Abstract
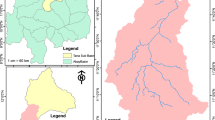
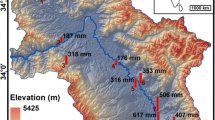
The efficacy of the standard performance metrics [mean bias (Bias), root mean square deviation (RMSD), and correlation coefficient (CC)] compared to a new symmetric index of agreement (λ) for the evaluation of numerical weather prediction models is investigated in this study. It evaluates the weather research and forecasting (WRF) model with the global precipitation measurement’s (GPM) Integrated Multi-satellitE Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) and station rainfall, as the reference datasets. This study uses three IMERG products, namely: GPM infrared-microwave merged gauge corrected (GMS), GPM microwave-calibrated infrared (GIR), and GPM inter-calibrated microwave (GMW) rainfall. The analysis showed that WRF rainfall when compared to different reference datasets is producing similar RMSD values but significantly different Bias values. This behavior is because of the inverse relationship between Bias and standard deviation of residual (\(\sigma_{{\text{R}}}\)). It is so because RMSD is a function of both. However, λ is able to appropriately represent the distinct performances of WRF. The regions with contradictory behavior of RMSD and CC are also appropriately represented in λ. The evaluation using λ showed that WRF is comparable to GMS and GIR, except for GMW. The performance of WRF was not found to be very promising when compared to station rainfall, which is attributed to WRFs representation efficiency and the effect of topography. However, a comparison of IMERG products with station rainfall showed that GMS was the most agreeable followed by GIR and GMW. The study also showed that the efficacy of λ is related to its non-linear relationship with Bias and CC.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbe C (1901) The physical basis of long-range weather forecasts. Mon Weather Rev. https://doi.org/10.1175/15200493(1901)29[551c:TPBOLW]2.0.CO;2
Adnan M, Khan F, Rehman N, Ali S, Hassan SS, Dogar MM et al (2020) Variability and predictability of summer monsoon rainfall over Pakistan. Asia-Pacific J Atmos Sci 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-020-00178-2
Bauer P, Thorpe A, Brunet G (2015) The quiet revolution of numerical weather prediction. Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14956
Bharti V, Singh C (2015) Evaluation of error in TRMM 3B42V7 precipitation estimates over the Himalayan region. J Geophys Res Atmos 120(24):12458–12473. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JD023779
Bjerknes V (1910) Dynamic meteorology and hydrography (No. 88). Carnegie.
Cardoso RM, Soares PMM, Miranda PMA, Belo-Pereira M (2013) WRF high resolution simulation of Iberian mean and extreme precipitation climate. Int J Climatol. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.3616
Carpenter KM (1979) An experimental forecast using a non-hydrostatic mesoscale model. Quart J R Meteorolog Soc. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.49710544510
Chai T, Draxler RR (2014) Root mean square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE)?—arguments against avoiding RMSE in the literature. Geosci Model Dev. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-7-1247-2014
Chawla I, Osuri KK, Mujumdar PP, Niyogi D (2018) Assessment of the weather research and forecasting (WRF) model for simulation of extreme rainfall events in the upper Ganga Basin. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-22-1095-2018
Dudhia J (2014) A history of mesoscale model development. Asia-Pacific J Atmos Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-014-0031-8
Duveiller G, Fasbender D, Meroni M (2016) Revisiting the concept of a symmetric index of agreement for continuous datasets. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep19401
Ebert EE, Janowiak JE, Kidd C (2007) Comparison of near-real-time precipitation estimates from satellite observations and numerical models. Bull Am Meteor Soc. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-88-1-47
Fierro AO, Mansell ER, Ziegler CL, MacGorman DR (2012) Application of a lightning data assimilation technique in the WRF-ARW model at cloud-resolving scales for the tornado outbreak of 24 May 2011. Mon Weather Rev 140(8):2609–2627. https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR-D-11-00299.1
Foelsche U, Kirchengast G, Fuchsberger J, Tan J, Petersen WA (2017) Evaluation of GPM IMERG early, late, and final rainfall estimates using WegenerNet gauge data in southeastern Austria. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 21(12):6559–6572. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-21-6559-2017
Ghile YB, Schulze RE (2010) Evaluation of three numerical weather prediction models for short and medium range agrohydrological applications. Water Resour Manage 24(5):1005–1028. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-009-9483-5
Giannaros TM, Melas D, Daglis IA, Keramitsoglou I, Kourtidis K (2013) Numerical study of the urban heat island over Athens (Greece) with the WRF model. Atmos Environ 73:103–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.02.055
Giannaros TM, Kotroni V, Lagouvardos K (2015) Predicting lightning activity in Greece with the weather research and forecasting (WRF) model. Atmos Res 156:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2014.12.009
Giannaros TM, Kotroni V, Lagouvardos K (2016) WRF-LTNGDA: a lightning data assimilation technique implemented in the WRF model for improving precipitation forecasts. Environ Model Softw 76:54–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2015.11.017
Gilleland E, Ahijevych D, Brown BG, Casati B, Ebert EE (2009) Intercomparison of spatial forecast verification methods. Weather Forecast 24(5):1416–1430. https://doi.org/10.1175/2009WAF2222269.1
Hamada A, Takayabu YN (2016) Improvements in detection of light precipitation with the global precipitation measurement dual-frequency precipitation radar (GPM DPR). J Atmos Ocean Technol 33(4):653–667. https://doi.org/10.1175/JTECH-D-15-0097.1
He Z, Yang L, Tian F, Ni G, Hou A, Lu H (2017) Intercomparisons of rainfall estimates from TRMM and GPM multisatellite products over the upper Mekong River basin. J Hydrometeorol 18(2):413–430. https://doi.org/10.1175/JHM-D-16-0198.1
Hou AY, Kakar RK, Neeck S, Azarbarzin AA, Kummerow CD, Kojima M, Oki R, Nakamura K, Iguchi T (2014) The global precipitation measurement mission. Bull Am Meteor Soc 95(5):701–722. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-13-00164.1
Hsiao LF, Chen DS, Kuo YH, Guo YR, Yeh TC, Hong JS, Fong CT, Lee CS (2012) Application of WRF 3DVAR to operational typhoon prediction in Taiwan: impact of outer loop and partial cycling approaches. Weather Forecast 27(5):1249–1263. https://doi.org/10.1175/WAF-D-11-00131.1
Huffman GJ, Bolvin DT, Braithwaite D, Hsu K, Joyce R, Xie P, Yoo SH (2015) NASA global precipitation measurement (GPM) integrated multi-satellite retrievals for GPM (IMERG). Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document Version4.5. https://pmm.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/document_files/IMERG_ATBD_V4.5.pdf
Jiménez PA, Dudhia J (2013) On the ability of the WRF model to reproduce the surface wind direction over complex terrain. J Appl Meteorol Climatol 52(7):1610–1617. https://doi.org/10.1175/JAMC-D-12-0266.1
Kalnay E, Kanamitsu M, Baker WE (1990) Global numerical weather prediction at the National Meteorological Center. Bull Am Meteor Soc 71(10):1410–1428. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477(1990)071%3c1410:GNWPAT%3e2.0.CO;2
Kotroni V, Lagouvardos K, Retalis A (2011) The heat wave of June 2007 in Athens, Greece-Part 2: modeling study and sensitivity experiments. Atmos Res 100(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2010.12.007
Kottek M, Grieser J, Beck C, Rudolf B, Rubel F (2006) World map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification updated. Meteorolog Z 15(3):259–263. https://doi.org/10.1127/0941-2948/2006/0130
Kryza M, Szymanowski M, Migała K, Pietras M (2010) Spatial information on total solar radiation: application and evaluation of the r. sun model for the Wedel Jarlsberg Land, Svalbard. Pol Polar Res 31(1):17–32. https://doi.org/10.4202/ppres.2010.02
Kryza M, Werner M, Wałszek K, Dore AJ (2013) Application and evaluation of the WRF model for high-resolution forecasting of rainfall—a case study of SW Poland. Meteorolog Z 22(5):595–601. https://doi.org/10.1127/0941-2948/2013/0444
Kumar A, Dudhia J, Rotunno R, Niyogi D, Mohanty UC (2008) Analysis of the 26 July 2005 heavy rain event over Mumbai, India using the weather research and forecasting (WRF) model. Quart J R Meteorolog Soc 134(636):1897–1910. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.325
Kumar Das A, Bhowmick M, Kundu PK, Roy Bhowmik SK (2014) Verification of WRF rainfall forecasts over India during monsoon 2010: CRA method. Geofizika 31(2):106–126. https://doi.org/10.15233/gfz.2014.31.6
Lynch P (2008) The origins of computer weather prediction and climate modeling. J Comput Phys 227(7):3431–3444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2007.02.034
Madala S, Satyanarayana ANV, Rao TN (2014) Performance evaluation of PBL and cumulus parameterization schemes of WRF ARW model in simulating severe thunderstorm events over Gadanki MST radar facility—case study. Atmos Res 39:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2013.12.017
McCaul EW Jr, Goodman SJ, LaCasse KM, Cecil DJ (2009) Forecasting lightning threat using cloud-resolving model simulations. Weather Forecast 24(3):709–729. https://doi.org/10.1175/2008WAF2222152.1
Mielke Jr PW (1984) 34 Meteorological applications of permutation techniques based on distance functions. In: Krishnaiah PR, Sen PK (eds) Handbook of statistics. 4th vol. ScienceDirect, pp. 813–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-7161(84)04036-0
Mielke PW Jr (1991) The application of multivariate permutation methods based on distance functions in the earth sciences. Earth Sci Rev 31(1):55–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-8252(91)90042-E
Mitra AK, Kaushik N, Singh AK, Parihar S, Bhan SC (2018) Evaluation of INSAT-3D satellite derived precipitation estimates for heavy rainfall events and its validation with gridded GPM (IMERG) rainfall dataset over the Indian region. Remote Sens Appl Soc Environ 9:91–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsase.2017.12.006
Mohan M, Bhati S (2011) Analysis of WRF model performance over subtropical region of Delhi, India. Adv Meteorol 2011:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/621235
Naabil E, Lamptey BL, Arnault J, Olufayo A, Kunstmann H (2017) Water resources management using the WRF-hydro modelling system: case-study of the Tono dam in West Africa. J Hydrol Reg Stud 12:196–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2017.05.010
Nash JE, Sutcliffe JV (1970) River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—a discussion of principles. J Hydrol 10(3):282–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(70)90255-6
Orrell D, Smith L, Barkmeijer J, Palmer TN (2001) Model error in weather forecasting. Nonlin Process Geophys 8(6):357–371. https://doi.org/10.5194/npg-8-357-2001
Paredes-Trejo FJ, Barbosa HA, Kumar TL (2017) Validating CHIRPS-based satellite precipitation estimates in Northeast Brazil. J Arid Environ 139:26–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2016.12.009
Paul S, Wang CC, Chien FC, Lee DI (2018) An evaluation of the WRF Mei-yu rainfall forecasts in Taiwan, 2008–2010: differences in elevation and sub-regions. Meteorolog Appl 25(2):269–282. https://doi.org/10.1002/met.1689
Powers JG (2007) Numerical prediction of an Antarctic severe wind event with the weather research and forecasting (WRF) model. Mon Weather Rev 135(9):3134–3157. https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR3459.1
Powers JG, Klemp JB, Skamarock WC, Davis CA, Dudhia J, Gill DO, Coen JL, Gochis DJ, Ahmadov R, Peckham SE, Grell GA (2017) The weather research and forecasting model: overview, system efforts, and future directions. Bull Am Meteor Soc 98(8):1717–1737. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-15-00308.1
Prakash S, Mitra AK, Pai DS, AghaKouchak A (2016) From TRMM to GPM: how well can heavy rainfall be detected from space? Adv Water Resour 88:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2015.11.008
Raju PVS, Potty J, Mohanty UC (2011) Sensitivity of physical parameterizations on prediction of tropical cyclone Nargis over the Bay of Bengal using WRF model. Meteorol Atmos Phys 113(3–4):125–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-011-0151-y
Richardson LF (1922) Weather prediction by numerical process. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Rife DL, Davis CA (2005) Verification of temporal variations in mesoscale numerical wind forecasts. Mon Weather Rev 133(11):3368–3381. https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR3052.1
Roberts NM, Lean HW (2008) Scale-selective verification of rainfall accumulations from high-resolution forecasts of convective events. Mon Weather Rev 136(1):78–97. https://doi.org/10.1175/2007MWR2123.1
Shrestha DL, Robertson DE, Wang QJ, Pagano TC, Hapuarachchi HAP (2013) Evaluation of numerical weather prediction model precipitation forecasts for short-term streamflow forecasting purpose. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 17(5):1913–1931. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-17-1913-2013
Shuman FG (1989) History of numerical weather prediction at the National Meteorological Center. Weather Forecast 4(3):286–296. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0434(1989)004%3c0286:HONWPA%3e2.0.CO;2
Sikder S, Hossain F (2016) Assessment of the weather research and forecasting model generalized parameterization schemes for advancement of precipitation forecasting in monsoon-driven river basins. J Adv Model Earth Syst 8(3):1210–1228. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016MS000678
Skamarock WC, Klemp JB, Dudhia J, Gill DO, Barker D, Duda MG et al (2008) A description of the advanced research WRF Version 3 (No. NCAR/TN-475+STR). University Corporation for Atmospheric Research. https://doi.org/10.5065/D68S4MVH. https://opensky.ucar.edu/islandora/object/technotes%3A500/datastream/PDF/view
Skofronick-Jackson G, Petersen WA, Berg W, Kidd C, Stocker EF, Kirschbaum DB, Kakar R, Braun SA, Huffman GJ, Iguchi T, Kirstetter PE (2017) The global precipitation measurement (GPM) mission for science and society. Bull Am Meteor Soc 98(8):1679–1695. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-15-00306.1
Srinivas CV, Hariprasad D, Bhaskar Rao DV, Anjaneyulu Y, Baskaran R, Venkatraman B (2013) Simulation of the Indian summer monsoon regional climate using advanced research WRF model. Int J Climatol 33(5):1195–1210. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.3505
Srivastava PK, Han D, Rico-Ramirez MA, O’Neill P, Islam T, Gupta M, Dai Q (2015) Performance evaluation of WRF-Noah Land surface model estimated soil moisture for hydrological application: synergistic evaluation using SMOS retrieved soil moisture. J Hydrol 529:200–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.07.041
Tan J, Petersen WA, Tokay A (2016) A novel approach to identify sources of errors in IMERG for GPM ground validation. J Hydrometeorol 17(9):2477–2491. https://doi.org/10.1175/JHM-D-16-0079.1
Taylor KE (2001) Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram. J Geophys Res Atmos 106(D7):7183–7192. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000JD900719
Tie X, Brasseur G, Ying Z (2010) Impact of model resolution on chemical ozone formation in Mexico City: application of the WRF-Chem model. Atmos Chem Phys 10(18):8983–8995. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-10-8983-2010
Tolstykh MA, Frolov AV (2005) Some current problems in numerical weather prediction. Izvest Atmos Ocean Phys 41(3):285–295
Vasić S, Lin CA, Zawadzki I, Bousquet O, Chaumont D (2007) Evaluation of precipitation from numerical weather prediction models and satellites using values retrieved from radars. Mon Weather Rev 135(11):3750–3766. https://doi.org/10.1175/2007MWR1955.1
Wang H, Mu M, Huang XY (2011) Application of conditional non-linear optimal perturbations to tropical cyclone adaptive observation using the weather research forecasting (WRF) model. Tellus A Dyn Meteorol Oceanogr 63(5):939–957. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0870.2011.00536.x
Wang W, Lu H, Zhao T, Jiang L, Shi J (2017) Evaluation and comparison of daily rainfall from latest GPM and TRMM products over the Mekong River Basin. IEEE J Sel Topics Appl Earth Observ Remote Sens 10(6):2540–2549. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2672786
Watterson IG (1996) Non-dimensional measures of climate model performance. Int J Climatol 16(4):379–391. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-0088(199604)16:4%3c379::aid-joc18%3e3.0.co;2-u
Wernli H, Paulat M, Hagen M, Frei C (2008) SAL—a novel quality measure for the verification of quantitative precipitation forecasts. Mon Weather Rev 136(11):4470–4487. https://doi.org/10.1175/2008MWR2415.1
Wilks DS (2011) Statistical methods in the atmospheric sciences, vol 100. Academic press, USA
Willmott CJ (1981) On the validation of models. Phys Geogr 2(2):184–194. https://doi.org/10.1080/02723646.1981.10642213
Willmott CJ, Matsuura K (2005) Advantages of the mean absolute error (MAE) over the root mean square error (RMSE) in assessing average model performance. Climate Res 30:79–82. https://doi.org/10.3354/cr030079
Willmott CJ, Matsuura K, Robeson SM (2009) Ambiguities inherent in sums-of-squares-based error statistics. Atmos Environ 43(3):749–752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.10.005
Willmott CJ, Robeson SM, Matsuura K (2012) A refined index of model performance. Int J Climatol 32(13):2088–2094. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.2419
Zhao Q, Liu Z, Ye B, Qin Y, Wei Z, Fang S (2009) A snowmelt runoff forecasting model coupling WRF and DHSVM. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 13(10):1897–1906. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-13-1897-2009
Zhou G, Xu J, Xie Y, Chang L, Gao W, Gu Y, Zhou J (2017) Numerical air quality forecasting over eastern China: an operational application of WRF-Chem. Atmos Environ 153:94–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.01.020
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the North Eastern Space Applications Centre for providing the infrastructure required to undertake this work. The authors would also like to thank Ms. Ritu Anil Kumar for her valuable suggestions during the manuscript formulation process. The authors would also like to extend their gratitude to the anonymous reviewers for their constructive suggestions in improving the presentation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Emilia Kyung Jin.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chakravorty, A., Gogoi, R.B., Kundu, S.S. et al. Investigating the efficacy of a new symmetric index of agreement for evaluating WRF simulated summer monsoon rainfall over northeast India. Meteorol Atmos Phys 133, 479–493 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-020-00761-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-020-00761-2