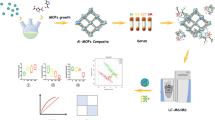
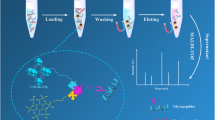
Abstract
A hydrophilic carbohydrate functionalized magnetic metal organic framework (Mag Zr-MOF@G6P) was synthesized via a facile one-step modification strategy for selective glycopeptide capture in virtue of hydrophilic interaction chromatography technique. The inherently hydrophilic Zr-MOF layer not only provides selective size-sieving pore structures but also offers large specific surface area to afford abundant affinity sites. Hydroxyl-rich glucose-6-phosphate was immobilized onto the Zr-MOF via a straightforward coordination manner to regulate its surface property, for the purpose of enhancing its hydrophilicity. Benefitting from the merits of Zr-MOF and glucose-6-phosphate, the as-designed composite exhibits good selectivity (the mass ratio of HRP digests to BSA digests was up to1:200) and low limit of detection (0.1 fmol μL−1) towards the recognition of glycopeptides from standard samples. More excitingly, glycopeptides in urine of healthy people and patients with kidney cancer were successfully enriched and identified by the combined liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry technology (LC-MS/MS). Further gene ontology analysis of molecular function and biological process revealed that 13 original glycoproteins of the identified glycopeptides from urine of patients significantly participate in diverse cancer-associated events, including collagen binding, immunoglobulin receptor binding, antigen binding, and complement activation process.

Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lundberg E, Borner GHH (2019) Spatial proteomics: a powerful discovery tool for cell biology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 20(5):285–302. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-018-0094-y
Christiansen MN, Chik J, Lee L, Anugraham M, Abrahams JL, Packer NH (2014) Cell surface protein glycosylation in cancer. Proteomics 14(4–5):525–546. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.201300387
Pinho SS, Reis CA (2015) Glycosylation in cancer: mechanisms and clinical implications. Nat Rev Cancer 15(9):540–555. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3982
Hu X, Liu Q, Wu Y, Deng Z, Long J, Deng C (2019) Magnetic metal-organic frameworks containing abundant carboxylic groups for highly effective enrichment of glycopeptides in breast cancer serum. Talanta 204:446–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.06.037
Kammeijer GSM, Nouta J, de la Rosette J, de Reijke TM, Wuhrer M (2018) An in-depth glycosylation assay for urinary prostate-specific antigen. Anal Chem 90(7):4414–4421. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b04281
Wu Y, Lin H, Xu Z, Li Y, Chen Z, Deng C (2020) Preparation of zwitterionic cysteine-modified silica microsphere capillary packed columns for the on-column enrichment and analysis of glycopeptides in human saliva. Anal Chim Acta 1096:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.11.032
Haj-Ahmad TA, Abdalla MA, Haj-Ahmad Y (2014) Potential urinary protein biomarker candidates for the accurate detection of prostate cancer among benign prostatic hyperplasia patients. J Cancer 5(2):103–114. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.6890
Gao Y (2015) Urine proteomics in kidney disease biomarker discovery. Springer Science+Business Media, London
Sun N, Wu H, Shen X, Deng C (2019) Nanomaterials in proteomics. Adv Funct Mater 29(26):1900253. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201900253
Suttapitugsakul S, Sun F, Wu R (2020) Recent advances in glycoproteomic analysis by mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 92(1):267–291. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04651
Chen Z, Huang J, Li L (2019) Recent advances in mass spectrometry (MS)-based glycoproteomics in complex biological samples. Trends Analyt Chem 118:880–892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.10.009
Sun N, Wang J, Yao J, Chen H, Deng C (2019) Magnetite nanoparticles coated with mercaptosuccinic acid-modified mesoporous titania as a hydrophilic sorbent for glycopeptides and phosphopeptides prior to their quantitation by LC-MS/MS. Mikrochim Acta 186(3):159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3274-3
Chu H, Hu X, Yao J, Yan G, Sun N, Deng C (2020) One-pot preparation of hydrophilic citric acid-magnetic nanoparticles for identification of glycopeptides in human saliva. Talanta 206:120178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120178
Li Y, Sun N, Hu X, Li Y, Deng C (2019) Recent advances in nanoporous materials as sample preparation techniques for peptidome research. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 120:115658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.115658
Liu Q, Sun N, Deng C-h (2019) Recent advances in metal-organic frameworks for separation and enrichment in proteomics analysis. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 110:66–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.10.033
Sun N, Wu H, Chen H, Shen X, Deng C (2019) Advances in hydrophilic nanomaterials for glycoproteomics. Chem Commun (Camb) 55(70):10359–10375. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9cc04124a
Lu J, Luan J, Li Y, He X, Chen L, Zhang Y (1615) Hydrophilic maltose-modified magnetic metal-organic framework for highly efficient enrichment of N-linked glycopeptides. J Chromatogr A 2020:460754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2019.460754
Liu Q, Deng CH, Sun N (2018) Hydrophilic tripeptide-functionalized magnetic metal-organic frameworks for the highly efficient enrichment of N-linked glycopeptides. Nanoscale 10(25):12149–12155. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nr03174f
Li J, Huan W, Xu K, Wang B, Zhang J, Zhu B, Wu M, Wang J (2020) Gold nanoparticle-glutathione-functionalized porous graphene oxide-based hydrophilic beads for the selective enrichment of N-linked glycopeptides. Mikrochim Acta 187(9):518. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04519-w
Zheng H, Wang J, Gao M, Zhang X (2019) Titanium(IV)-functionalized zirconium-organic frameworks as dual-metal affinity probe for recognition of endogenous phosphopeptides prior to mass spectrometric quantification. Mikrochim Acta 186(12):829. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3962-z
Garzon-Tovar L, Rodriguez-Hermida S, Imaz I, Maspoch D (2017) Spray drying for making covalent chemistry: postsynthetic modification of metal-organic frameworks. J Am Chem Soc 139(2):897–903. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.6b11240
Wang Z, Hu X, Sun N, Deng C (2019) Aptamer-functionalized magnetic metal organic framework as nanoprobe for biomarkers in human serum. Anal Chim Acta 1087:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.08.038
Arcuri C, Monarca L, Ragonese F, Mecca C, Bruscoli S, Giovagnoli S, Donato R, Bereshchenko O, Fioretti B, Costantino F (2018) Probing internalization effects and biocompatibility of ultrasmall zirconium metal-organic frameworks UiO-66 NP in U251 Glioblastoma Cancer cells. Nanomaterials 8(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8110867
Li Y, Wu H, Sun N, Deng C (2019) Fabrication of hydrophilic multilayer magnetic probe for salivary glycopeptidome analysis. J Chromatogr A 1587:24–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.11.040
Ryu JH, Messersmith PB, Lee H (2018) Polydopamine surface chemistry: a decade of discovery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(9):7523–7540. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b19865
Katz MJ, Brown ZJ, Colon YJ, Siu PW, Scheidt KA, Snurr RQ, Hupp JT, Farha OK (2013) A facile synthesis of UiO-66, UiO-67 and their derivatives. Chem Commun (Camb) 49(82):9449–9451. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cc46105j
Yao J, Wang J, Sun N, Deng C (2017) One-step functionalization of magnetic nanoparticles with 4-mercaptophenylboronic acid for a highly efficient analysis of N-glycopeptides. Nanoscale 9(41):16024–16029. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nr04206j
Wang J, Li J, Yan G, Gao M, Zhang X (2019) Preparation of a thickness-controlled mg-MOFs-based magnetic graphene composite as a novel hydrophilic matrix for the effective identification of the glycopeptide in the human urine. Nanoscale 11(8):3701–3709. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nr10074h
Nam H, Kundu A, Brinkley GJ, Chandrashekar DS, Kirkman RL, Chakravarthi B, Orlandella RM, Norian LA, Sonpavde G, Ghatalia P, Fei F, Wei S, Varambally S, Sudarshan S (2020) PGC1alpha suppresses kidney cancer progression by inhibiting collagen-induced SNAIL expression. Matrix Biol 89:43–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matbio.2020.01.001
Sirolli V, Pieroni L, Di Liberato L, Urbani A, Bonomini M (2019) Urinary peptidomic biomarkers in kidney diseases. Int J Mol Sci 21(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010096
Morais M, Dias F, Teixeira AL, Medeiros R (2020) Telomere length in renal cell carcinoma: the Jekyll and Hyde biomarker of ageing of the kidney. Cancer Manag Res 12:1669–1679. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S211225
Hong Q, Wang S, Liu S, Chen X, Cai G (2020) LRG1 may accelerate the progression of ccRCC via the TGF-beta pathway. Biomed Res Int 2020:1285068–1285069. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1285068
Huang H (2018) Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) as a cancer biomarker and MMP-9 biosensors: recent advances. Sensors (Basel) 18(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103249
He XM, Liang XC, Chen X, Yuan BF, Zhou P, Zhang LN, Feng YQ (2017) High strength and hydrophilic chitosan microspheres for the selective enrichment of N-glycopeptides. Anal Chem 89(18):9712–9721. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b01283
Peng J, Hu Y, Zhang H, Wan L, Wang L, Liang Z, Zhang L, Wu R (2019) High anti-interfering profiling of endogenous glycopeptides for human plasma by the dual-hydrophilic metal-organic framework. Anal Chem 91(7):4852–4859. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b00542
Zunder SM, Gelderblom H, Tollenaar RA, Mesker WE (2020) The significance of stromal collagen organization in cancer tissue: an in-depth discussion of literature. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 151:102907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2020.102907
Gadwa J, Karam SD (2020) Deciphering the intricate roles of radiation therapy and complement activation in cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 108:46–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.06.067
Funding
This work was financially supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFA0507501) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21425518).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2320 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X., Wu, Y. & Deng, C. Recognition of urinary N-linked glycopeptides in kidney cancer patients by hydrophilic carbohydrate functionalized magnetic metal organic framework combined with LC-MS/MS. Microchim Acta 187, 616 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04595-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04595-y