(1):94–101
Ayaz L, Dinç E (2018) Evaluation of microRNA responses in ARPE-19 cells against the oxidative stress. Cutan Ocul Toxicol 37(2):121–126
Chan CM, Huang DY, Huang YP, Hsu SH, Kang LY, Shen CM, Lin WW (2016) Methylglyoxal induces cell death through endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated ROS production and mitochondrial dysfunction. J Cell Mol Med 20(9):1749–1760
Chan CM, Huang DY, Sekar P, Hsu SH, Lin WW (2019) Reactive oxygen species-dependent mitochondrial dynamics and autophagy confer protective effects in retinal pigment epithelial cells against sodium iodate-induced cell death. J Biomed Sci 26(1):40
Cui R, Tian L, Lu D, Li H, Cui J (2019) Exendin-4 protects human retinal pigment epithelial cells from H2O2-induced oxidative damage via activation of NRF2 signaling. Ophthalmic Res 63:404–412
Dalvi S, Galloway CA, Winschel L, Hashim A, Soto C, Tang C, MacDonald LA, Singh R (2019) Environmental stress impairs photoreceptor outer segment (POS) phagocytosis and degradation and induces autofluorescent material accumulation in hiPSC-RPE cells. Cell Death Discov 5:96
Datta S, Cano M, Ebrahimi K, Wang L, Handa JT (2017) The impact of oxidative stress and inflammation on RPE degeneration in non-neovascular AMD. Prog Retin Eye Res 60:201–218
Donato L, Scimone C, Nicocia G, Denaro L, Robledo R, Sidoti A, D’Angelo R (2018a) GLO1 gene polymorphisms and their association with retinitis pigmentosa: a case-control study in a Sicilian population. Mol Biol Rep 45(5):1349–1355
Donato L, Bramanti P, Scimone C, Rinaldi C, Giorgianni F, Beranova-Giorgianni S, Koirala D, D’Angelo R, Sidoti A (2018b) miRNAexpression profile of retinal pigment epithelial cells under oxidative stress conditions. FEBS Open Bio 8(2):219–233
Donato L, Scimone C, Rinaldi C, Aragona P, Briuglia S, D’Ascola A, D’Angelo R, Sidoti A (2018c) Stargardt phenotype associated with two ELOVL4 promoter variants and ELOVL4 downregulation: new possible perspective to etiopathogenesis? Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 59(2):843–857
Fujii R, Yamada H, Yamazaki M, Munetsuna E, Ando Y, Ohashi K, Ishikawa H, Shimoda H, Sakata K, Ogawa A, Kobayashi S, Suzuki K (2019) Circulating microRNAs (miR-126, miR-197, and miR-223) are associated with chronic kidney disease among elderly survivors of the Great East Japan Earthquake. BMC Nephrol 20(1):474
Gorin MB, daSilva MJ (2020) Predictive genetics for AMD: hype and hopes for genetics-based strategies for treatment and prevention. Exp Eye Res 191:107894
Gulinaer AJ, Ju AN, Gao M, Luo Y, Bo YL (2019) Over-expression of miR-187 inhibited cell proliferation and metastasis of glioma via down-regulating SMAD1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23(24):10908–10917
Hwang N, Kwon MY, Woo JM, Chung SW (2019) Oxidative stress-induced pentraxin 3 expression human retinal pigment epithelial cells is involved in the pathogenesis of age-related macular degeneration. Int J Mol Sci 20(23):6028
Jarrett SG, Boulton ME (2012) Consequences of oxidative stress in age-related macular degeneration. Mol Aspects Med 33(4):399–417
Ji Cho M, Yoon SJ, Kim W, Park J, Lee J, Park JG, Cho YL, Kim JH, Jang H, Park YJ, Lee SH, Min JK (2019) Oxidative stress-mediated TXNIP loss causes RPE dysfunction. Exp Mol Med 51(10):1–13
Jing H, Zhang X, Luo K, Luo Q, Yin M, Wang W, Zhu Z, Zheng J, He X (2020) miR-381-abundant small extracellular vesicles derived from kartogenin-preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells promote chondrogenesis of MSCs by targeting TAOK1. Biomaterials 231:119682
Kauppinen A, Paterno JJ, Blasiak J, Salminen A, Kaarniranta K (2016) Inflammation and its role in age-related macular degeneration. Cell Mol Life Sci 73(9):1765–1786
Li DD, Zhong BW, Zhang HX, Zhou HY, Luo J, Liu Y, Xu GC, Luan CS, Fang J (2016) Inhibition of the oxidative stress-induced miR-23a protects the human retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells from apoptosis through the upregulation of glutaminase and glutamine uptake. Mol Biol Rep 43(10):1079–1087
Lin JB, Moolani HV, Sene A, Sidhu R, Kell P, Lin JB, Dong Z, Ban N, Ory DS, Apte RS (2018) Macrophage microRNA-150 promotes pathological angiogenesis as seen in age-related macular degeneration. JCI Insight 3(7):e120157
Martín-Rufián M, Nascimento-Gomes R, Higuero A, Crisma AR, Campos-Sandoval JA, Gómez-García MC, Cardona C, Cheng T, Lobo C, Segura JA, Alonso FJ, Szeliga M, Albrecht J, Curi R, Márquez J, Colquhoun A, Deberardinis RJ, Matés JM (2014) Both GLS silencing and GLS2 overexpression synergize with oxidative stress against proliferation of glioma cells. J Mol Med 92(3):277–290
O’Neill HC, Limnios IJ, Barnett NL (2020) Advancing a stem cell therapy for age-related macular degeneration. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther 15(2):89–97
Reynolds MR, Lane AN, Robertson B, Kemp S, Liu Y, Hill BG, Dean DC, Clem BF (2014) Control of glutamine metabolism by the tumor suppressor Rb. Oncogene 33(5):556–566
Romano GL, Platania CBM, Drago F, Salomone S, Ragusa M, Barbagallo C, Di Pietro C, Purrello M, Reibaldi M, Avitabile T, Longo A, Bucolo C (2017) Retinal and circulating miRNAs in age-related macular degeneration: an in vivo animal and human study. Front Pharmacol 8:168
Sastre D, Baiochi J, de Souza Lima IM, Canto de Souza F, Corveloni AC, Thomé CH, Faça VM, Schiavinato J, Covas DT, Panepucci RA (2019) Focused screening reveals functional effects of microRNAs differentially expressed in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 19(1):1239
Sato T, Takeuchi M, Karasawa Y, Takayama K, Enoki T (2019) Comprehensive expression patterns of inflammatory cytokines in aqueous humor of patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Sci Rep 9(1):19447
Shao Y, Yu H, Yang Y, Li M, Hang L, Xu X (2019) A solid dispersion of quercetin shows enhanced Nrf2 Activation and protective effects against oxidative injury in a mouse model of dry age-related macular degeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:1479571
Simmons KT, Mazzilli JL, Mueller-Ortiz SL, Domozhirov AY, Garcia CA, Zsigmond EM, Wetsel RA (2020) Complement Receptor 1 (CR1/CD35)-expressing retinal pigment epithelial cells as a potential therapy for age-related macular degeneration. Mol Immunol 118:91–98
van den Heuvel AP, Jing J, Wooster RF, Bachman KE (2012) Analysis of glutamine dependency in non-small cell lung cancer: GLS1 splice variant GAC is essential for cancer cell growth. Cancer Biol Ther 13(12):1185–1194
Yan J, Qin Y, Yu J, Peng Q, Chen X (2018) MiR-340/iASPP axis affects UVB-mediated retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cell damage. J Photochem Photobiol B 186:9–16
Yan L, Zhang Y, Li K, Wang M, Li J, Qi Z, Wu J, Wang Z, Ling L, Liu H, Wu Y, Lu X, Xu L, Zhu Y, Zhang Y (2020) miR-593-5p inhibit cell proliferation by targeting PLK1 in non small cell lung cancer cells. Pathol Res Pract 216(2):152786
Zhang Z, Liu R, Shuai Y, Huang Y, Jin R, Wang X, Luo J (2020) ASCT2 (SLC1A5)-dependent glutamine uptake is involved in the progression of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer 122(1):82–93
Zhao H, Tao Z, Wang R, Liu P, Yan F, Li J, Zhang C, Ji X, Luo Y (2014) MicroRNA-23a-3p attenuates oxidative stress injury in a mouse model of focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Brain Res 1592:65–72
Funding
This work was supported by the Youth Science and Innovation Research Fund of Xinjiang Province (No. WJWY-202039).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YZ and MY designed and conducted all the experiments in this study, besides, they wrote the draft. TZ was responsible for data collection and analysis, figures design and language modification. JW financially supported this study, and provide guidance for this work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the co-authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest in this study.
Ethics approval
All the experiment procedures involved in this study were approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumchi, Xinjiang Province, China.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Yusufu, M., Zhang, T. et al. Silencing of miR-23a attenuates hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) induced oxidative damages in ARPE-19 cells by upregulating GLS1: an in vitro study. Cytotechnology 72, 873–884 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-020-00431-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-020-00431-6