Abstract
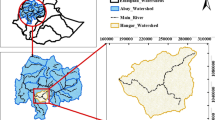
The escalating demand for anthropic needs and urban development has highlighted the importance of monitoring and change detection of land use land cover (LULC). With an increase in agricultural expansion and infrastructural development, every land surface on earth calls for a long-term investigation of land modification patterns and their underlying contributory factors. The present investigation monitors the LULC changes and assesses the process controls in Kohima and Dimapur districts of Nagaland, India. Currently, these two districts encompassing the main urban cities of the hilly state are experiencing rapid urbanization and unplanned developmental activities. Alike any other LULC changes observed in unplanned and developing cities, these districts are likely to face environmental degradation, and particularly, the occurrence of frequent landslides and flash floods. The study has three objectives—(i) LULC mapping of Kohima and Dimapur districts for three periods (1998, 2008, and 2018), (ii) comparative analysis of LULC change patterns in the two districts during the three epochs (1998–2008, 2008–2018, and 1998–2018), and (iii) assessment of the contributory factors. For the study, remotely sensed LANDSAT images (TM and OLI) in Geographical Information System (GIS) platform were utilized along with field surveys. Supervised classification technique was employed and four major LULC classes were identified using Landsat level-1 classification system. The overall accuracy of the classification varied between 91 and 98%. Results showed that Built Up areas have increased significantly in both the districts at the rate of 322.6 ha/year in Kohima and 301.9 ha/year in Dimapur during 1998–2018. On the other hand, Agricultural Land and Forest Land declined in both districts. Changes in LULC were mainly due to marginalization of shifting cultivation, deforestation, infrastructural development, urban migration, and flourishing of aquaculture farming. This study furnishes baseline information on LULC in the data-scarce region of Northeast India and is an insinuation to the policy-makers to ensure sustainable land use planning in the face of rapid urbanization.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary information files.
References
Abd El-Kawy, O. R., Rød, J. K., Ismail, H. A., & Suliman, A. S. (2011). Land use and land cover change detection in the western Nile delta of Egypt using remote sensing data. Applied Geography, 31(2), 483–494.
Achumi, B., Phom, L., Zevelou, M. A., Lal, P., & Yenisetti, S. C. (2014). Ecogeographic Biodiversity pattern of Genus Drosophila (Insecta, Diptera: Drosophilidae) in Nagaland state, India. Nagaland University Research Journal, 7, 332–337.
Ahearn, D. S., Sheibley, R. W., Dahlgren, R. A., Anderson, M., Johnson, J., & Tate, K. W. (2005). Land use and land cover influence on water quality in the last free-flowing river draining the western Sierra Nevada, California. Journal of Hydrology, 313(3–4), 234–247.
Aier, A., & Kithan, T. (2011). Rural-urban migration: a thematic report (A Project of Government of India and UNDP). Kohima: Department of Planning and Coordination, Government of Nagaland.
Alexakis, D. D., Grillakis, M. G., Koutroulis, A. G., Agapiou, A., Themistocleous, K., Tsanis, I. K., Michaelides, S., Pashiardis, S., Demetriou, C., Aristeidou, K., Retalis, A., Tymvios, F., & Hadjimitsis, D. G. (2014). GIS and remote sensing techniques for the assessment of land use change impact on flood hydrology: the case study of Yialias basin in Cyprus. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 14, 413–426.
Anon. (2000). Basic statistics of North Eastern Region 2000. Shillong: North Eastern Council, Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India.
Arunachalam, A., Khan, M. L., & Arunachalam, K. (2002). Balancing traditional jhum cultivation with modern agroforestry in eastern Himalaya—a biodiversity hot spot. Current Science, 83(2), 117.
Aspinall, R. (2004). Modelling land use change with generalized linear models—a multi-model analysis of change between 1860 and 2000 in Gallatin Valley, Montana. Journal of Environmental Management, 72(1–2), 91–103.
Ayele, G. T., Demissie, S. S., Mengistu, K. T., Tilahun, S. A., & Melesse, A. M. (2016). Multitemporal land use/land cover change detection for the Batena Watershed, Rift Valley Lakes Basin, Ethiopia. Landscape Dynamics, Soils and Hydrological Processes in Varied Climates, 51–72.
Basha, U. I., Suresh, U., Raju, G. S., Rajasekhar, M., Veeraswamy, G., & Balaji, E. (2018). Landuse and landcover analysis using remote sensing and GIS: a case study in Somavathi River, Anantapur District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Nature, Environment and Pollution Technology, 17(3), 1029–1033.
Bastawesy, M. A., Khalaf, F. I., & Arafat, S. M. (2008). The use of remote sensing and GIS for the estimation of water loss from Tushka lakes, southwestern desert, Egypt. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 52(3), 73–80.
Bhatta, B. (2009). Analysis of urban growth pattern using remote sensing and GIS: a case study of Kolkata, India. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 30(18), 4733–4746.
Bisht, B. S., & Kothyari, B. P. (2001). Land-cover change analysis of garur Ganga watershed using GIS/remote sensing technique. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 29(3), 137–141.
Boyaj, A., Dasari, H. P., Hoteit, I., & Ashok, K. (2020). Increasing heavy rainfall events in South India due to changing land use land cover. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.3826.
Bromley, R., & Gerry, C. (1979). Who are the casual poor. In Casual work and poverty in Third World cities (pp. 3–26).
Cairns, M., Keitzar, S., & Yaden, T. A. (2010). Shifting forests in Northeast India: management of Alnusnepalensis as an improved fallow in Nagaland. In Voices from the Forest. Routledge.
Census (2011a). Census of India, 2011, https://www.census2011.co.in/census/state/nagaland.html (Last accessed on 29-02-2020).
Census (2011b). Census of India, 2011, https://www.census2011.co.in/census/state/districtlist/nagaland.html (Last accessed on 29-02-2020).
Chander, G., Markham, B. L., & Helder, D. L. (2009). Summary of current radiometric calibration coefficients for Landsat MSS, TM, ETM+, and EO-1 ALI sensors. Remote Sensing of Environment, 113(5), 893–903.
Chen, L., Wang, H. Y., Wang, T. S., & Kou, C. H. (2019). Remote sensing for detecting changes of land use in Taipei City, Taiwan. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 47(11), 1847–1856.
Choudhury, D., & Sundriyal, R. C. (2003). Factors contributing to the marginalization of shifting cultivation in north-east India: micro-scale issues. Outlook on Agriculture, 32(1), 17–28.
Dewan, A. M., & Yamaguchi, Y. (2009). Land use and land cover change in Greater Dhaka, Bangladesh: using remote sensing to promote sustainable urbanization. Applied Geography, 29(3), 390–401.
Dhinwa, P. S., Pathan, S. K., Sastry, S. V. C., Rao, M., Majumder, K. L., Chotani, M. L., Singh, J. P., & Sinha, R. L. P. (1992). Land use change analysis of Bharatpur district using GIS. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 20(4), 237–250.
Dimyati, M., Mizuno, K., Kobayashi, S., & Kitamura, T. (1996). An analysis of land use/cover change in Indonesia. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 17(5), 931–944.
Eduful, M., & Shively, D. (2015). Perceptions of urban land use and degradation of water bodies in Kumasi, Ghana. Habitat International, 50, 206–213.
Esmail, M., Masria, A., & Negm, A. (2016). Monitoring land use/land cover changes around Damietta Promontory, Egypt, using RS/GIS. Procedia Engineering, 154, 936–942.
Ganasri, B.P., & Dwarakish, G. S. (2015). Study of land use/land cover dynamics through classification algorithms for Harangi catchment Area, Karnataka State, India. Aquatic Procedia, 4, 1413–1420.
Ghosh, S., Sen, K. K., Rana, U., Rao, K. S., & Saxena, K. G. (1996). Application of GIS for land-use/land-cover change analysis in a mountainous terrain. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 24(3), 193–202.
Halmy, M. W. A., Gessler, P. E., Hicke, J. A., & Salem, B. B. (2015). Land use/land cover change detection and prediction in the north-western coastal desert of Egypt using Markov-CA. Applied Geography, 63, 101–112.
Hansen, M. C., & Loveland, T. R. (2012). A review of large area monitoring of land cover change using Landsat data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 122, 66–74.
Hazarika, N., Das, A. K., & Borah, S. B. (2015). Assessing land-use changes driven by river dynamics in chronically flood affected Upper Brahmaputra plains, India, using RS-GIS techniques. Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Science, 18(1), 107–118.
Hazarika, N., Barman, D., Das, A. K., Sarma, A. K., & Borah, S. B. (2016). Assessing and mapping flood hazard, vulnerability and risk in the Upper Brahmaputra River valley using stakeholders’ knowledge and multicriteria evaluation (MCE). Journal of Flood Risk Management, 11, S700–S716.
He, Y., Lee, E., & Mankin, J. S. (2020). Seasonal tropospheric cooling in Northeast China associated with cropland expansion. Environmental Research Letters, 15(3), 034032. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ab6616.
Hossain, A. M. M., & Rahman, S. (2011). Hydrography of Dhaka city catchment and impact of urbanization on water flows: a review. Asian Journal of Water, Environment and Pollution, 8(4), 27–36.
Hossain, F., Arnold, J., Beighley, E., Brown, C., Burian, S., Chen, J., Madadgar, S., Mitra, A., Niyogi, D., Pielke Sr., R., & Tidwell, V. (2015). Local-to-regional landscape drivers of extreme weather and climate: Implications for water infrastructure resilience. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 02515002, 02515002. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0001210.
Jaiswal, R. K., Saxena, R., & Mukherjee, S. (1999). Application of remote sensing technology for land use/land cover change analysis. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 27(2), 123–128.
Jayakumar, S., & Arockiasamy, D. I. (2003). Land use/land cover mapping and change detection in part of Eastern Ghats of Tamilnadu using remote sensing and GIS. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 31(4), 251–260.
Jha, C. S., Dutt, C. B. S., & Bawa, K. S. (2000). Deforestation and land use changes in Western Ghats, India. Current Science, 79(2), 231–238.
Kalkhajeh, R. G., & Jamali, A. A. (2019). Analysis and predicting the trend of land use/cover changes using neural network and Systematic Points Statistical Analysis (SPSA). Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 47, 1471–1485.
Kishtawal, C. M., Niyogi, D., Tewari, M., Pielke Sr., R. A., & Shepherd, J. M. (2009). Urbanization signature in the observed heavy rainfall climatology over India. International Journal of Climatology, 30, 1908–1916. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.2044.
Kiyasetuo & Khare, M. K. (1986). A new genus of frog (Anura: Ranidae) from Nagaland at the north-eastern hills of India. Asian Journal of Experimental Sciences, 1, 12–17.
Kolios, S., & Stylios, C. D. (2013). Identification of land cover/land use changes in the greater area of the Preveza peninsula in Greece using Landsat satellite data. Applied Geography, 40, 150–160.
Li, Z., Li, X., Wang, Y., Ma, A., & Wang, J. (2004). Land-use change analysis in Yulin prefecture, northwestern China using remote sensing and GIS. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 25(24), 5691–5703.
Liu, J., Daily, G. C., Ehrlich, P. R., & Luck, G. W. (2003). Effects of household dynamics on resource consumption and biodiversity. Nature, 421(6922), 530–533.
Mas, J. F., Velázqueza, A., Díaz-Gallegos, J. R., Saucedo, R. M., Alcántara, C., Bocco, G., Castro, R., Fernández, T., & Pérez-Vega, A. (2004). Assessing land use/cover changes: a nationwide multidate spatial database for Mexico. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 5, 249–261.
McAlpine, C. A., Ryan, J. G., Seabrook, L., Thomas, S., Dargusch, P. J., Syktus, J. I., Pielke Sr., R. A., Etter, A. E., Fearnside, P. M., & Laurance, W. F. (2010). More than CO2: a broader paradigm for managing climate change and variability to avoid ecosystem collapse. Current Opinion in Environment Sustainability, 2(5–6), 334–346.
Mukherjee, S., Shashtri, S., Singh, C. K., Srivastava, P. K., & Gupta, M. (2009). Effect of canal on land use/land cover using remote sensing and GIS. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 37, 527–537.
Niyogi, D., Chang, H. I., Chen, F., Gu, L., Kumar, A., Menon, S., & Pielke, R. A. (2007). Potential impacts of aerosol–land–atmosphere interactions on the Indian monsoonal rainfall characteristics. Natural Hazards, 42(2), 345–359.
Nongkynrih, J. M., Pohshna, C., & Sarma, K. K. (2018). Dynamics of shifting cultivation in relation to slope and elevation in parts of Nagaland, India. Current Science, 114(5), 1094.
Pandey, D. K., Adhiguru, P., & De, H. K. (2019). Attachment to shifting cultivation among Konyak Naga tribe in Eastern Himalaya: choice or compulsion? Current Science, 116(8), 1387.
Pant, R. M., Tiwari, B. K., & Choudhury, D. (2018). Report of Working Group III, shifting cultivation: towards a transformational approach. New Delhi: NITI Aayog.
Pathan, S. K., Jothimahi, P., Kumar, D. S., & Pendharkar, S. P. (1989). Urban land use mapping and zoning of Bombay Metropolitan Region using remote sensing data. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 17(3), 11–22.
Pathan, S., Shukla, V., Patel, R., Patel, B., & Mehta, K. (1991). Urban land use mapping: a case study of Ahmedabad city and its environs. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 19(2), 95–112.
Peng, J., Wu, J., Yin, H., Li, Z., Chang, Q., & Mu, T. (2008). Rural land use change during 1986–2002 in Lijiang, China, based on remote sensing and GIS data. Sensors, 8, 8201–8223.
Pielke Sr., R. A., Adegoke, J., Beltraán-Przekurat, A., Hiemstra, C. A., Lin, J., Nair, U. S., Niyogi, D., & Nobis, T. E. (2007). An overview of regional land use and land cover impacts on rainfall. Tellus Series B: Chemical and Physical Meteorology, 59(3), 587–601.
Pielke Sr., R. A., Mahmood, R., & McAlpine, C. (2016). Land’s complex role in climate change. Physics Today, 69(11), 40–46.
Pielke, R. A., Pitman, A., Niyogi, D., Mahmood, R., McAlpine, C., Hossain, F., Goldewijk, K. K., Nair, U., Betts, R., Fall, S., Reichstein, M., Kabat, P., & Noblet, N. D. (2011). Land use/land cover changes and climate: modeling analysis and observational evidence. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Climate Change, 2(6), 828–850.
Poleto, C., & Beier, E. V. (2012). Siltation and erosion processes on a tributary of lake itaipu due a dam reservoir. Lakes Reservoirs and Ponds, 6(2), 108–119.
Rahman, A., Kumar, S., & Fazal, S. (2012). Assessment of land use/land cover change in the North-West District of Delhi using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 40(4), 689–697.
Rao, R. R., & Jamir, N. S. (1982). Ethnobotanical studies in Nagaland. I. medicinal plants. Economic Botany, 36(2), 176–181.
Rawat, J. S., & Kumar, M. (2015). Monitoring land use/cover change using remote sensing and GIS techniques: a case study of Hawalbagh block, district Almora, Uttarakhand, India. The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Sciences, 18, 77–84.
Reddy, C. S., Dutta, K., & Jha, C. S. (2013). Analysing the gross and net deforestation rates in India. Current Science, 105(11), 1492–1500.
Reddy, C. S., Jha, C. S., Dadhwal, V. K., Krishna, P. H., Pasha, S. V., Satish, K. V., Dutta, K., Saranya, K. R. L., Rakesh, F., Rajashekar, G., & Diwakar, P. G. (2016). Quantification and monitoring of deforestation in India over eight decades (1930–2013). Biodiversity and Conservation, 25(1), 93–116.
Reis, S. (2008). Analyzing land use/land cover changes using remote sensing and GIS in Rize, North-East Turkey. Sensors, 8(10), 6188–6202.
Roy, S. S., Mahmood, R., Niyogi, D., Lei, M., Foster, S. A., Hubbard, K. G., Douglas, E., & Pielke Sr., R. A. (2007). Impacts of the agricultural Green Revolution—induced land use changes on air temperatures in India. Journal of Geophysical Research, 112, D21108. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007JD008834.
Ruiz-Luna, A., & Berlanga-Robles, C. A. (2003). Land use, land cover changes and coastal lagoon surface reduction associated with urban growth in northwest Mexico. Landscape Ecology, 18(2), 159–171.
Samant, H., & Subramanyan, V. (1998). Landuse/land cover change in Mumbai-Navi Mumbai cities and its effects on the drainage basins and channels—a study using GIS. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 26(1–2), 1–6.
Sarma, V. V. L. N., Krishna, G. M., Malini, B. H., & Rao, K. N. (2001). Landuse/landcover change detection through remote sensing and its climatic implications in the Godavari Delta Region. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 29, 85–91.
Scanlon, B. R., Reedy, R. C., Tonestrom, D. A. S., Prudic, D. E., & Dennehy, K. F. (2005). Impact of land use and land cover change on groundwater recharge and quality in the southwestern US. Global Change Biology, 11, 1577–1593.
Sharma, A., Bendangjungla, & Sharma, R. (2018). Factors influencing entrepreneurial behavior of fishery growers in Dimapur district of Nagaland. Agricultural Science Digest-A Research Journal, 38(2), 118–122.
Sundersingh, S. D. (1990). Effect of heat islands over urban Madras and measures for its mitigation. Energy and Buildings, 15(1–2), 245–252.
The World Bank (2018). World Urbanization Prospects: 2018 Revision, United Nations Population Division. Urban Population (% of Total Population)-India. https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.URB.TOTL.IN.ZS?locations=IN. (last accessed on 26-02-2020).
Turner II, B. L., & Meyer, B. L. (1994). Global land use and land cover change: an overview. In W. B. Meyer & B. L. Turner II (Eds.), Changes in land use and land cover: a global perspective. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Walker, R., & Homma, A. K. O. (1996). Land use land cover dynamics in the Brazilian Amazon: an overview. Ecological Economics, 18, 67–80.
Weng, Q. (2001). A remote sensing-GIS evaluation of urban expansion and its impact on surface temperature in the Zhujiang Delta, China. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 22(10), 1999–2014.
Wu, S., Mickley, L. J., Kaplan, J. O., & Jacob, D. J. (2012). Impacts of changes in land use and land cover on atmospheric chemistry and air quality over the 21st century. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 12(3), 1597–1609.
Xiuwan, C. (2002). Using remote sensing and GIS to analyse land cover change and its impacts on regional sustainable development. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 23(1), 107–124.
Yin, J., He, F., Xiong, Y. J., & Qiu, G. Y. (2017). Effects of land use/land cover and climate changes on surface runoff in a semi-humid and semi-arid transition zone in northwest China. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 21(1), 183–196.
Yirsaw, E., Wu, W., Temesgen, H., & Bekele, B. (2016). Effect of temporal land use/land cover changes on ecosystem services value in coastal area of China: the case of Su-Xi-Chang region. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 14(3), 409–422.
Yuan, F., Sawaya, K. E., Loeffelholz, B. C., & Bauer, M. E. (2005). Land cover classification and change analysis of the Twin Cities (Minnesota) Metropolitan Area by multitemporal Landsat remote sensing. Remote Sensing of Environment, 98(2–3), 317–328.
Zhao, D., & Wu, J. (2017). The impact of land use and land cover changes on East Asian summer monsoon precipitation using the WRF-mosaic approach. Atmospheric Science Letters, 18(12), 450–457.
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. A. K. Das, Tezpur University for providing lab facilities and support. We also thank USGS for the LANDSAT dataset utilized in the study.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 28 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ritse, V., Basumatary, H., Kulnu, A.S. et al. Monitoring land use land cover changes in the Eastern Himalayan landscape of Nagaland, Northeast India. Environ Monit Assess 192, 711 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08674-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08674-8