Abstract
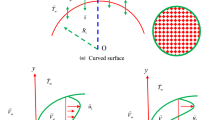
Cancer is the most deadly and dangerous of mainly its patients. The current research has suggested that the nanoparticle containing gold can treat and trounce it since these materials have a lofty atomic quantity that produces the temperature and guides to the handling of malignant tumors. The enthusiasm of current research deals with the steady 2D flow with heat diffusion of blood which transmits the micropolar nanoliquid with gold particles through a curved shrinking/stretched surface. The impact of radiation is also invoked. The coordinates in the curvilinear form are utilized to formulate the mathematical model of flow equations. The similarity technique is employed to transmute the leading PDEs into nonlinear ODEs. The altered nonlinear ODEs are solved through a bvp4c based on a 3-stage Lobatto technique. The numerical outcomes for the heat transport rate and the skin factor along with the micro-rotation, temperature, and velocity fields are presented via plots. The dual natures of solutions are observed for precise values of stretched/shrinking parameter. The physical enlightenments of the sketches are presented to distinguish the phenomena of blood flow by heat transfer in distinct conditions. The results suggest that the blood velocity increases due to suction in the first solution, and decreases in the second solution, while the micro-rotation upsurges and temperature declines in both solutions. Also, the nanofluid temperature uplifts due to the radiation in both solutions.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Huang, M.A. El-Sayed, Gold nanoparticles: optical properties and implementations in cancer diagnosis and photothermal therapy. J. Adv. Res. 1, 13–28 (2010)
P.K. Kumar, W. Paul, C.P. Sharma, Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles with Zingiber officinale extract: characterization and blood compatibility. Process Biochem. 46, 2007–2013 (2011)
M. Hatami, J. Hatami, D.D. Ganji, Computer simulation of MHD blood conveying gold nanoparticles as a third grade non-Newtonian nanofluid in a hollow porous vessel. Comput. Meth. Prog. Biomed. 113, 632–641 (2014)
K.S. Mekheimer, T. Elnaqeeb, M.A. El Kot, F. Alghamdi, Simultaneous effect of magnetic field and metallic nanoparticles on a micropolar fluid through an overlapping stenotic artery: blood flow model. Phys. Ess. 29, 272–283 (2016)
T. Elnaqeeba, K.S. Mekheimer, F. Alghamdi, Cu-blood flow model through a catheterized mild stenotic artery with a thrombosis. Math. Biosci. 282, 135–146 (2016)
A. Rahbari, M. Fakour, A. Hamzehnezhad, M.A. Vakilabadi, D.D. Ganji, Heat transfer and fluid flow of blood with nanoparticles through porous vessels in a magnetic field; a quasi-one dimensional analytical approach. Math. Biosci. 283, 38–47 (2017)
Z. Shah, A. Khan, W. Khan, M.K. Alam, S. Islam, P. Kumam, P. Thounthong, Micropolar gold blood nanofluid flow and radiative heat transfer between permeable channels. Comput. Method Prog. Biomed. 186, 105197 (2020)
B. Ghanbari, S. Kumar, R. Kumar, A study of behaviour for immune and tumor cells in immunogenetic tumour model with non-singular fractional derivative. Chaos Solit. Fract. 133, 109619 (2020)
M.K. Bansal, S. Lal, D. Kumar, S. Kumar, J. Singh, Fractional differential equation pertaining to an integral operator involving incomplete H-function in the kernel. Math. Meth. Appl. Sci. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/mma.6670
S. Kumar, R. Kumar, C. Cattani, B. Samet, Chaotic behaviour of fractional predator-prey dynamical system. Chaos Solit. Fract. 135, 109811 (2020)
J. Singh, D. Kumar, S. Kumar, An efficient computational method for local fractional transport equation occurring in fractal porous media. Comput. Appl. Math. 39, 137 (2020)
P. Veeresha, D.G. Prakasha, S. Kumar, A fractional model for propagation of classical optical solitons by using nonsingular derivative. Math. Meth. Appl. Sci. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/mma.6335
A. Alshabanat, M. Jleli, S. Kumar, B. Samet, Generalization of Caputo-Fabrizio fractional derivative and applications to electrical circuits. Front. Phys. 20, 1–10 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3389/fphy.2020.00064
S. Kumar, R. Kumar, R.P. Agarwal, B. Samet, A study of fractional Lotka-Volterra population model using Haar wavelet and Adams-Bashforth-Moulton methods. Math. Method Appl. Sci. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/mma.6297
S. Kumar, K.S. Nisar, R. Kumar, C. Cattani, B. Samet, A new Rabotnov fractional-exponential function-based fractional derivative for diffusion equation under external force. Math. Method Appl. Sci. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/mma.6208
S. Kumar, S. Ghosh, B. Samet, E.F.D. Goufo, An analysis for heat equations arises in diffusion process using new Yang-Abdel-Aty-Cattani fractional operator. Math. Method Appl. Sci. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/mma.6347
S. Kumar, A. Ahmadian, R. Kumar, D. Kumar, J. Singh, D. Baleanu, M. Salimi, An Efficient numerical method for fractional SIR epidemic model of infectious disease by using Bernstein Wavelets. Math 8(4), 558 (2020)
A.C. Eringen, Simple microfluids. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2, 205–217 (1964)
A.C. Eringen, Theory of micropolar fluids. J. Math. Mech. 16, 1–18 (1966)
G. Lukaszewicz, Micropolar Fluids: Theory and Applications (Springer, Berlin, 1999)
J. Peddieson, R.P. McNitt, Boundary layer theory for micropolar fluid. Adv. Eng. Sci. 5, 405–426 (1970)
S.S. Chawla, Boundary layer growth of a micropolar fluid. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 10, 981–987 (1972)
I.A. Hassanien, A. Shamardan, N.M. Moursy, R.S.R. Gorla, Flow and heat transfer in the boundary layer of a micropolar fluid on a continuous moving surface. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Heat Fluid Flow 9, 643–659 (1999)
R. Nazar, N. Amin, D. Filip, I. Pop, Stagnation point flow of a micropolar fluid towards a stretching sheet. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 39, 1227–1235 (2004)
A.R.M. Kasim, N.F. Mohammad, S. Shafie, Unsteady MHD mixed convection flow of a micropolar fluid along an inclined stretching plate. Heat Transf. Asian Res. 42, 89–99 (2013)
B. Mohanty, S.R. Mishra, H.B. Pattanayak, Numerical investigation on heat and mass transfer effect of micropolar fluid over a stretching sheet through porous media. Alex. Eng. J. 54, 223–232 (2015)
H. Waqas, S. Hussain, H. Sharif, S. Khalid, MHD forced convective flow of micropolar fluids past a moving boundary surface with prescribed heat flux and radiation. Br. J. Math. Comput. Sci. 21, 1–14 (2017)
A. Hussanan, M.Z. Salleh, I. Khan, Microstructure and inertial characteristics of a magnetite ferrofluid over a stretching/shrinking sheet using effective thermal conductivity model. J. Mol. Liq. 255, 64–75 (2018)
A. Zaib, R. Haq, Magnetohydrodynamics mixed convective flow driven through a static wedge including TiO2 nanomaterial with micropolar liquid: Similarity dual solutions via finite difference method. Proc. IMechE Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 233, 5813–5825 (2019)
T. Shabbir, M. Mushtaq, M.I. Khan, T. Hayat, Modeling and numerical simulation of micropolar fluid over a curved surface: Keller box method. Comput. Meth. Prog. Biomed. 187, 105220 (2020)
J.C. Chato, Heat transfer to blood vessels. J. Biomech. Eng. 102, 110–118 (1980)
E.E. Tzirtzilakis, N.G. Kafoussias, Biomagnetic fluid flow over a stretching sheet with non-linear temperature dependent magnetization. J. Appl. Math. Phys. (ZAMP) 54, 551–565 (2003)
Z. Abbas, M. Naveed, M. Sajid, Heat transfer analysis for stretching flow over a curved surface with magnetic field. J. Eng. Thermophys. 22(4), 337–345 (2013)
S.H.M. Saleh, N. Md Arifin, R. Nazar, I. Pop, Unsteady micropolar fluid over a permeable curved stretching shrinking surface. Math. Prob. Eng. 2017, 1–13 (2017)
S. Srinivas, A. Vijayalakshmi, A.S. Reddy, Flow and heat transfer of gold-blood nanofluid in a porous channel with moving/stationary walls. J. Mech. 33(3), 395–404 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the Deanship of Scientific Research at Prince Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University under the research project No. 2020/01/16436.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nisar, K.S., Khan, U., Zaib, A. et al. A novel study of radiative flow involving micropolar nanoliquid from a shrinking/stretching curved surface including blood gold nanoparticles. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 135, 842 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-020-00830-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-020-00830-w