Abstract
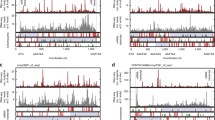
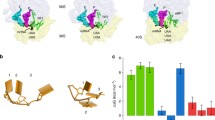
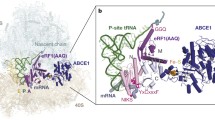
Translation termination is a finishing step of protein biosynthesis. The significant role in this process belongs not only to protein factors of translation termination but also to the nearest nucleotide environment of stop codons. There are numerous descriptions of stop codons readthrough, which is due to specific nucleotide sequences behind them. However, represented data are segmental and don’t explain the mechanism of the nucleotide context influence on translation termination. It is well known that stop codon UAA usage is preferential for A/T-rich genes, and UAG, UGA—for G/C-rich genes, which is related to an expression level of these genes. We investigated the connection between a frequency of nucleotides occurrence in 3' area of stop codons in the human genome and their influence on translation termination efficiency. We found that 3' context motif, which is cognate to the sequence of a stop codon, stimulates translation termination. At the same time, the nucleotide composition of 3' sequence that differs from stop codon, decreases translation termination efficiency.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Zhouravleva G., Frolova L., Le Goff X., Le Guellec R., Inge-Vechtomov S., Kisselev L., Philippe M. 1995. Termination of translation in eukaryotes is governed by two interacting polypeptide chain release factors, eRF1 and eRF3. EMBO J.14, 4065–4072.
Stansfield I., Jones K.M., Ter-Avanesyan M.D., Tuite M.F. 1995. The products of the SUP45 (eRF1) and SUP35 genes interact to mediate translation termination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.EMBO J.14, 4365–4373.
Brown C.M., Stockwell P.A., Trotman C.N., Tate W.P. 1990. Sequence analysis suggests that tetra-nucleotides signal the termination of protein synthesis in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res.18, 6339–6345.
Cavener D.R., Ray S.C. 1991. Eukaryotic start and stop translation sites. Nucleic Acids Res.19, 3185–3192.
Angenon G., Van Montagu M., Depicker A. 1990. Analysis of the stop codon context in plant nuclear genes. FEBS Lett.271, 144–146.
Sun J., Chen M., Xu J., Luo J. 2005. Relationships among stop codon usage bias, its context, isochores, and gene expression level in various eukaryotes. J. Mol. Evol.61, 437–444.
Brown C.M., Stockwell P.A., Trotman C.N.A., Tate W.P. 1990. The signal for the termination of protein synthesis in procaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res.18 (8), 2079–2086.https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/18.8.2079
Namy O., Hatin I., Rousset J.P. 2001. Impact of the six nucleotides downstream of the stop codon on translation termination. EMBO Rep.2, 787–793.
Poole E.S., Major L.L., Mannering S.A., Tate W.P. 1998. Translational termination in Escherichia coli: Three bases following the stop codon crosslink to release factor 2 and affect the decoding efficiency of UGA-containing signals. Nucleic Acids Res.26 (4), 954–960. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/26.4.954
Cridge A.G., Major L.L., Mahagaonkar A.A., Poole E.S., Isaksson L.A., Tate W.P. 2006. Comparison of characteristics and function of translation termination signals between and within prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms. Nucleic Acids Res.34, 1959–1973.
Bertram G., Innes S., Minella O., Richardson J.P., Stansfield I. 2001. Endless possibilities: Translation termination and stop codon recognition. Microbiology.147, 255–269.
Poole E.S., Brown C.M., Tate W.P. 1995. The identity of the base following the stop codon determines the efficiency of in vivo translational termination in Escherichia coli.EMBO J.14 (1), 151–158. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb06985.x
Zhang S., Rydén-Aulin M., Isaksson L.A. 1999. Interaction between a mutant release factor one and P-site peptidyl-tRNA is influenced by the identity of the two bases downstream of the stop codon UAG. FEBS Lett.455 (3), 355–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(99)00912-6
Mccaughan K.K., Brown C.M., Dalphin M.E., Berry M.J., Tate W.P. 1995. Translational termination efficiency in mammals is influenced by the base following the stop codon. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.92 (12), 5431–5435. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.92.12.5431
Bonetti B., Fu L., Moon J., Bedwell D.M. 1995. The efficiency of translation termination is determined by a synergistic interplay between upstream and downstream sequences in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J. Mol. Biol.251, 334–345.
Williams I., Richardson J., Starkey A., Stansfield I. 2004. Genome-wide prediction of stop codon readthrough during translation in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Nucleic Acids Res.32 (22), 6605–6616.https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh1004
Cridge A.G., Crowe-Mcauliffe C., Mathew S.F., Tate W.P. 2018. Eukaryotic translational termination efficiency is influenced by the 3 nucleotides within the ribosomal mRNA channel. Nucleic Acids Res.6 (4), 1927–1944. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx1315
Alkalaeva E.Z., Pisarev A.V., Frolova L.Y., Kisselev L.L., Pestova T.V. 2006. In vitro reconstitution of eukaryotic translation reveals cooperativity between release factors eRF1 and eRF3. Cell.125, 1125–1136.
Alkalaeva E., Eliseev B., Ambrogelly A., Vlasov P., Kondrashov F.A., Gundllapalli S., Frolova L., Söll D., Kisselev L. 2009. Translation termination in pyrrolysine-utilizing archaea. FEBS Lett.583, 3455–3460.
Susorov D., Mikhailova T., Ivanov A., Sokolova E., Alkalaeva E. 2015. Stabilization of eukaryotic ribosomal termination complexes by deacylated tRNA. Nucleic Acids Res.43, 3332–3343.
Kryuchkova P., Grishin A., Eliseev B., Karyagina A., Frolova L., Alkalaeva E. 2013. Two-step model of stop codon recognition by eukaryotic release factor eRF1. Nucleic Acids Res.41, 4573–4586.
Ivanov A., Mikhailova T., Eliseev B., Yeramala L., Sokolova E., Susorov D., Shuvalov A., Schaffitzel C., Alkalaeva E. 2016. PABP enhances release factor recruitment and stop codon recognition during translation termination. Nucleic Acids Res.44 (16), 7766–7776. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw635
Song H., Mugnier P., Das A.K., Webb H.M., Evans D.R., Tuite M.F., Hemmings B.A., Barford D. 2000. The crystal structure of human eukaryotic release factor eRF1: Mechanism of stop codon recognition and peptidyl-tRNA hydrolysis. Cell.100, 311–321.
Wangen J.R., Green R. 2020. Stop codon context influences genome-wide stimulation of termination codon readthrough by aminoglycosides. eLife. pii: e52611. https://doi.org/7554/elife.52611
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We would like to thank the staff of CCU Genome for sequencing, Tat’yana Pestova, Christopher Helen, and Lyudmila Yur’evna Frolova for the plasmids provided, as well as the laboratory staff for productive discussion of the results. We also thank former laboratory employees Yuliya Vladimirovna Bocharova and Polina Nikolaevna Kryuchkova for the exceptional contribution to the present work.
FUNDING
The work was carried out with the support of the Russian Science Foundation (RSF) (grant no. 19-74-10078).
COMPLIANCE WITH ETHICAL STANDARDS
The work did not use animals as subjects of study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sokolova, E.E., Vlasov, P.K., Egorova, T.V. et al. The Influence of A/G Composition of 3' Stop Codon Contexts on Translation Termination Efficiency in Eukaryotes. Mol Biol 54, 739–748 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893320050088
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893320050088