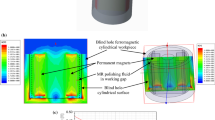
Abstract
The cylindrical mold is an essential part used in industries for the manufacturing of various cylindrical products such as beverages canes, domestics appliances, glass beakers, and polyvinyl chloride pipes. These products require features in its surfaces such as defect-free surfaces with high-quality, stable dimensions, the high extent of cylindricity, and functional transparency in glass material products. To acquire such features in the cylindrical products, the rotary magnetorheological honing (R-MRH) process is developed. In this work, the response surface methodology technique is employed for optimizing the process parameters for internal surface finishing of the cast-iron (CI) cylindrical workpieces. With the optimized process parameters, the experiments are performed to find out the effectiveness of the present finishing process for CI cylindrical molds. On the final MR-finished surface after 40 min of finishing, the roughness parameters (Ra, Rz, and Rq) get reduced to 0.05 µm, 0.4 µm, and 0.07 µm from the respective initial values of 0.420 µm, 2.4 µm, and 0.52 µm. The waviness parameters (Wa, Wz, and Wq) achieved on the final finished surface are 0.04 µm, 0.20 µm, and 0.06 µm from the initial values of 0.17 µm, 0.90 µm, and 0.22 µm, respectively. Also, the circularity (C) on the MR-finished cylindrical surface is improved to 0.0437 from the initial circularity value of 0.1207. The significant changes in Ra, Wa, and C values as well as visuals of scanning electron microscopy images reveal a better sense of functionality improvement of the cast-iron cylindrical molds.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Razak, A.A.A.; Hameed, A.M.; Sultan, S.R.: Modeling of the cure of epoxy based composite, heated at constant temperature in cylindrical mould. Diy. J. Eng. Sci. 4, 1–11 (2011)
Kryvyi, P.; Dzyura, V.; Maruschak, P.; et al.: Influence of curvature and cross-sectional shape of cylindrical surface formed by turning on its roughness. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 45, 5615–5622 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04512-8
Maan, S.; Singh, G.; Singh, A.K.: Nano-surface-finishing of permanent mold punch using magnetorheological fluid-based finishing processes. Mater. Manuf. Process. 32, 1004–1010 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2016.1232823
Pawar, P.; Ballav, R.; Kumar, A.: A review on machining process of glass materials. IEEE Conference on Emerging Trends in Engineering, Business and Disaster Management” [ICBDM 2015]: Noorul Islam University, Kumaracoil, Tamilnadu, India, Print ISSN: 0976-2558:5(1) Online ISSN:2455-6432. Int. J. Eng. F Technol. (2015)
Acker, R.; Martin, S.; Meltke, K.; et al.: Casting of Fe–CrMnNi and ZrO2-based metal–matrix composites and their wear properties. Steel Res. Int. 87, 1111–1117 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.201500471
Singh, M.; Singh, A.K.: Magnetorheological finishing of micro-punches for enhanced performance of micro-extrusion process. Mater. Manuf. Process. 34, 1646–1657 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2019.1689262
Murthy, I.N.; Rao, J.B.: Molding and casting behavior of ferro chrome slag as a mold material in ferrous and non-ferrous foundry industries. Mater. Manuf. Process. 32, 507–516 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2016.1257796
Mishra, V.; Goel, H.; Mulik, R.S.; et al.: Determining work–brush interface temperature in magnetic abrasive finishing process. J. Manuf. Process. 16, 248–256 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2013.10.004
Darvell, B.W.: Chapter 18—Casting. Materials Science for Dentistry, 10 edn, pp. 484–498 (2018). ISBN 9780081010358. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-08-101035-8.50018-3
Grover, V.; Singh, A.K.: A novel magnetorheological honing process for nano-finishing of variable cylindrical internal surfaces. Mater Manufac Process. 32, 573–580 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2016.1257801
Paswan, S.K.; Singh, A.K.: Theoretical and experimental investigations on nano-finishing of internal cylindrical surfaces with a newly developed rotary magnetorheological honing (R-MRH) process. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 234, 363–383 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1177/0954406219875773
Sirwal, S.A.; Singh, A.K.; Paswan, S.K.: Experimental analysis of magnetorheological finishing of blind hole surfaces using permanent magnet designed tools. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 42, 140 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-020-2225-6
Kataria, M.; Mangal, S.K.: Development of continuous flow magnetorheological fluid finishing process for finishing of small holes. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 41, 551 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-019-2027-x
Mangal, S.K.; Sharma, V.: Multi-parameter optimization of magnetorheological fluid with high on-state yield stress and viscosity. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 39, 4191–4206 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-017-0889-3
Paswan, S.K.; Singh, A.K.: Analysis of surface finishing mechanism in a newly developed rotary magnetorheological honing process for its productivity improvement. Wear 426–427, 68–82 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2019.01.001
Sankar, M.R.; Jain, V.K.; Ramkumar, J.: Rotational abrasive flow finishing (R-AFF) process and its effects on finished surface topography. Int. J. Mach. Tool Manuf. 50, 637–650 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2010.03.007
Gumienny, G.; Giętka, T.: Continuous cooling transformation (CCT) diagrams of carbidic nodular cast-iron. Arch. Metall. Mater. 60, 705–710 (2015)
Das, M.; Jain, V.K.; Ghoshdastidar, P.S.: Nanofinishing of flat workpieces using rotary-magnetorheological abrasive flow finishing (R-MRAFF) process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 62, 405–420 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-011-3808-2
Grover, V.; Singh, A.K.: Analysis of particles in magnetorheological polishing fluid for finishing of ferromagnetic cylindrical workpiece. Part. Sci. Technol. 36, 799–807 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/02726351.2017.1302535
Hazir, E.; Ozcan, T.: Response surface methodology integrated with desirability function and genetic algorithm approach for the optimization of CNC machining parameters. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 44, 2795–2809 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3559-6
Bedi, T.S.; Singh, A.K.: Magnetorheological finishing of ferromagnetic blind-hole type surfaces. Mater. Manuf. Process. 33, 1169–1176 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2017.1328120
Das, M.; Jain, V.K.; Ghoshdastidar, P.S.: Nano-finishing of stainless-steel tubes using rotary magnetorheological abrasive flow finishing process. Mach. Sci. Technol. 14, 365–389 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1080/10910344.2010.511865
Martorelli, M.; Gerbino, S.; Lanzotti, A.; et al.: Flatness, circularity and cylindricity errors in 3D printed models associated to size and position on the working plane. In: Eynard, B., Nigrelli, V., Oliveri, S., Peris-Fajarnes, G., Rizzuti, S. (eds.) Advances on Mechanics, Design Engineering and Manufacturing. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-45781-9_21
Singaravel, B.; Marulaswami, C.; Selvaraj, T.: Analysis of the effect of process parameters for circularity and cylindricity errors in turning process. Appl. Mech. Mater. 852, 255–259 (2016). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.852.255
Wu, C.; Li, B.; Yang, J.; et al.: Prediction of grinding force for brittle materials considering co-existing of ductility and brittleness. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 87, 1967–1975 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8594-4
Acknowledgements
The authors with gratitude recognize the financial support provided by the Science and Engineering Research Board, Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi, India (Project No. EMR/2015/000330).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paswan, S.K., Singh, A.K. Investigation of Optimized Parameters for Magnetorheological Finishing the Internal Surface of the Cast-Iron Cylindrical Molds. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 2147–2164 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05018-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05018-z