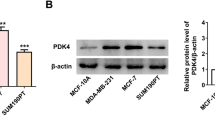
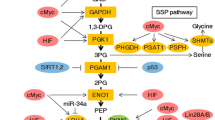
Abstract
The antiapoptotic protein Mcl-1, which is an attractive target for cancer treatment, is degraded under nutrient deprivation conditions in different types of cancer. This process sensitizes cancer cells to chemotherapy. It has been found that nutrient deprivation leads to suppression of Mcl-1 synthesis; however, the mechanisms of Mcl-1 degradation under such conditions remain to be elucidated. In this study, we have investigated the contribution of autophagy and proteasomal degradation to the regulation of the level of Mcl-1 protein under nutrient deprivation conditions. We found that these circumstances cause a decrease in the level of Mcl-1 in cancer cells in a macroautophagy-independent manner via proteasomal degradation.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Atg proteins:
-
proteins encoded by autophagy-related genes
- Bcl-2:
-
B-cell leukemia/lymphoma-2 protein
- ECL:
-
enhanced chemiluminescent substrate
- ERK:
-
extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- FACS:
-
fluorescence activated cell sorting
- FITC:
-
fluorescein isothiocyanate
- GAPDH:
-
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase
- HBSS:
-
Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- Mcl-1:
-
myeloid cell leukemia-1 protein
- mTORC1:
-
mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1
- ND:
-
nutrient deprivation
- PARP:
-
poly (ADP-ribose)-polymerase
- PCD:
-
programmed cell death
- PI:
-
propidium iodide
- PI3K:
-
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- PBS:
-
phosphate buffered saline
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- SD:
-
serum deprivation
- Ub:
-
ubiquitin
- USP9X:
-
ubiquitin-specific peptidase 9, X-linked
References
Jin, Z., and El-Deiry, W. S. (2005) Overview of cell death signaling pathways, Cancer Biol. Ther., 4, 139-163, doi: https://doi.org/10.4161/cbt.4.2.1508.
Hanahan, D., and Weinberg, R. A. (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation, Cell, 144, 646-674, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013.
Rogers, S., Wells, R., and Rechsteiner, M. (1986) Amino acid sequences common to rapidly degraded proteins: the PEST hypothesis, Science, 234, 364-368, doi: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.2876518.
Kale, J., Osterlund, E. J., and Andrews, D. W. (2018) BCL-2 family proteins: changing partners in the dance towards death, Cell Death Differ., 25, 65-80, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2017.186.
Senichkin, V. V., Streletskaia, A. Y., Zhivotovsky, B., and Kopeina, G. S. (2019) Molecular comprehension of Mcl-1: from gene structure to cancer therapy, Trends Cell Biol., 29, 549-562, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2019.03.004.
Senichkin, V. V., Streletskaia, A. Y., Gorbunova, A. S., Zhivotovsky, B., and Kopeina, G. S. (2020) Saga of Mcl-1: regulation from transcription to degradation, Cell Death Differ., 27, 405-419, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-019-0486-3.
Pervushin, N. V., Senichkin, V. V., Zhivotovsky, B., and Kopeina, G. S. (2020) Mcl-1 as a “barrier” in cancer treatment: can we target it now? Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol., 351, 23-55, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.ircmb.2020.01.002.
Senichkin, V. V., Kopeina, G. S., Prokhorova, E. A., Zamaraev, A. V., Lavrik, I. N., and Zhivotovsky, B. (2018) Modulation of Mcl-1 transcription by serum deprivation sensitizes cancer cells to cisplatin, Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj., 1862, 557-566, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.11.021.
Meynet, O., Zunino, B., Happo, L., Pradelli, L. A., Chiche, J., et al. (2013) Caloric restriction modulates Mcl-1 expression and sensitizes lymphomas to BH3 mimetic in mice, Blood, 122, 2402-2411, doi: https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-01-478651.
Bhat, M., Yanagiya, A., Graber, T., Razumilava, N., Bronk, S., et al. (2017) Metformin requires 4E-BPs to induce apoptosis and repress translation of Mcl-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells, Oncotarget, 8, 50542-50556, doi: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.10671.
Mizushima, N. (2007) Autophagy: process and function, Genes Dev., 21, 2861-2873, doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1599207.
Mijaljica, D., Prescott, M., and Devenish, R. J. (2011) Microautophagy in mammalian cells: revisiting a 40-year-old conundrum, Autophagy, 7, 673-682, doi: https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.7.7.14733.
Klionsky, D. J., Baehrecke, E. H., Brumell, J. H., Chu, C. T., Codogno, P., et al. (2011) A comprehensive glossary of autophagy-related molecules and processes (2nd Edn.), Autophagy, 7, 1273-1294, doi: https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.7.11.17661.
Cuervo, A. M., and Wong, E. (2014) Chaperone-mediated autophagy: roles in disease and aging, Cell Res., 24, 92-104, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2013.153.
Levin, V. A., Panchabhai, S. C., Shen, L., Kornblau, S. M., Qiu, Y., and Baggerly, K. A. (2010) Different changes in protein and phosphoprotein levels result from serum starvation of high-grade glioma and adenocarcinoma cell lines, J. Proteome Res., 9, 179-191, doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/pr900392b.
Pirkmajer, S., and Chibalin, A. V. (2011) Serum starvation: caveat emptor, Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol., 301, 272-279, doi: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00091.2011.
Green, D. R., Galluzzi, L., and Kroemer, G. (2014) Cell biology. Metabolic control of cell death, Science, 345, 1250256, doi: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1250256.
Mejlvang, J., Olsvik, H., Svenning, S., Bruun, J. A., Abudu, Y. P., et al. (2018) Starvation induces rapid degradation of selective autophagy receptors by endosomal microautophagy, J. Cell Biol., 217, 3640-3655, doi: https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201711002.
Maiuri, M. C., Le Toumelin, G., Criollo, A., Rain, J. C., Gautier, F., et al. (2007) Functional and physical interaction between Bcl-XL and a BH3-like domain in Beclin-1, EMBO J., 26, 2527-2539, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601689.
Elgendy, M., Ciro, M., Abdel-Aziz, A. K., Belmonte, G., Zuffo, R. D., et al. (2014) Beclin 1 restrains tumorigenesis through Mcl-1 destabilization in an autophagy-independent reciprocal manner, Nat. Commun., 5, 5637, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6637.
Maiuri, M. C., Criollo, A., Tasdemir, E., Vicencio, J. M., Tajeddine, N., Hickman, J. A., Geneste, O., and Kroemer, G. (2007) BH3-only proteins and BH3 mimetics induce autophagy by competitively disrupting the interaction between Beclin 1 and Bcl-2/Bcl-X(L), Autophagy, 3, 374-376, doi: https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.4237.
Zhao, Y., Yang, J., Liao, W., Liu, X., Zhang, H., Wang, S., Wang, D., Feng, J., Yu, L., and Zhu, W. G. (2010) Cytosolic FoxO1 is essential for the induction of autophagy and tumour suppressor activity, Nat. Cell Biol., 12, 665-675, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2069.
Steiger-Barraissoul, S., and Rami, A. (2009) Serum deprivation induced autophagy and predominantly an AIF-dependent apoptosis in hippocampal HT22 neurons, Apoptosis, 14, 1274-1288, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-009-0396-9.
Mizushima, N., and Yoshimori, T. (2007) How to interpret LC3 immunoblotting, Autophagy, 3, 542-545, doi: https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.4600.
Tanida, I., Ueno, T., and Kominami, E. (2008) LC3 and autophagy, Methods Mol. Biol., 445, 77-88, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-157-4_4.
Kaminskyy, V. O., Piskunova, T., Zborovskaya, I. B., Tchevkina, E. M., and Zhivotovsky, B. (2012) Suppression of basal autophagy reduces lung cancer cell proliferation and enhances caspase-dependent and -independent apoptosis by stimulating ROS formation, Autophagy, 8, 1032-1044, doi: https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.20123.
Lazebnik, Y. A., Kaufmann, S. H., Desnoyers, S., Poirier, G. G., and Earnshaw, W. C. (1994) Cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase by a proteinase with properties like ICE, Nature, 371, 346-347, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/371346a0.
Sui, X., Chen, R., Wang, Z., Huang, Z., Kong, N., et al. (2013) Autophagy and chemotherapy resistance: a promising therapeutic target for cancer treatment, Cell Death Dis., 4, e838, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2013.350.
Mercer, C. A., Kaliappan, A., and Dennis, P. B. (2009) A novel, human Atg13 binding protein, Atg101, interacts with ULK1 and is essential for macroautophagy, Autophagy, 5, 649-662, doi: https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.5.5.8249.
Kaminskyy, V., Abdi, A., and Zhivotovsky, B. (2011) A quantitative assay for the monitoring of autophagosome accumulation in different phases of the cell cycle, Autophagy, 7, 83-90, doi: https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.7.1.13893.
Allavena, G., Cuomo, F., Baumgartner, G., Bele, T., Sellgren, A., et al. (2018) Suppressed translation as a mechanism of initiation of CASP8 (caspase 8)-dependent apoptosis in autophagy-deficient NSCLC cells under nutrient limitation, Autophagy, 14, 252-268, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2017.1405192.
Hoeller, D., and Dikic, I. (2016) How the proteasome is degraded, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 113, 13266-13268, doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1616535113.
Pal, D., and Basu, A. (2017) Protein kinase C-eta regulates Mcl-1 level via ERK1, Cell. Signal., 40, 166-171, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2017.09.012.
Marshall, R. S., and Vierstra, R. D. (2018) To save or degrade: balancing proteasome homeostasis to maximize cell survival, Autophagy, 14, 2029-2031, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2018.1515531.
Ryu, Y. K., Hall, C. P., Patrick Reynolds, C., and Kang, M. H. (2014) Caspase-dependent Mcl-1 cleavage and effect of Mcl-1 phosphorylation in ABT-737-induced apoptosis in human acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines, Exp. Biol. Med., 239, 1390-1402, doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/1535370214538745.
Herrant, M., Jacquel, A., Marchetti, S., Belhacene, N., Colosetti, P., Luciano, F., and Auberger, P. (2004) Cleavage of Mcl-1 by caspases impaired its ability to counteract Bim-induced apoptosis, Oncogene, 23, 7863-7873, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208069.
Kopeina, G. S., Senichkin, V. V., and Zhivotovsky, B. (2017) Caloric restriction – a promising anti-cancer approach: from molecular mechanisms to clinical trials, Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer, 1867, 29-41, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2016.11.002.
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (project no. 19-15-00125). The work in the authors’ laboratories is also supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (projects nos. 18-29-09005, 20-015-00500), and by the Swedish (project no. 190345) and Stockholm (project no. 181301) Cancer Societies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflict of interest in financial or any other sphere. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pervushin, N.V., Senichkin, V.V., Kapusta, A.A. et al. Nutrient Deprivation Promotes MCL-1 Degradation in an Autophagy-Independent Manner. Biochemistry Moscow 85, 1235–1244 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297920100119
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297920100119