Abstract
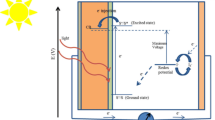
Quasi-solid electrolytes based on silica nanopowder are well known in literature and these electrolytes are able to match in performance with that of liquid electrolytes. However, contrasting results are observed in literature regarding stability of dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) with most of the reported articles projecting silica-loaded quasi-solid electrolyte-based cells as a stable alternative to liquid electrolyte-based cells, while a few others contradicting the same. The present study demonstrates the effect of ageing under heat (60°C) and illumination on the performance of liquid electrolyte and silica-loaded electrolyte-based DSSCs. It has been observed that DSSC based on silica-loaded electrolyte are less stable than DSSC based on liquid electrolyte even though independent study on both electrolytes by thermal analysis shows silica-loaded electrolyte to be more stable than liquid electrolyte. Segregation of silica in electrolyte has been confirmed through cryo-field emission gun-scanning electron microscopy. Zeta potential measurements show that ions are desorbed from the surface of silica on ageing under heat and illumination.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mathew S, Yella A, Gao P, Humphry-Baker R, Curchod Basile F E, Ashari-Astani N et al 2014 Nat. Chem. 6 242
Chiba Y, Islam A, Watanabe Y, Komiya R, Koide N and Han L 2006 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 45 L638
Han L, Islam A, Chen H, Malapaka C, Chiranjeevi B, Zhang S et al 2012 Energy Environ. Sci. 5 6057
Yella A, Lee H W, Tsao H N, Yi C, Chandiran A K, Nazeeruddin M K et al 2011 Science 334 629
Wang P, Zakeeruddin S M, Moser J E, Nazeeruddin M K, Sekiguchi T and Grätzel M 2003 Nat. Mater. 2 402
Wang P, Zakeeruddin S M, Comte P, Exnar I and Grätzel M 2003 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125 1166
Berginc M, Hocevar M, Krasovec U O, Hinsch A, Sastrawan R and Topic M 2008 Thin Solid Films 516 4645
Usui H, Matsui H, Tanabe N and Yanagida S 2004 J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 164 97
Wang P, Zakeeruddin S M and Grätzel M 2004 J. Fluorine Chem. 125 1241
Lee H F, Wu J L, Hsu P Y, Tung Y L, Ouyang F Y and Kai J J 2013 Thin Solid Films 529 2
Han D M, Ko K W, Han C H and Kim Y S 2013 J. Mater. Chem. A 1 8529
Olsen E, Hagen G and Eric Lindquist S 2000 Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 63 267
Syrrokostas G, Siokou A, Leftheriotis G and Yianoulis P 2012 Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 103 119
Ueno K, Inaba A, Kondoh M and Watanabe M 2008 Langmuir 24 5253
Xue G, Guo Y, Yu T, Guan J, Yu X, Zhang J et al 2012 Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 7 1496
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Corning Inc., USA and DST, India (project codes: 10DST030 and 11DST073) for financial support. Industrial Research and Consultancy Centre (IRCC), IIT Bombay, is also acknowledged for providing Cryo-FEG-SEM facility. We also thank Evonik Industries, India, for providing silica nanopowders for the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MOHANTY, S.P., BHARGAVA, P. Characteristics of ionic adsorption on silica nanoparticles and its impact on the long term stability of dye-sensitized solar cells. Bull Mater Sci 43, 290 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-020-02260-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-020-02260-x