Abstract
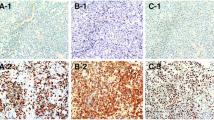
Patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) have a prognosis poorer than that of systemic lymphoma patients. In patients with this condition, TLR4/STAT3 pathway alterations and the MYD88 L265P mutation may be viable targets for therapeutic intervention. The present study was, therefore, designed to identify clinicopathologic correlates of MYD88 mutations and TLR4/STAT3 pathway alterations in PCNSL. We detected TLR4 and p-STAT3 in 41.5% (22/53) and 43.4% (23/53) of PCNSL patients, respectively, while 60.4% of these patients (32/53) were found to harbor the MYD88 L265P mutation. TLR4 expression was found to be significantly associated with the presence of multiple brain lesions, while p-STAT3 expression was significantly linked to advanced age, the presence of multiple brain lesions, non-GCB histological findings, and non-CR status. The presence of the MYD88 L265P mutation was significantly linked to advanced age, the presence of multiple brain lesions, and DLBCL molecular subtype. Multivariate analyses additionally confirmed that elevated TLR4 and p-STAT3 expression levels are associated with a poorer PCNSL patient prognosis. Based on these findings, we hypothesize that signaling through the TLR4/MYD88/STAT3 pathway plays a key role in the pathogenesis of PCNSL.



Similar content being viewed by others
Code availability
Not applicable (software application or custom code).
References
Deckert M, Engert A, Bruck W et al (2011) Modern concepts in the biology, diagnosis, differential diagnosis and treatment of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Leukemia 25(12):1797–1807
Lupi LA, Cucielo MS, Silveira HS et al (2020) The role of Toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway in ovarian, cervical, and endometrial cancers. Life Sci 247:117435
Vijay K (2018) Toll-like receptors in immunity and inflammatory diseases: past, present, and future. Int Immunopharmacol 59:391–412
Akhter A, Masir N, Elyamany G et al (2015) Differential expression of Toll-like receptor (TLR) and B cell receptor (BCR) signaling molecules in primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the central nervous system. J Neurooncol 121(2):289–296
Chapuy B, Roemer MG, Stewart C et al (2016) Targetable genetic features of primary testicular and primary central nervous system lymphomas. Blood 127(7):869–881
Zhu F, Wang KB, Rui L (2019) STAT3 activation and oncogenesis in lymphoma. Cancers (Basel) 12(1):19
Ruggieri S, Tamma R, Resta N et al (2017) Stat3-positive tumor cells contribute to vessels neoformation in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Oncotarget 8(19):31254–31269
Komohara Y, Horlad H, Ohnishi K et al (2011) M2 macrophage/microglial cells induce activation of STAT3 in primary central nervous system lymphoma. J Clin Exp Hematop 51(2):93–99
Yang X, Wang Y, Sun X et al (2020) STAT3 activation is associated with interleukin-10 expression and survival in primary central nervous system lymphoma. World Neurosurg 134:e1077–e1084
Vajpayee N, Hussain J, Tolocica I et al (2010) Expression of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) in primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a retrospective analysis of 17 cases. J Neurooncol 100(2):249–253
Fu XQ, Liu B, Wang YP et al (2020) Activation of STAT3 is a key event in TLR4 signaling-mediated melanoma progression. Cell Death Dis 11(4):246
Hans CP, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC et al (2004) Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood 103(4):275–282
Luciano J, Costa Andrew L, Feldman Ivana N et al (2007) Germinal center B (GCB) and non-GCB cell-like diffuse large B cell lymphomas have similar outcomes following autologous haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. BJM 142(6):404–142
Sethi TK, Kovach AE, Grover NS et al (2019) Clinicopathologic correlates of MYD88 L265P mutation and programmed cell death (PD-1) pathway in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 60(12):2880–2889
Wang EL, Qian ZR, Nakasono M et al (2010) High expression of Toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation factor 88 signals correlates with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 102(5):908–915
Kim KH, Jo MS, Suh DS et al (2012) Expression and significance of the TLR4/MYD88 signaling pathway in ovarian epithelial cancers. World J Surg Oncol 10:193
Wang X, Li X, Zhang X et al (2015) Toll-like receptor 4-induced inflammatory responses contribute to the tumor-associated macrophages formation and infiltration in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Ann Diagn Pathol 19(4):232–238
Zhao S, Sun M, Meng H et al (2019) TLR4 expression correlated with PD-L1 expression indicates a poor prognosis in patients with peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Cancer Manag Res 11:4743–4756
Adam P, Schmausser B, Gobeler-Kolve M et al (2008) Gastric extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphomas of MALT type exclusively express Toll-like receptor 4 in contrast to other lymphomas infiltrating the stomach. Ann Oncol 19(3):566–569
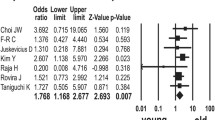
Lee JH, Jeong H, Choi JW et al (2017) Clinicopathologic significance of MYD88 L265P mutation in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a meta-analysis. Sci Rep 7(1):1785
Bruno A, Boisselier B, Labreche K et al (2014) Mutational analysis of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Oncotarget 5(13):5065–5075
Fukumura K, Kawazu M, Kojima S et al (2016) Genomic characterization of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Acta Neuropathol 131(6):865–875
Hattori K, Sakata-Yanagimoto M, Okoshi Y et al (2017) MYD88 (L265P) mutation is associated with an unfavourable outcome of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Br J Haematol 177(3):492–494
Poulain S, Boyle EM, Tricot S et al (2015) Absence of CXCR4 mutations but high incidence of double mutant in CD79A/B and MYD88 in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Br J Haematol 170(2):285–287
Yamawaki Y, Kimura H, Hosoi T et al (2010) MYD88 plays a key role in LPS-induced Stat3 activation in the hypothalamus. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 298(2):R403-410
Liu BS, Stoop JN, Huizinga TW et al (2013) IL-21 enhances the activity of the TLR-MYD88-STAT3 pathway but not the classical TLR-MYD88-NF-kappaB pathway in human B cells to boost antibody production. J Immunol 191(8):4086–4094
Lin S, YuJun L, XiaoMing X et al (2014) Expression and significance of leptin receptor, p-STAT3 and p-AKT in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Acta Histochem 116(1):126–130
Ok CY, Chen J, Xu-Monette ZY et al (2014) Clinical implications of phosphorylated STAT3 expression in De Novo diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 20(19):5113–5123
Kwon HJ, Yang JM, Lee JO et al (2018) Clinicopathologic implication of PD-L1 and phosphorylated STAT3 expression in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. J Transl Med 16(1):320
Wu ZL, Song YQ, Shi YF et al (2011) High nuclear expression of STAT3 is associated with unfavorable prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Hematol Oncol 4(1):31
Treon SP, Xu L, Hunter Z (2015) MYD88 mutations and response to Ibrutinib in Waldenstrom’s Macroglobulinemia. N Engl J Med 373(6):584–586
Wilson WH, Young RM, Schmitz R et al (2015) Targeting B cell receptor signaling with ibrutinib in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Nat Med 21(8):922–926
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Heilongjiang Postdoctoral Financial Assistance, NO. LBH-Z18169, by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, NO. 2019M651306, and by National Natural Science Foundation of China, NO. 81903063
Funding
This study was supported by Heilongjiang Postdoctoral Financial Assistance, NO. LBH-Z18169, by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, NO. 2019M651306, and by National Natural Science Foundation of China, NO. 81903063.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by DT, WS, XW, ZC, and LZ. The first draft of the manuscript was written by DT, WZ, JZ, and QZ. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval
The study was approved by the ethics committee of the Harbin medical university cancer hospital and the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin medical university.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, D., Su, W., Wang, X. et al. Clinicopathologic significance of MYD88 L265P mutation and expression of TLR4 and P-STAT3 in primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Brain Tumor Pathol 38, 50–58 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10014-020-00386-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10014-020-00386-8