Abstract
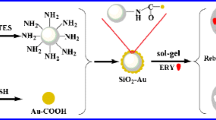
A novel molecularly imprinted ratiometric fluorescent probe was fabricated by simple sol–gel polymerization for selective and sensitive assay of C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP) in biosamples. Both the nitrobenzoxadiazole (NBD) and carbon dots (CDs) were located on the surface of silica, used as the detection signal and reference signal, respectively. For the turn-on-based probe, the fluorescence intensity of NBD could be quantitatively enhanced by CNP based on the strategy of photo-induced electron transfer (PET), while the fluorescence of CDs remained unchanged. The obtained probe exhibited excellent recognition selectivity and fast kinetics to CNP templates, and also showed good stability. The linear range of CNP determination was 5–80 pg mL−1 with a low detection limit of 2.87 pg mL−1. Finally, the probe was successfully applied to determine CNP in human serum samples and attained high recoveries between 97.3 and 104% with precisions below 4.7%. The result indicates that the proposed method has promising potential for the assay of trace peptides in complex matrices.

Schematic illustration for the formation and determination mechanism of the probe






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barr CS, Rhodes P, Struthers AD (2010) C-type natriuretic peptide. Peptides 17(7):1243–1251
Moyes AJ, Hobbs AJ (2019) C-type natriuretic peptide: a multifaceted paracrine regulator in the heart and vasculature. Int J Mol Sci 20(9):2281
Kalra PR, Clague JR, Bolger AP, Anker SD, Poole-Wilson PA, Struthers AD, Coats AJ (2003) Myocardial production of C-type natriuretic peptide in chronic heart failure. Circulation 107(4):571–573
Prickett TC, Espiner EA (2020) Circulating products of C-type natriuretic peptide and links with organ function in health and disease. Peptides 132:170363
Wei CM, Heublein DM, Perrella MA, Lerman A, Rodeheffer RJ, McGregor CGA, Edwards WD, Schaff HV, Burnett JC (1993) Natriuretic peptide system in human heart failure. Circulation 88(3):1004–1009
Prickett TCR, Olney RC, Cameron VA, Ellis MJ, Richards AM, Espiner EA (2013) Impact of age, phenotype and cardio-renal function on plasma C-type and B-type natriuretic peptide forms in an adult population. Clin Endocrinol 78(5):783–789
Lok DJ, Klip IT, Voors AA, Lok SI, Bruggink-André de la Porte PW, Hillege HL, Jaarsma T, van Veldhuisen DJ, van der Meer P (2014) Prognostic value of N-terminal pro C-type natriuretic peptide in heart failure patients with preserved and reduced ejection fraction. Eur J Heart Fail 16(9):958–966
Smith LM, Sanders JZ, Kaiser RJ, Hughes P, Dodd C, Connell CR, Heiner C, Kent SBH, Hood LE (1986) Fluorescence detection in automated DNA sequence analysis. Nature 321(6071):674–679
Xie RR, Liu YY, Yang PP, Huang L, Zou X, Liu JM, Ren QF, Tao J, Zhao P (2020) “French fries”-like luminescent metal organic frameworks for the fluorescence determination of cytochrome c released by apoptotic cells and screening of anticancer drug activity. Microchim Acta 187(4):221
Cao XD, Zhang KR, Yan WW, Xia ZH, He SD, Xu X, Ye YK, Wei ZJ, Liu SQ (2020) Calcium ion assisted fluorescence determination of microRNA-167 using carbon dots-labeled probe DNA and polydopamine-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 187(4):212
Yan X, Li HX, Li Y, Su XG (2014) Visual and fluorescent detection of acetamiprid based on the inner filter effect of gold nanoparticles on ratiometric fluorescence quantum dots. Anal Chim Acta 852:189–195
Li M, Fan JL, Li HD, Du JJ, Long SR, Peng XJ (2018) A ratiometric fluorescence probe for lysosomal polarity. Biomaterials 164:98–105
Katz A, Davis ME (2000) Molecular imprinting of bulk, microporous silica. Nature 403(6767):286–289
He HL, Gu XL, Shi LY, Hong JL, Zhang HJ, Gao YK, Du SH, Chen LN (2015) Molecularly imprinted polymers based on SBA-15 for selective solid-phase extraction of baicalein from plasma samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 407(2):509–519
Gao WR, Li P, Qin S, Huang Z, Cao YA, Liu X (2019) A highly sensitive tetracycline sensor based on a combination of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles and surface plasmon resonance detection. Microchim Acta 186(9):637
Zahedi P, Ziaee M, Abdouss M, Farazin A, Mizaikoff B (2016) Biomacromolecule template-based molecularly imprinted polymers with an emphasis on their synthesis strategies: a review. Polym Adv Technol 27(9):1124–1142
Wang X, Huang K, Zhang HX, Zeng LS, Zhou YK, Jing T (2019) Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymers on hemin-graphene surface for recognition of high molecular weight protein. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 105:110141
Lv PP, Xie DD, Zhang ZH (2018) Magnetic carbon dots based molecularly imprinted polymers for fluorescent detection of bovine hemoglobin. Talanta 188:145–151
Xu XM, Xu GH, Wei FD, Cen Y, Shi ML, Cheng X, Chai YY, Sohail M, Hu Q (2018) Carbon dots coated with molecularly imprinted polymers: a facile bioprobe for fluorescent determination of caffeic acid. J Colloid Interf Sci 529:568–574
Chaowana R, Bunkoed O (2019) A nanocomposite probe of polydopamine/molecularly imprinted polymer/quantum dots for trace sarafloxacin detection in chicken meat. Anal Bioanal Chem 411(23):6081–6090
Sun CH, Pan LL, Zhang L, Huang JJ, Yao DD, Wang CZ, Zhang Y, Jiang N, Chen LN, Yuan CS (2019) A biomimetic fluorescent nanosensor based on imprinted polymers modified with carbon dots for sensitive detection of alpha-fetoprotein in clinical samples. Analyst 144(2):6760–6772
Yang CH, Wang LH, Zhang Z, Chen YJ, Deng QL, Wang S (2020) Fluorometric determination of fipronil by integrating the advantages of molecularly imprinted silica and carbon quantum dots. Microchim Acta 187(1):12
Li QJ, Jiang LD, Kamra T, Ye L (2018) Synthesis of fluorescent molecularly imprinted nanoparticles for turn-on fluorescence assay using one-pot synthetic method and a preliminary microfluidic approach. Polymer 138:352–358
Wang XY, Yu JL, Wu XQ, Fu JQ, Kang Q, Shen DZ, Li JH, Chen LX (2016) A molecular imprinting-based turn-on ratiometric fluorescence sensor for highly selective and sensitive detection of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D). Biosens Bioelectron 81:438–444
Zhang L, Chen LG (2018) Visual detection of melamine by using a ratiometric fluorescent probe consisting of a red emitting CdTe core and a green emitting CdTe shell coated with a molecularly imprinted polymer. Microchim Acta 185(2):135
Liu MY, Gao Z, Yu YJ, Su RX, Huang RL, Qi W, He ZM (2018) Molecularly imprinted core-shell CdSe@SiO2/CDs as a ratiometric fluorescent probe for 4-nitrophenol sensing. Nanoscale Res Lett 13(1):27
Xu SF, Lu HZ (2015) One-pot synthesis of mesoporous structured ratiometric fluorescence molecularly imprinted sensor for highly sensitive detection of melamine from milk samples. Biosens Bioelectron 73:160–166
Wang XY, Yu JL, Kang Q, Shen DZ, Li JH, Chen LX (2016) Molecular imprinting ratiometric fluorescence sensor for highly selective and sensitive detection of phycocyanin. Biosens Bioelectron 77:624–630
Burns A, Ow H, Wiesner U (2006) Fluorescent core-shell silica nanoparticles: towards “lab on a particle” architectures for nanobiotechnology. Chem Soc Rev 35(11):1028–1042
Geng JL, Liu P, Liu BH, Guan GJ, Zhang ZP, Han MY (2010) A reversible dual-response fluorescence switch for the detection of multiple analytes. Chem Eur J 16(12):3720–3727
Liu ZP, Liu H, Liu LL, Su XG (2016) Aptamer based lysozyme assay using fluorescent CuInS2 quantum dots and graphene oxide, and its application to inhibitor screening. Microchim Acta 183(11):2907–2916
Nakagawaa Y, Nishikimia T, Kuwahara K (2019) Atrial and brain natriuretic peptides: hormones secreted from the heart. Peptides 111:18–25
Del Ry S, Passino C, Maltinti M, Emdin M, Giannessi D (2005) C-type natriuretic peptide plasma levels increase in patients with chronic heart failure as a function of clinical severity. Eur J Heart Fail 7(7):1145–1148
Espiner E, Prickett T, Olney R (2018) Plasma C-type natriuretic peptide: emerging applications in disorders of skeletal growth. Horm Res Paediat 90(6):345–357
Zakeri R, Sangaralingham SJ, Sandberg SM, Heublein DM, Scott CG, Burnett JC (2013) Urinary C-type natriuretic peptide: a new heart failure biomarker. JACC Heart Fail 1(2):170–177
Sangaralingham SJ, Huntley BK, Martin FL, McKi PM, Bellavia D, Ichiki T, Harders GE, Chen HH, Burnett JC (2011) The aging heart, myocardial fibrosis, and its relationship to circulating C-type natriuretic peptide. Hypertension 57(2):201–207
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20191352), Jiangsu Salt Industry Group Co., Ltd. (NMU-SY201805), and Nanjing Health Science and Technology Development Special Fund (YKK19173) in China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All work presented was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Sir Run Run Hospital, Nanjing Medical University. The serum samples were donated under informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Hongliang He and Min Cao are co-first authors
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 465 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, H., Cao, M., Hu, J. et al. Fluorescent turn-on assay of C-type natriuretic peptide using a molecularly imprinted ratiometric fluorescent probe with high selectivity and sensitivity. Microchim Acta 187, 614 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04583-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04583-2