Abstract
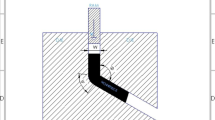
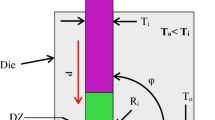
Fine-grained metals and alloys with a homogeneous microstructure can be produced in bulk quantities using the equal channel angular pressing (ECAP) technique. In the ECAP process, improvements in desired properties and grain refinement depend on die geometry, number of passes, strain per pass, plunger speed, friction conditions, processing temperature, etc. In the present study, Al-6063 alloy cylindrical samples are processed by ECAP varying three critical parameters: die channel angle, number of passes, and intermediate processing temperature. Optical microscopy, electron back scattered diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, and transmission electron microscopy techniques are used for observing grain size and refinement, deformation patterns, the formation of precipitates etc. The main consequence of the thermomechanical effect is a reduction in grain size from micro to nano is observed. This transformation makes the material better, which shows outstanding promises on ECAP results. The developed material can be highly applicable in research as well as in the automotive industry.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, C.P.; Li, F.G.; Wang, L.; Qiao, H.J.: Review on modified and novel techniques of severe plastic deformation. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 55, 2377–2390, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-012-4954-y.
Kapoor, R.: Severe plastic deformation of materials. In: Tyagi, A.K., Banerjee, S. (eds.) Materials Under Extreme Conditions (Recent Trends and Future Prospects), Chapter 20, pp. 717–754. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2017)
Kadiyan, S.; Dehiya, B.S.: Evaluating the influence of various routes on micro-structure and mechanical properties of AA-6063 after equal channel angular pressing. Mater. Res. Express 6(8), 0865f9, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab2618.
Fatemi-Varzaneh, S.M.; Zarei-Hanzaki, A.: Accumulative back extrusion (ABE) processing as a novel bulk deformation method. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 504(1–2), 104–106, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2008.10.027.
Huang, J.; Zhu, Y.T.; Alexander, D.J.; Liao, X.; Lowe, T.C.; Asaro, R.J.: Development of repetitive corrugation and straightening. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 371(1–2), 35–39, 2004. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(03)00114-X.
Jahedi, M.; Paydar, M.H.: Study on the feasibility of the torsion extrusion (TE) process as a severe plastic deformation method for consolidation of Al powder. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 527(20), 5273–5279, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2010.04.088.
Segal, V.M.: Materials processing by simple shear. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 197(2), 157–164, 1995. https://doi.org/10.1016/0921-5093(95)09705-8.
Valiev, R.Z.; Langdon, T.G.: Principles of equal-channel angular pressing as a processing tool for grain refinement. Prog. Mater. Sci. 51, 881–981, 2006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2006.02.003.
Ye, R.: Lapovok, The role of back-pressure in equal channel angular extrusion. J. Mater. Sci. 40, 341–346, 2005. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-005-6088-0.
Alah, S.; Tiji, N.; Gholipour, H.; Djavanroodi, F.: Modeling of equal channel forward extrusion force using response surface approach. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. B J. Eng. Manuf. 232(4), 713–719, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954405416654088.
Cabibbo, M.: A TEM Kikuchi pattern study of ECAP AA1200 via routes A, C, BC. Mater. Charact. 61(6), 613–625, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2010.03.007.
Kadiyan, S.; Dehiya, B.: Importance of ECAP die design for producing improved hardness and ultra fine grains of aluminum alloy-6xxx series. i-Manager’s J. Future Eng. Technol. 13(1), 30–35, 2017. https://doi.org/10.26634/jfet.13.1.13760.
Kadiyan, S.; Dehiya, B.S.: Effects of severe plastic deformation by ECAP on the microstructure and mechanical properties of a commercial copper alloy. Mater. Res. Express 6(11), 116570, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab4a44.
Djavanroodi, F.; Ebrahimi, M.; Rajabifar, B.; Akramizadeh, S.: Fatigue design factors for ECAPed materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528(2), 745–750, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2010.09.080.
Lefstad, M.; Pedersen, K.; Dumoulin, S.: Up-scaled equal channel angular pressing of AA6060 and subsequent mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 535, 235–240, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2011.12.073.
Ramesh Kumar, S.; Gudimetla, K.; Mohanlal, S.; Ravisankar, B.: Effect of mechanically alloyed graphene-reinforced aluminium by equal channel angular pressing (ECAP). Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 72(6), 1437–1441, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01715-y.
Ebrahimi, M.; Pashmforoush, F.; Gode, C.: Evaluating influence degree of equal-channel angular pressing parameters based on finite element analysis and response surface methodology. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng., 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-019-1597-y.
Khamei, A.A.; Dehghani, K.: Effects of strain rate and temperature on hot tensile deformation of severe plastic deformed 6061 aluminum alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2014.12.081.
Goyal, A.; Garg, R.K.: Mechanical and microstructural behaviour of Al–Mg4.2 alloy friction stir butt welds. Mater. Res. Express 6(5), 056514, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab00c2.
Dehghani, A.; Bakhshi, S.; Kalayeh, K.: Hot and cold tensile behavior of Al 6061 produced by equal channel angular pressing and subsequent cold rolling. Iran. J. Mater. Form. 2(1), 30–42, 2015. https://doi.org/10.22099/ijmf.2015.2913.
Levitasetal, V.; Roy, A.M.; Preston, D.L.: Multiple twinning and variant-variant transformations in martensite: phase-field approach. Phys. Rev. B 88, 054113, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.88.054113.
Ghangas, G.; Singhal, S.: Modelling and optimization of process parameters for friction stir welding of armor alloy using RSM and GRA-PCA approach. Mater. Res. Express 6(2), 026553, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aaed9b.
Goyal, A.; Garg, R.K.: Establishing mathematical relationships to study tensile behavior of friction stir welded AA5086-H32 aluminium alloy joints. Silicon 11(1), 51–65, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-018-9858-4.
Chari, R.N.; Kami, A.; Dariani, B.M.: Modeling and optimization of equivalent plastic strain in equal-channel angular rolling using response surface methodology. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 229(11), 1963–1975, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954405414542855.
Sabirov, I.; Perez-Prado, M.T.; Murashkin, M.; Molina-Aldareguia, J.M.; Bobruk, E.V.; Yunusova, N.F.; Valiev, R.Z.: Application of equal channel angular pressing with parallel channels for grain refinement in aluminium alloys and its effect on deformation behavior. Int. J. Mater. Form. 3(1), 411–414, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954405414542855.
Mukhopadhyay, P.: Alloy designation, processing, and use of AA6XXX series aluminium alloys. ISRN Metall. Article No. 165082, pp. 1–15 (2012)
Totten, G.E.; Tiryakioglu, M.; Kessler, O.: Encyclopedia of Aluminum and Its Alloys. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2018)
Xu, C.; Száraz, Z.; Trojanová, Z.; Lukac, P.; Langdon, T.G.: Evaluating plastic anisotropy in two aluminum alloys processed by equal-channel angular pressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 497(1–2), 206–211, 2008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2008.06.045.
Lv, X.; Wu, C.S.; Yang, C.; Padhy, G.K.: Weld microstructure and mechanical properties in ultrasonic enhanced friction stir welding of Al alloy to Mg alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 254, 145–157, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.11.031.
Cerri, E.; De Marco, P.P.; Leo, P.: FEM and metallurgical analysis of modified 6082 aluminium alloys processed by multipass ECAP: influence of material properties and different process settings on induced plastic strain. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209(3), 1550–1564, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.04.013.
Li, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, D.: On the selection of outlet channel length and billet length in equal channel angular extrusion. Comput. Mater. Sci. 49(2), 293–298, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2010.05.009.
Salcedo, D.; Luis, C.J.; León, J.; Puertas, I.; Fuertes, J.P.; Luri, R.: Simulation and analysis of isothermal forging of AA6063 obtained from material processed by equal channel angular pressing severe plastic deformation. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 229(5), 727–743, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954405414532628.
Agwa, M.A.; Ali, M.N.; Al-Shorbagy, A.E.: Optimum processing parameters for equal channel angular pressing. Mech. Mater. 100, 1–11, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmat.2016.06.003.
Vinogradov, A.; Estrin, Y.: Analytical and numerical approaches to modelling severe plastic deformation. Prog. Mater. Sci. 95, 172–242, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2018.02.001.
Karon, M.; Kopysc, A.; Adamiak, M.; Konieczny, J.: Microstructure and mechanical properties of the annealed 6060 aluminium alloy processed by ECAP method. Arch. Mater. Sci. Eng. 80(1), 31–36, 2016. https://doi.org/10.5604/18972764.1229616.
Sahai, A.; Raj, K.H.; Gupta, N.K.: Mechanical behaviour and surface profile analysis of Al6061 alloy processed by equal channel angular extrusion. Procedia Eng. 173, 956–963, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2016.12.155.
Ghalehbandi, S.M.; FallahiArezoodar, A.; Hosseini-Toudeshky, H.: Influence of aging on mechanical properties of equal channel angular pressed aluminum alloy 7075. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 231(10), 1803–1811, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954405415612370.
Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Shi, Q.; Qi, H.: Research on grain refinement mechanism of 6061 aluminum alloy processed by combined SPD methods of ECAP and MAC. Materials 11(7), 1246, 2018. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071246.
Myers, R.H.; Montgomery, D.C.; Anderson-Cook, C.M.: Response Surface Methodology: Process and Product Optimization Using Designed Experiments, 4th edn Wiley, New York (2016)
Hill, W.J.; Hunter, W.G.: A review of response surface methodology: a literature survey. Am. Soc. Qual. 8(4), 571–590, 2019. https://doi.org/10.2307/1266632.
Gholinia, A.; Prangnell, P.B.; Markushev, M.V.: Effect of strain path on the development of deformation structures in severely deformed aluminium alloys processed by ECAE. Acta Mater. 48(5), 1115–1130, 2000. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6454(99)00388-2.
Kim, K.J.; Yang, D.Y.; Yoon, J.W.: Investigation of microstructure characteristics of commercially pure aluminum during equal channel angular extrusion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 485(1–2), 621–626, 2008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.08.038.
Cabibbo, M.: Microstructure strengthening mechanisms in different equal channel angular pressed aluminum alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 560, 413–432, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2012.09.086.
Djavanroodi, F.; Ebrahimi, M.: Effect of die parameters and material properties in ECAP with parallel channels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 527(29–30), 7593–7599, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2010.08.022.
Cabibbo, M.; Evangelista, E.; Latini, V.: Thermal stability study on two aluminum alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 9, 5659–5667, 2004. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSC.0000040073.78798.d4.
Morozova, A.; Kaibyshev, R.: Grain refinement and strengthening of a Cu–0.1Cr–0.06Zr alloy subjected to equal channel angular pressing. Philos. Mag. 97(24), 1–24, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786435.2017.1324649.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kadiyan, S., Dehiya, B.S., Garg, R.K. et al. A Statistical Method to Predict the Hardness and Grain Size After Equal Channel Angular Pressing of AA-6063 with Intermediate Annealing. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 2055–2070 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04999-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04999-1