Abstract
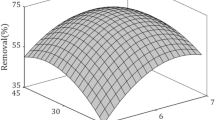
Due to the harmful effects to environment and public health, lead has to be removed from wastewater. The novelty of this study is the investigation of the adsorption of lead by a cross-linked polycarboxylate-based adsorbent synthesized, the characterization of adsorbent with FTIR, SEM–EDS, XRD and the optimization of the effective parameters such as initial lead concentration, pH and temperature by response surface methodology. In here, Box–Behnken experimental design was applied by using ANOVA-supported Design Expert software. It was statistically confirmed that the surface representing the adsorption process conforms to the reduced cubic model. The common effects of the parameters were determined, and the equation was obtained to predict lead removal under the desired conditions. It was understood that both Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms can be used to describe the adsorption data. The negative free energy of adsorption process indicated the spontaneous reaction. The values of enthalpy and entropy were determined as − 12.57 kJ mol−1 and − 0.036 kJ mol−1 K−1, respectively. Maximum lead removal reached to 79.7% at the initial concentration of 480.7 ppm, pH 8 and 25 °C. The selectivity of adsorbent in both lead- and cadmium-containing aqueous solution was also studied. Adsorption was found to be in favor of metal ions with higher initial concentration, and lead was adsorbed more by the effect of electronegativity when the concentration of two ions was equal. Desorption experiments of lead showed that the adsorption process was highly chemical and less physical, and only the physical part of it was desorbed.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
Yes.
References
Basheer, A.A.; Ali, I.: Stereoselective uptake and degradation of (±)-o, p-DDD pesticide stereomers in water-sediment system. Chirality 30, 1088–1095 (2018)
Al-Shaalan, N.H.; Ali, I.; Alothman, Z.A.; Al-Wahaibi, L.H.; Alabdulmonem, H.: High performance removal and simulation studies of diuron pesticide in water on MWCNTs. J. Mol. Liq. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111039
Ali, I.; Alothman, Z.A.; Alwarthan, A.: Supra molecular mechanism of the removal of 17-β-estradiol endocrine disturbing pollutant from water on functionalized iron nano particles. J. Mol. Liq. 241, 123–129 (2017)
Basheer, A.A.: Chemical chiral pollution: impact on the society and science and need of the regulations in the 21st century. Chirality 30, 402–406 (2018)
Basheer, A.A.: New generation nano-adsorbents for the removal of emerging contaminants in water. J. Mol. Liq. 261, 583–593 (2018)
Ali, I.; Jain, C.K.: Groundwater contamination and health hazards by some of the most commonly used pesticides. Curr. Sci. 75(10), 1011–1014 (1998)
Ali, I.; Gupta, V.K.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y.: Metal ion speciation and capillary electrophoresis: application in the new millennium. Electrophoresis 26, 3988–4002 (2005)
Badruddoza, A.Z.M.; Shawon, Z.B.Z.; Tay, W.J.D.; Hidajat, K.; Uddin, M.S.: Fe3O4/cyclodextrin polymer nanocomposites for selective heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater. Carbohydr. Polym. 91(1), 322–332 (2013)
Fu, F.; Wang, Q.: Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: a review. J. Environ. Manag. 92(3), 407–418 (2011)
Erdem, M.; Özverdi, A.: Lead adsorption from aqueous solution onto siderite. Sep. Purif. Technol. 42(3), 259–264 (2005)
Ali, I.; Khan, T.A.; Hussain, I.: Treatment and remediation methods for arsenic removal from the ground water. Int. J. Environ. Eng. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1504/IJEE.2011.037873
An, H.K.; Park, B.Y.; Kim, D.S.: Crab shell for the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution. Water Res. 35(15), 3551–3556 (2001)
Li, Y.H.; Wang, S.; Wei, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, C.; Luan, Z.; Wu, D.; Wei, B.: Water treatment materials based on carbon nanotubes. Chem. Phys. Lett. 357, 263–266 (2002)
Sekar, M.; Sakthi, V.; Rengaraj, S.: Kinetics and equilibrium adsorption study of lead(II) onto activated carbon prepared from coconut shell. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 279(2), 307–313 (2004)
Amer, M.W.; Khalili, F.I.; Awwad, A.M.: Adsorption of lead, zinc and cadmium ions on polyphosphate-modified kaolinite clay. J. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2(1), 1–8 (2010)
Wang, J.; Chen, C.: Biosorption of heavy metals by Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a review. Biotechnol. Adv. 24(5), 427–451 (2006)
Turkyilmaz, H.; Kartal, T.; Yildiz, S.Y.: Optimization of lead adsorption of mordenite by response surface methodology: characterization and modification. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/2052-336X-12-5
Bhat, A.; Megeri, G.B.; Thomas, C.; Bhargava, H.; Jeevitha, C.; Chandrashekar, S.; Madhu, G.M.: Adsorption and optimization studies of lead from aqueous solution using γ-Alumina. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 3(1), 30–39 (2015)
Lugo-Lugo, V.; Hernandez-Lopez, S.; Barrera-Diaz, C.; Urena-Nunez, F.; Bilyeu, B.: A comparative study of natural, formaldehyde-treated and copolymer-grafted orange peel for Pb(II) adsorption under batch and continuous mode. J. Hazard. Mater. 161(2–3), 1255–1264 (2009)
Li, M.; Liu, J.; Han, W.: Recycling and management of waste lead-acid batteries: a mini-review. Waste Manag. Res. 34(4), 298–306 (2016)
Soltani, R.D.C.; Khorramabadi, G.S.; Khataee, A.R.; Jorfi, S.: Silica nanopowders/alginate composite for adsorption of lead (II) ions in aqueous solutions. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 45(3), 973–980 (2014)
Yao, Q.; Xie, J.; Liu, J.; Kang, H.; Liu, Y.: Adsorption of lead ions using a modified lignin hydrogel. J. Polym. Res. 21(465), 1–16 (2014)
Song, M.; Wei, Y.; Yu, L.: The application of prepared porous carbon materials: effect of different components on the heavy metal adsorption. Waste Manag. Res. 34(6), 534–541 (2016)
Ali, I.; Basheer, A.A.; Mbianda, X.Y.; Burakov, A.; Galunin, E.; Burakova, I.; Mkrtchyan, E.; Tkachev, A.; Grachev, V.: Graphene based adsorbents for remediation of noxious pollutants from wastewater. Environ. Int. 127, 160–180 (2019)
Ali, I.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y.: Speciation of metal ions by capillary electrophoresis. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 32(4), 337–350 (2002)
Yan, H.; Dai, J.; Yang, Z.; Yang, H.; Cheng, R.: Enhanced and selective adsorption of copper(II) ions on surface carboxymethylated chitosan hydrogel beads. Chem. Eng. J. 174(2–3), 586–594 (2011)
Saleh, T.A.; Gupta, V.K.; Al-Saadi, A.A.: Adsorption of lead ions from aqueous solution using porous carbon derived from rubber tires: experimental and computational study. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 396, 264–269 (2013)
Ge, H.; Hu, T.; Chen, X.: Selective adsorption of lead on grafted and crosslinked chitosan nanoparticles prepared by using Pb2+ as template. J. Hazard. Mater. 308, 225–232 (2016)
Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E.; Wilson, L.D.; Morin-Crini, N.: Conventional and non-conventional adsorbents for wastewater treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 17, 195–213 (2019)
Mahmud, H.N.M.E.; Huq, A.K.O.; Binti Yahya, R.: The removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater/aqueous solution using polypyrrole-based adsorbents: a review. RSC Adv 6, 14778–14791 (2016)
Ravikumar, K.; Pakshirajan, K.; Swaminathan, T.; Balu, K.: Optimization of batch process parameters using response surface methodology for dye removal by a novel adsorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 105(3), 131–138 (2005)
Sahan, T.; Ozturk, D.: Investigation of Pb(II) adsorption onto pumice samples: application of optimization method based on fractional factorial design and response surface methodology. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 16, 819–831 (2014)
Preetha, B.; Viruthagiri, T.: Application of response surface methodology for the biosorption of copper using Rhizopus arrhizus. J. Hazard. Mater. 143(1–2), 506–510 (2007)
Wang, X.; Yang, G.; Li, F.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G.: Response surface optimization of methane potentials in anaerobic co-digestion of multiple substrates: dairy, chicken manure and wheat straw. Waste Manag. Res. 31(1), 60–66 (2013)
Zhang, B.; Cui, Y.; Yin, G.; Li, X.: Adsorption of copper (II) and lead (II) Ions onto cottonseed protein-PAA hydrogel composite. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 51(6), 612–619 (2012)
Özdemir, E.; Duranoğlu, D.; Beker, Ü.; Avcı, A.Ö.: Process optimization for Cr(VI) adsorption onto activated carbons by experimental design. Chem. Eng. J. 172(1), 207–218 (2011)
Anirudhan, T.S.; Divya, L.; Suchithra, P.S.: Kinetic and equilibrium characterization of uranium(VI) adsorption onto carboxylate-functionalized poly(hydroxyethylmethacrylate)-grafted lignocellulosics. J. Environ. Manag. 90(1), 549–560 (2009)
Amorim, D.J.; Rezende, H.C.; Oliveira, E.L.; Almeida, I.L.S.; Coelho, N.M.M.; Matos, T.N.; Araujo, C.S.T.: Characterization of Pequi (Caryocar brasiliense) shells and evaluation of their potential for the adsorption of PbII ions in aqueous systems. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 27(3), 616–623 (2016)
Ribeiro, R.F.L.; Soares, V.C.; Costa, L.M.; Nascentes, C.C.: Efficient removal of Cd2+ from aqueous solutions using by-product of biodiesel production. J. Hazard. Mater. 237–238, 170–179 (2012)
Meitei, M.D.; Prasad, M.N.V.: Lead (II) and cadmium (II) biosorption on Spirodela polyrhiza (L.) Schleiden biomass. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 1(3), 200–207 (2013)
Liu, Y.; Xu, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, C.; Li, G.; Meng, Y.: Graphene oxides cross-linked with hyperbranched polyethylenimines: preparation, characterization and their potential as recyclable and highly efficient adsorption materials for lead (II) ions. Chem. Eng. J. 285, 698–708 (2016)
Wang, H.; Zhou, A.; Peng, F.; Yu, H.; Yang, J.: Mechanism study on adsorption of acidified multiwalled carbon nanotubes to Pb(II). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 316(2), 277–283 (2007)
Arulkumar, M.; Sathishkumar, P.; Palvannan, T.: Optimization of Orange G dye adsorption by activated carbon of Thespesia populnea pods using response surface methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 186(1), 827–834 (2011)
Ali, I.; Alharbi, O.M.L.; Alothman, Z.A.; Al-Mohaimeed, A.M.; Alwarthan, A.: Modeling of fenuron pesticide adsorption on CNTs for mechanistic insight and removal in water. Environ. Res. 170, 389–397 (2019)
Nodeh, H.R.; Ibrahim, W.A.W.; Ali, I.; Sanagi, M.M.: Development of magnetic graphene oxide adsorbent for the removal and preconcentration of As(III) and As(V) species from environmental water samples. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 23, 9759–9773 (2016)
Ali, I.: Microwave assisted economic synthesis of multi walled carbon nanotubes for arsenic species removal in water: batch and column operations. J. Mol. Liq. 271, 677–685 (2018)
Ali, I.; Alharbi, O.M.L.; Alothman, Z.A.; Alwarthan, A.: Facile and eco-friendly synthesis of functionalized iron nanoparticles for cyanazine removal in water. Colloid Surf. B 171, 606–613 (2018)
Kamga, F.T.: Modeling adsorption mechanism of paraquat onto Ayous (Triplochiton scleroxylon) wood sawdust. Appl. Water Sci. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0879-3
Ali, I.; Alharbi, O.M.L.; Alothman, Z.A.; Badjah, A.Y.: Kinetics, thermodynamics, and modeling of amido black dye photodegradation in water using Co/TiO2 nanoparticles. Photochem. Photobiol. 94, 935–941 (2018)
Ali, I.; Alharbi, O.M.L.; Alothman, Z.A.; Alwarthan, A.; Al-Mohaimeed, A.M.: Preparation of a carboxymethylcellulose-iron composite for uptake of atorvastatin in water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 132, 244–253 (2019)
Ali, I.; Burakov, A.E.; Melezhik, A.V.; Babkin, A.V.; Burakova, I.V.; Neskomornaya, E.A.; Galunin, E.V.; Tkachev, A.G.; Kuznetsov, D.V.: Removal of copper(II) and zinc(II) ions in water on a newly synthesized polyhydroquinone/graphene nanocomposite material: kinetics, thermodynamics and mechanism. Chem. Sel 4, 12708–12718 (2019)
Chaleshtori, A.A.N.; Meghadddam, F.M.; Sadeghi, M.M.; Rahimi, R.R.; Hemati, S.; Ahmadi, A.A.: Removal of acid red 18 (azo-dye) from aqueous solution by adsorption onto activated charcoal prepared from almond shell. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 20, 9–16 (2017)
Das, B.; Mondal, N.K.; Bhaumik, R.; Roy, P.: Insight into adsorption equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics of lead onto alluvial soil. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 11, 1101–1114 (2014)
Senthilkumar, P.; Ramalingam, S.; Sathyaselvabala, V.; Dinesh Kirupha, S.; Sivanesan, S.: Removal of copper(II) ions from aqueous solution by adsorption using cashew nut shell. Desalination 266(1–3), 63–71 (2011)
Rahimi, S.; Moattari, R.M.; Rajabi, L.; Derakhshan, A.A.; Keyhani, M.: Iron oxide/hydroxide (α, γ-FeOOH) nanoparticles as high potential adsorbents for lead removal from polluted aquatic media. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 23, 33–43 (2015)
Agarwal, S.; Tyagi, I.; Gupta, V.K.; Bagheri, A.R.; Ghaedi, M.; Asfaram, A.; Hajati, S.; Bazrafshan, A.A.: Rapid adsorption of ternary dye pollutants onto copper (I) oxide nanoparticle loaded on activated carbon: experimental optimization via response surface methodology. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 4(2), 1769–1779 (2016)
Zulkali, M.M.D.; Ahmad, A.L.; Norulakmal, N.H.: Oryza sativa L. husk as heavy metal adsorbent: optimization with lead as model solution. Bioresour. Technol. 97(1), 21–25 (2006)
Sedighi, M.; Ghasemi, M.; Hassan, S.H.A.; Daud, W.R.W.; Ismail, M.; Abdallah, E.: Process optimization of batch biosorption of lead using Lactobacillius bulgaricus in an aqueous phase system using response surface methodology. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 28, 2047–2055 (2012)
Murugesan, A.; Vidhyadevi, T.; Kalaivani, S.S.; Thiruvengadaravi, K.V.; Ravikumar, L.; Anuradha, C.D.; Sivanesan, S.: Modelling of lead(II) ion adsorption onto poly(thiourea imine) functionalized chelating resin using response surface methodology (RSM). J. Water Process Eng. 3, 132–143 (2014)
Ibrahim, M.N.M.; Ngah, W.S.W.; Norliyana, M.S.; Daud, W.R.W.; Rafatullah, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Hashim, R.: A novel agricultural waste adsorbent for the removal of lead (II) ions from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 182(1–3), 377–385 (2010)
Huang, M.R.; Peng, Q.Y.; Li, X.G.: Rapid and effective adsorption of lead ions on fine poly(phenylenediamine) microparticles. Chem. Eur. J. 12(16), 4341–4350 (2006)
Sonmezay, A.; Oncel, M.S.; Bektas, N.: Adsorption of lead and cadmium ions from aqueous solutions using manganoxide minerals. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(12), 3131–3139 (2012)
Fan, T.; Liu, Y.; Feng, B.; Zeng, G.; Yang, C.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, H.; Tan, Z.; Wang, X.: Biosorption of cadmium(II), zinc(II) and lead(II) by Penicillium simplicissimum: isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. J. Hazard. Mater. 160(2–3), 655–661 (2008)
Sheela, T.; Nayaka, Y.A.: Kinetics and thermodynamics of cadmium and lead ions adsorption on NiO nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 191, 123–131 (2012)
Acknowledgements
This study was conducted at the Department of Chemical Engineering in Suleyman Demirel University. The authors wish to thank to Innovative Technologies Application and Research Center (YETEM) for the analyses of FTIR, SEM and XRD.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific Grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RT (25%); SY (25%); SGE (corresponding author-50%).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taşdemir, R., Yiğitarslan, S. & Erzengin, S.G. Optimization of Lead (II) Adsorption onto Cross-Linked Polycarboxylate-Based Adsorbent by Response Surface Methodology. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 6287–6301 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05029-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05029-w