Abstract
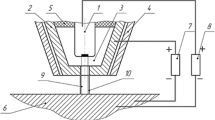
An efficient low-temperature plasma generator with direct arc for plasma remelting was developed and studied with direct and reverse polarity. It has an expanding nozzle channel and the remelted metal acts as a second electrode. An efficiency of ≈90% and a long service life with a current strength of up to 200 A were obtained. It is shown that the nozzle increases arc stability at an opening angle of 12°. It is established that a super-equilibrium nitrogen content (up to 0.22%) in the molten metal can be obtained.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Krasnov, A.N., Sharivker, S.Yu., and Zil’berberg, V.G., Nizkotemperaturnaya plazma v metallurgii (Low-Temperature Plasma in Metallurgy), Moscow: Metallurgiya, 1970.
Lakomskii, V.I., Plazmenno-dugovoi pereplav (Plasma-Arc Remelting), Kiev: Tekhnika, 1974.
Isakaev, E.Kh., Sinel’nikov, V.A., and Filippov, G.A., Chern. Metall., Byull. Nauchno-Tekh. Ekon. Inf., 2005, no. 7, p. 59.
Paisov, I.V., Termicheskaya obrabotka stali i chuguna. Uchebnoe posobie (Heat Treatment of Steel and Cast Iron: A Textbook), Moscow: Metallurgiya, 1970.
Averin, V.V., Revyakin, A.V., Fedorchenko, V.I., et al., Azot v metallakh (Nitrogen in Metals), Moscow: Metallurgiya, 1976.
Morozov, A.N., Vodorod i azot v stali (Hydrogen and Nitrogen in Steel), Moscow: Metallurgiya, 1968.
Shlyamnev, A.P., Uglov, V.A., Filippov, G.A., et al., Chern. Metall., Byull. Nauchno-Tekh. Ekon. Inf., 2013, no. 2, p. 12.
Shpaidel’, M.O., Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., 2005, no. 11, p. 9.
Muradyan, S.O., Cand. Sci. (Eng.) Dissertation, Moscow: Inst. Math. Model., Russ. Acad. Sci., 2016.
Hänninen, H.E., Application and performance of high nitrogen steels, in Proc. Int. Conf. on High Nitrogen Steels, HNS’2004, Ostend, 2004, p. 371.
Stein, G. and Diehl, V., High nitrogen alloyed steels on the move-fields of application, in Proc. Int. Conf. on High Nitrogen Steels, HNS’2004, Ostend, 2004, p. 421.
Kostina, M.V., Bannykh, O.A., and Blinov, V.M., Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., 2000, no. 12, p. 3.
Slovetskii, D.I., Modelirovanie i metody rascheta fiziko-khimicheskikh protsessov v nizkotemperaturnoi plazme (Simulation and Calculation of Physicochemical Processes in Low-Temperature Plasma), Moscow: Nauka, 1974.
Rykalin, N.N., Uglov, A.A., and Anishchenko, L.M., Vysokotemperaturnye tekhnologicheskie protsessy. Teplofizicheskie osnovy (High-Temperature Processes: Thermophysical Basics), Moscow: Nauka, 1986.
Houdremont, E., Handbuch der Sonderstahlkunde, Berlin: Springer, 1956.
Gol’dshtein, M.I., Grachev, C.B., and Veksler, Yu.G., Spetsial’nye stali (Special Steels), Moscow: Mosk. Inst. Stali Splavov, 1999, 2nd ed.
Rashev, Ts., High Nitrogen Steels, Metallurgy under High Pressure, Sofia: Bulgar. Acad. Sci., 1995.
Holzgruber, W., New ESR technology for new and improved products, in Proc. 7th Int. Conf. on Vacuum Metallurgy, Tokyo, 1982, vol. 2, p. 1452.
Farnasov, G.A., Fridman, A.G., and Karinskii, V.N., Plazmennaya plavka (Plasma Melting), Moscow: Metallurgiya, 1968.
Il’ichev, M.V., Tyuftyaev, A.S., Livanova, O.V., and Filippov, G.A., Metallurgist, 2008, vol. 52, p. 561.
Tyuftyaev, A.S., Gadzhiev, M.Kh., Il’ichev, M.V., Khromov, M.A., and Filippov, G.A., Metallurgist, 2019, vol. 63, p. 156.
Koroteev, A.S., Mironov, V.M., and Svirchuk, Yu.S., Plazmotrony: konstruktsii, kharakteristiki, raschet (Plasmatrons: Designs, Characteristics, Calculation), Moscow: Mashinostroenie, 1993.
Glebov, I.A. and Rutberg, F.G., Moshchnye generatory plazmy (Powerful Plasma Generators), Moscow: Energoatomizdat, 1985.
Zhukov, M.F., Eksperimental’nye issledovaniya plazmotronov (Experimental Studies of Plasmatrons), Novosibirsk: Nauka, 1977.
Zhukov, M.F., Zasypkin, I.M., Timoshevskii, A.N., et al., Elektrodugovye generatory termicheskoi plazmy (Thermal Plasma Arc Generators), Novosibirsk: Nauka, 1999.
Asinovskii, E.I., Kirillin, A.V., and Nizovskii, V.L., Stabilizirovannye elektricheskie dugi i ikh primenenie v teplofizicheskom eksperimente (Stabilized Electric Arcs and Their Application in a Thermophysical Experiment), Moscow: Fizmatlit, 2008, 2nd ed.
Klimenko, G.K. and Lyapin, A.A., Konstruktsii elektrodugovykh plazmotronov (Designs of Electric Arc Plasmatrons), Moscow: Mosk. Gos. Tekh. Univ. im. N.E. Baumana, 2011.
Cherednichenko, V.S., An’shakov, A.S., and Kuz’min, M.G., Plazmennye elektrotekhnologicheskie ustanovki (Plasma Electrotechnological Installations), Novosibirsk: Novosibirsk. Gos. Tekh. Univ., 2008.
Shapovalov, V.A. and Latash, Yu.V., Probl. Spets. Elektrometall., 1999, no. 4, p. 50.
Shapovalov, V.A., Tsykulenko, K.A., Sheiko, I.V., and Kolesnichenko, V.I., Sovrem. Elektrometall., 2010, no. 4, p. 20.
Rutberg, F.G., Kuznetsov, V.A., Serba, E.O., Nakonechnyi, G.V., Nikonov, A.V., Popov, S.D., and Surov A.V., High Temp., 2013, vol. 51, no. 5, p. 608.
Gadzhiev, M.Kh., Isakaev, E.Kh., Tyuftyaev, A.S., and Yusupov, D.I., Tech. Phys. Lett., 2016, vol. 42, no. 1, p. 79.
Dautov, G.Yu., Kashapov, N.F., Dautov, I.G., and Sofronitskiy, A.O., J. Phys.: Conf. Ser., 2018, vol. 1058, 012035.
Gadzhiev, M.Kh., Kulikov, Yu.M., Son, E.E., Tyuftyaev, A.S., Sargsyan, M.A., and Yusupov, D.I., High Temp., 2020, vol. 58, no. 1, p. 12.
Isakaev, E.Kh., Sinkevich, O.A., Tyuftyaev, A.S., and Chinnov, V.F., High Temp., 2010, vol. 48, no. 1, p. 97.
Isakaev, E.Kh., Tyuftyaev, A.S., and Gadzhiev, M.Kh., Inorg. Chem.: Appl. Res., 2017, vol. 8, p. 396.
Ochkin, V.N., Spektroskopiya nizkotemperaturnoi plazmy (Low-Temperature Plasma Spectroscopy), Moscow: Fizmatlit, 2006.
Biberman, L.M., Vorob’ev, V.S., and Yakubov, I.T., Kinetika neravnovesnoi nizkotemperaturnoi plazmy (Kinetics of Nonequilibrium Low-Temperature Plasma), Moscow: Nauka, 1982.
Sargsyan, M.A., Tereshonok, D.V., Valyano, G.E., Scherbakov, V.V., Konovalov, P.A., and Gadzhiev, M.Kh., Phys. Plasmas, 2020, vol. 27, 023506.
Chinnov, V.F., Izluchatel’nye svoistva i spektroskopiya nizkotemperaturnoi plazmy (Emissive Properties and Spectroscopy of Low-Temperature Plasma), Moscow: Mosk. Energ. Inst., 2012.
Plasma Diagnostics, Lochte-Holtgreven, W., Ed., Amsterdam: North Holland, 1968.
Funding
The study was supported in part by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, project nos. 19-08-0100a, 20-08-00224a.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gadzhiev, M.K., Ilyichev, M.V., Tyuftyaev, A.S. et al. Low-Temperature Plasma Generator with Direct Arc for Plasma Remelting. High Temp 58, 539–544 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0018151X20040033
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0018151X20040033