Abstract
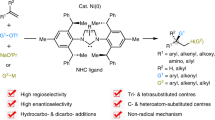
Enantioselective difunctionalization of alkenes constitutes an efficient strategy to assemble complex chiral molecules from simple racemic or achiral starting materials. Here we present an intermolecular nickel-catalysed enantioselective 1,1-arylboration of unactivated terminal alkenes. The high regio- and enantioselectivities of the reactions arise from a judicious choice of the nickel catalyst rather than the incorporation of a directing group. Moreover, excellent regioselectivities can also be obtained from the reactions of allylbenzenes. We also conducted a series of stereospecific downstream transformations for the enantioenriched secondary boronic esters. These examples represent an efficient catalyst-controlled enantioselective 1,1-difunctionalization of unactivated alkenes.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The findings of this study are available within the paper and its Supplementary Information. All data are available from the authors upon reasonable request.
References
DeRosa, T. F. Advances in Synthetic Organic Chemistry and Methods Reported in US Patents 60–61 (Elsevier, 2006).
Beller, M., Seayad, J., Tillack, A. & Jiao, H. Catalytic Markovnikov and anti-Markovnikov functionalization of alkenes and alkynes: recent developments and trends. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 43, 3368–3398 (2004).
Chemler, S. R. The enantioselective intramolecular aminative functionalization of unactivated alkenes, dienes, allenes and alkynes for the synthesis of chiral nitrogen heterocycles. Org. Biomol. Chem. 7, 3009–3019 (2009).
McDonald, R. I., Liu, G. & Stahl, S. S. Palladium (ii)-catalyzed alkene functionalization via nucleopalladation: stereochemical pathways and enantioselective catalytic applications. Chem. Rev. 111, 2981–3019 (2011).
Yin, G., Mu, X. & Liu, G. Palladium (ii)-catalyzed oxidative difunctionalization of alkenes: bond forming at a high-valent palladium center. Acc. Chem. Res. 49, 2413–2423 (2016).
Dhungana, R. K., Kc, S., Basnet, P. & Giri, R. Transition metal-catalyzed dicarbofunctionalization of unactivated olefins. Chem. Rec. 18, 1314–1340 (2018).
Zhang, J.-S., Liu, L., Chen, T. & Han, L.-B. Transition-metal-catalyzed three-component difunctionalizations of alkenes. Chem. Asian J. 13, 2277–2291 (2018).
Sauer, G. S. & Lin, S. An electrocatalytic approach to the radical difunctionalization of alkenes. ACS Catal. 8, 5175–5187 (2018).
Tu, H., Zhu, S., Qing, F. & Chu, L. Recent advances in nickel-catalyzed three-component difunctionalization of unactivated alkenes. Synthesis 52, 1346–1356 (2020).
Coombs, J. R. & Morken, J. P. Catalytic enantioselective functionalization of unactivated terminal alkenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 2636–2649 (2016).
Wang, Z.-X., Bai, X.-Y. & Li, B.-J. Metal-catalyzed substrate-directed enantioselective functionalization of unactivated alkenes. Chin. J. Chem. 37, 1174–1180 (2019).
Li, Z.-L., Fang, G.-C., Gu, Q.-S. & Liu, X.-Y. Recent advances in copper-catalysed radical-involved asymmetric 1,2-difunctionalization of alkenes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 49, 32–48 (2020).
Li, Y., Wu, D., Cheng, H.-G. & Yin, G. Difunctionalization of alkenes involving metal migration. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 7990–8003 (2020).
Vasseur, A., Bruffaerts, J. & Marek, I. Remote functionalization through alkene isomerization. Nat. Chem. 8, 209–219 (2016).
Sommer, H., Julia-Hernandez, F., Martin, R. & Marek, I. Walking metals for remote functionalization. ACS Cent. Sci. 4, 153–165 (2018).
Miry, J., Pozo, C., Toste, F. D. & Fustero, S. Enantioselective palladium-catalyzed oxidative β,β-fluoroarylation of α,β-unsaturated carbonyl derivatives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 9045–9049 (2016).
Yamamoto, E. et al. Development and analysis of a Pd(0)-catalyzed enantioselective 1,1-diarylation of acrylates enabled by chiral anion phase transfer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 15877–15880 (2016).
He, Y., Yang, Z., Thornbury, R. T. & Toste, F. D. Palladium-catalyzed enantioselective 1,1-fluoroarylation of aminoalkenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 12207–12210 (2015).
Maity, S., Potter, T. J. & Ellman, J. A. α-Branched amines by catalytic 1,1-addition of C–H bonds and aminating agents to terminal alkenes. Nat. Catal. 2, 756–762 (2019).
Collins, B. S. L., Wilson, C. M., Myers, E. L. & Aggarwal, V. K. Asymmetric synthesis of secondary and tertiary boronic esters. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 11700–11733 (2017).
Lovinger, G. J. & Morken, J. P. Ni-catalyzed enantioselective conjunctive coupling with C(sp3) electrophiles: a radical–ionic mechanistic dichotomy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 17293–17296 (2017).
Sun, C., Potter, B. & Morken, J. P. A catalytic enantiotopic-group-selective Suzuki reaction for the construction of chiral organoboronates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 6534–6537 (2014).
Wang, Z., Bachman, S., Dudnik, A. S. & Fu, G. C. Nickel-catalyzed enantioconvergent borylation of racemic secondary benzylic electrophiles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 14529–14532 (2018).
Basch, C. H., Cobb, K. M. & Watson, M. P. Nickel-catalyzed borylation of benzylic ammonium salts: stereospecific synthesis of enantioenriched benzylic boronates. Org. Lett. 18, 136–139 (2016).
Pound, S. M. & Watson, M. P. Asymmetric synthesis via stereospecific C–N and C–O bond activation of alkyl amine and alcohol derivatives. Chem. Commun. 54, 12286–12301 (2018).
Noh, D., Chea, H., Ju, J. & Yun, J. Highly regio- and enantioselective copper-catalyzed hydroboration of styrenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 48, 6062–6064 (2009).
Chen, X., Cheng, Z., Guo, J. & Lu, Z. Asymmetric remote C–H borylation of internal alkenes via alkene isomerization. Nat. Commun. 9, 3939 (2018).
Pang, Y. et al. Rhodium-catalyzed B−H bond insertion reactions of unstabilized diazo compounds generated in situ from tosylhydrazones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 10663–10668 (2018).
Nelson, H. M., Williams, B. D., Miro, J. & Toste, F. D. Enantioselective 1,1-arylborylation of alkenes: merging chiral anion phase transfer with Pd catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 3213–3216 (2015).
Bergmann, A. M., Dorn, S. K., Smith, K. B., Logan, K. M. & Brown, M. K. Catalyst-controlled 1,2-and 1,1-arylboration of α-alkyl alkenyl arenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 1719–1723 (2019).
Suginome, M. Catalytic carboborations. Chem. Rec. 10, 348–358 (2010).
Jin, S. & Larionov, O. V. A radical new look for alkene carboboration. Chem 4, 1194–1207 (2018).
Liu, Z., Gao, Y., Zeng, T. & Engle, K. M. Transition-metal-catalyzed 1,2-carboboration of alkenes: strategies, mechanisms, and stereocontrol. Isr. J. Chem. 60, 219–229 (2020).
Perry, G. J. P., Jia, T. & Procter, D. J. Copper-catalyzed functionalization of 1,3-dienes: hydrofunctionalization, borofunctionalization, and difunctionalization. ACS Catal. 10, 1485–1499 (2020).
Logan, K. M., Sardini, S. R., White, S. D. & Brown, M. K. Nickel-catalyzed stereoselective arylboration of unactivated alkenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 159–162 (2018).
Logan, K. M., Smith, K. B. & Brown, M. K. Copper/palladium synergistic catalysis for the syn- and anti-selective carboboration of alkenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54, 5228–5231 (2015).
Chen, L.-A., Lear, A. R., Gao, P. & Brown, M. K. Nickel-catalyzed arylboration of alkenylarenes: synthesis of boron substituted quaternary carbons and regiodivergent reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 10956–10960 (2019).
Joung, S., Bergmann, A. M. & Brown, M. K. Ni-catalyzed 1,2-benzylboration of 1,2-disubstituted unactivated alkenes. Chem. Sci. 10, 10944–10947 (2019).
Wang, W. et al. Migratory arylboration of unactivated alkenes enabled by nickel catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 4612–4616 (2019).
Wang, W., Ding, C., Pang, H. & Yin, G. Nickel-catalyzed 1,2-arylboration of vinylarenes. Org. Lett. 21, 3968–3971 (2019).
Li, Y. et al. Nickel-catalyzed 1,1-alkylboration of electronically unbiased terminal alkenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 8872–8876 (2019).
Guo, J., Cheng, B., Shen, X. & Lu, Z. Cobalt-catalyzed asymmetric sequential hydroboration/hydrogenation of internal alkynes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 15316–15319 (2017).
Sardini, S. R. et al. Ni-catalyzed arylboration of unactivated alkenes: scope and mechanistic studies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 9391–9400 (2019).
Anthony, D., Lin, Q., Baudet, J. & Diao, T. Nickel-catalyzed asymmetric reductive diarylation of vinylarenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 3198–3202 (2019).
Gutierrez, O. et al. Nickel-catalyzed cross-coupling of photoredox-generated radicals: uncovering a general manifold for stereoconvergence in nickel-catalyzed cross-couplings. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 4896–4899 (2015).
Leonori, D. & Aggarwal, V. K. Stereospecific couplings of secondary and tertiary boronic esters. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54, 1082–1096 (2015).
Wu, W. et al. Iridium catalysts with f-amphox ligands: asymmetric hydrogenation of simple ketones. Org. Lett. 18, 2938–2941 (2016).
Matteson, D. S. α-Halo boronic esters: intermediates for stereodirected synthesis. Chem. Rev. 89, 1535–1551 (1989).
Acknowledgements
We thank Q. Zhou, W.-B. Liu, A. Lei and X. Zhang at Wuhan University for lending lab space and sharing the basic instruments. We are grateful for the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21702151, 21871211) and the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities (2042019kf0208). We thank S. Liu for her help with the NMR measurements. We acknowledge W. Reid (RWTH Aachen University) for his insightful discussion and generous help on the manuscript preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
W.W. designed and carried out most of the chemical reactions and analysed the data. W.W. and C.D. supported the design and performance of synthetic experiments. G.Y. designed and supervised the project. G.Y. and W.W. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Methods, Figs. 1–279, Tables 1–3 and references.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Ding, C. & Yin, G. Catalyst-controlled enantioselective 1,1-arylboration of unactivated olefins. Nat Catal 3, 951–958 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41929-020-00523-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41929-020-00523-8
This article is cited by
-
Modulation of metal species as control point for Ni-catalyzed stereodivergent semihydrogenation of alkynes with water
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Ligand-modulated nickel-catalyzed regioselective silylalkylation of alkenes
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Chemoselective chromium-catalysed cross-coupling enables three-component tertiary alkane synthesis
Nature Synthesis (2023)
-
Enantioselective C–C cross-coupling of unactivated alkenes
Nature Catalysis (2023)
-
Alkene 1,1-difunctionalizations via organometallic-radical relay
Nature Catalysis (2023)