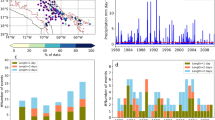
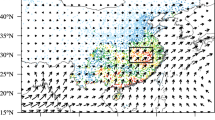
Abstract
Northern Chile is a region characterised by an extremely dry climate; however, there is a brief rainy season from December to March (austral summer), mainly above 3000 m a.s.l. It is interesting to consider where the humid air masses that generate such rain come from. For this purpose, daily precipitation data from 161 meteorological stations located in this area (18° S–19° S) were considered, and four clusters formed by k-means clustering. For each cluster, days of extreme precipitation (above 90th percentile) were selected to obtain flow strength (F), direction (D), and vorticity (Z) for each event according to the Jenkinson and Collison (JC) method. The back trajectory, for the previous 72 h, of air masses affecting the centroid of each cluster was determined by means of the Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory (HYSPLIT) model. The analyses were carried out at sea level (1013 hPa) and in the middle (500 hPa) and upper (250 hPa) troposphere. Surface circulation was not a determining factor in the occurrence of extreme events, but it did influence circulation at 500 and 250 hPa. For stations located in the northern Altiplano, moisture advection from the Amazon basin is evident due to the configuration of the Bolivian high—an upper level anticyclone that develops over the Bolivian Altiplano during austral summer. For stations located in the southern part of the study area, the main source of moisture is the Pacific Ocean, and the weather is related to the arrival of frontal systems and to the configuration of cut-off low pressure systems in the mid-troposphere.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexandersson H (1986) A homogeneity test applied to precipitation data. Int J Climatol 6:661–675. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.3370060607
Baez-Villanueva OM, Zambrano-Bigiarini M, Ribbe L, Nauditt A, Giraldo-Osorio JD, Thinh NX (2018) Temporal and spatial evaluation of satellite rainfall estimates over different regions in Latin-America. Atmos Res 213:34–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2018.05.011
Baltazar Fernández A, Meseguer-Ruiz O (2019) Regionalization of the Concentration Index in northern Chile and its relation with the orographic component (1966-2015). Investig Geogr 57:32–48. https://doi.org/10.5354/0719-5370.2019.53440
Barlow M, Gutowski WJ Jr, Gyakum JR, Katz RW, Lim YK, Schumacher RS, Wehner MF, Agel L, Bosilovich M, Collow A, Gershunov A, Grotjahn R, Leung R, Milrad S, Min SK (2019) North American extreme precipitation events and related large-scale meteorological patterns: a review of statistical methods, dynamics, modeling, and trends. Clim Dyn 53:6835–6875. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-019-04958-z
Bombi P (2018) Potential impacts of climate change on Welwitschia mirabilis populations in the Namib Desert, southern Africa. J Arid Land 10:663–672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40333-018-0067-1
Bracken C, Rajagopalan B, Alexander M, Gangopadhyay S (2015) Spatial variability of seasonal extreme precipitation in the western United States. J Geophys Res Atmos 120:4522–4533. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JD023205
Casado MJ, Pastor MA (2016) Circulation types and winter precipitation in Spain. Int J Climatol 36:2727–2742. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.3860
Castino F, Bookhagen B, Strecker MR (2017) Rainfall variability and trends of the past six decades (1950–2014) in the subtropical NW Argentine Andes. Clim Dyn 48:1049–1067. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-016-3127-2
Chen Y, Zhai P (2016) Mechanisms for concurrent low-latitude circulation anomalies responsible for persistent extreme precipitation in the Yangtze River Valley. Clim Dyn 47:989–1006. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2885-6
Chilean Government (2015) Plan de Adaptación al Cambio Climático. Departamento de Cambio Climático del Ministerio del Medio Ambiente, Santiago
De Vries AJ, Ouwersloot HG, Feldstein SB, Riemer M, El Kenawy AM, McCabe MF, Lelieveld J (2018) Identification of Tropical-Extratropical Interactions and Extreme Precipitation Events in the Middle East Based On Potential Vorticity and Moisture Transport. J Geophys Res Atmos 123:861–881. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JD027587
Donat M, Lowry A, Alexander L, O’Gorman P, Maher N (2016) More extreme precipitation in the world’s dry and wet regions. Nat Clim Change 6:508–513. https://doi.org/10.1038/NCLIMATE2941
Draxler RR, Hess GD (1998) An overview of the HYSPLIT_4 modeling system for trajectories, dispersion, and deposition. Aust Meteor Mag 47:295-308. Geophys Res Atmos 123:861–881. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JD027587
Falvey M, Garreaud R (2005) Moisture variability over the South American Altiplano during the South American low level jet experiment (SALLJEX) observing season. J Geophys Res 110:D22105. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JD00615
Fealey R, Mills G (2018) Deriving Lamb weather types suited to regional climate studies: a case study on the synoptic origins of precipitation over Ireland. Int J Climatol 38:3439–3448. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.5495
Fleming ZL, Monks PS, Manning AJ (2012) Review: untangling the influence of air-mass history in interpreting observed atmospheric composition. Atmos Res 104–105:1–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2011.09.009
Garreaud RD (2009) The Andes climate and weather. Adv Geosci 22:3–11. https://doi.org/10.5194/adgeo-22-3-2009
Garreaud R, Aceituno P (2001) Interannual rainfall variability over the South American Altiplano. J Clim 14:2779–2789. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2001)014%3c2779:IRVOTS%3e2.0.CO;2
Green B, Marshall J, Campin JM (2019) The ‘sticky’ ITCZ: ocean-moderated ITCZ shifts. Clim Dyn 53:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-019-04623-5
Grimm AM (2019) Madden–Julian Oscillation impacts on South American summer monsoon season: precipitation anomalies, extreme events, teleconnections, and role in the MJO cycle. Clim Dyn 53:907–932. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-019-04622-6
Guijarro JA (2016) Package “climatol” Climate Tools (Series Homogenization and Derived Products). https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=climatol. Accessed 8 June 2017
Gustafsson M, Rayner D, Chen D (2010) Extreme rainfall events in southern Sweden: where does the moisture come from? Tellus A 62(5):605–616. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0870.2010.00456.x
Houston J, Hartley AJ (2003) The central Andean west-slope rainshadow and its potential contribution to the origin of hyper-aridity in the Atacama Desert. Int J Climatol 23:1453–1464. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.938
Insel N, Poulsen CJ, Ehlers TA (2010) Influence of the Andes Mountains on South American moisture transport, convection, and precipitation. Clim Dyn 35:1477–1492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-009-0637-1
Jenkinson AF, Collison P (1977) An initial climatology of gales over the North Sea. Synoptic Climatology Branch Memorandum no 62, Bracknell. Meteorological Office, London
Jones C, Carvalho LMV (2013) Climate change in the South American Monsoon System: present climate and CMIP5 projections. J Climate 26:6660–6678. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00412.1
Junquas C, Li L, Vera CS, Le Treut H, Takahashi K (2016) Influence of South America orography on summertime precipitation in Southeastern South America. Clim Dyn 46:3941–3963. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2814-8
Junquas C, Takahashi K, Condom T, Espinoza JC, Chavez S, Sicart JE, Lebel T (2018) Understanding the influence of orography on the precipitation diurnal cycle and the associated atmospheric processes in the central Andes. Clim Dyn 50:3995–4017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-3858-8
Kalnay E, Kanamitsu M, Kistler R, Collins W, Deaven D, Gandin L, Iredell M, Saha S, White G, Woollen J, Zhu Y, Chelliah M, Ebisuzaki W, Higgins W, Janowiak J, Mo KC, Ropelewski C, Wang J, Leetmaa A, Reynolds R, Jenne R, Joseph D (1996) The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull Am Meteor Soc 77:437–470. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477(1996)077%3C0437:TNYRP%3E2.0.CO;2
Khansalari S, Mohebalhojeh AR, Ahmadi-Givi F, Sprenger M (2020) On the determining factors in cases of moderate to heavy precipitation in Tehran. Theor Appl Climatol 140:1107–1123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-020-03133-3
Kirtman B, Power SB, Adedoyin JA, Boer GJ, Bojariu R, Camilloni I, Doblas-Reyes FJ, Fiore AM, Kimoto M, Meehl GA, Prather M, Sarr A, Schär C, Sutton R, van Oldenborgh GJ, Vecchi G, Wang HJ (2013) Near-term climate change: projections and predictability. In: Stocker TF, Qin D, Plattner GK, Tignor M, Allen SK, Boschung J, Nauels A, Xia Y, Bex V, Midgley PM (eds) Climate change 2013: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 953–1028
Kock ST, Schittek K, Mächtle B, Maldonado A, Vos H, Lupo LC, Kulemeter JJ, Wissel H, Schäbitz F, Lücke A (2020) Multi-centennial-scale variations of South American summer monsoon intensity in the southern central Andes (24-27°S) during the late Holocene. Geophys Res Lett 47:e2019GL084157. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019GL084157
Li L, Zhang R, Wen M, Duan J, Qi Y (2019) Characteristics of the Tibetan Plateau vortices and the related large-scale circulations causing different precipitation intensity. Theor Appl Climatol 138:849–860. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-019-02870-4
Maloney ED, Adames AF, Bui HX (2019) Madden–Julian oscillation changes under anthropogenic warming. Nat Clim Change 9:26–33. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-018-0331-6
Marengo JA, Liebmann B, Grimm AM, Misra V, Silva Dias PL, Cavalcanti IFA, Carvalho LMV, Berbery EH, Ambrizzi T, Vera CS, Saulo AC, Nogues-Paegle J, Zipser E, Seth A, Alves LM (2012) Recent developments on the South American monsoon system. Int J Climatol 32:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.2254
Marjani S, Alizadeh Choobari O, Irannejad P (2019) Frequency of extreme El Niño and La Niña events under global warming. Clim Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-019-04902-1
Meseguer-Ruiz O, Ponce-Philimon PI, Guijarro JA, Sarricolea P (2019a) Spatial distribution and trends of different precipitation variability indices based on daily data in Northern Chile between 1966 and 2015. Int J Climatol 39:4595–4610. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.6089
Meseguer-Ruiz O, Osborn TJ, Sarricolea P, Jones PD, Olcina J, Serrano-Notivoli R, Martín-Vide J (2019b) Definition of a temporal distribution index for high temporal resolution precipitation data over Peninsular Spain and the Balearic Islands: the fractal dimension; and its synoptic implications. Clim Dyn 52:439–456. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-018-4159-6
Meseguer-Ruiz O, Cortesi N, Guijarro JA, Sarricolea P (2020) Weather regimes linked to daily precipitation anomalies in Northern Chile. Atmos Res 236:104802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2019.104802
Miró JR, Pepin N, Peña JC, Martin-Vide J (2020) Daily atmospheric circulation patterns for Catalonia (northeast Iberian Peninsula) using a modified version of Jenkinson and Collison method. Atmos Res 231:104674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2019.104674
Otero N, Sillmann J, Butler T (2018) Assessment of an extended version of the Jenkinson–Collison classification on CMIP5 models over Europe. Clim Dyn 50:1559–1579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-3705-y
Pliscoff P, Luebert F, Hilger HH, Guisan A (2014) Effects of alternative sets of climatic predictors on species distribution models and associated estimates of extinction risk: a test with plants in an arid environment. Ecol Model 288:166–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2014.06.003
Power SB, Delage F, Colman R, Moise A (2012) Consensus on 21st century rainfall projections in climate models more widespread than previously thought. J Clim 25:3792–3809. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00354.1
Putniković S, Tošić I (2018) Relationship between atmospheric circulation weather types and seasonal precipitation in Serbia. Meteorol Atmos Phys 130:393–403. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-017-0524-y
Putniković S, Tošić I, Durdević V (2016) Circulation weather types and their influence on precipitation in Serbia. Meteorol Atmos Phys 128:649–662. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-016-0432-6
Rohde RF, Hoffman MT, Durbach I, Venter Z, Jack S (2019) Vegetation and climate change in the Pro-Namib and Namib Desert based on repeat photography: insights into climate trends. J Arid Environ 165:119–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2019.01.007
Sarricolea P, Romero H (2015) Variabilidad y cambios climáticos observados y esperados en el Altiplano del norte de Chile. Rev Geogr Norte Gd 62:169–183. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-34022015000300010
Sarricolea P, Herrera-Ossandon MJ, Meseguer-Ruiz O (2017a) Climatic regionalisation of continental Chile. J Maps 13(2):66–73. https://doi.org/10.1080/17445647.2016.1259592
Sarricolea P, Meseguer-Ruiz O, Romero Aravena H (2017b) Tendencias de la precipitación en el Norte Grande de Chile y su relación con las proyecciones de cambio climático. Diálogo Andino, Revista de Historia, Geografía y Cultura Andina 54:41–50. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0719-26812017000300041
Schneider T, Bischoff T, Haug GH (2014) Migrations and dynamics of the intertropical convergence zone. Nature 513:45–53. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13636
Segura H, Espinoza JC, Junquas C, Takahashi K (2016) Evidencing decadal and interdecadal hydroclimatic variability over the Central Andes. Environ Res Lett 11:094016. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/11/9/094016
Segura H, Junquas C, Espinoza JC, Vuille M, Jauregui YR, Rabatel A, Condom T, Lebel T (2019) New insights into the rainfall variability in the tropical Andes on seasonal and interannual time scales. Clim Dyn 53:405–426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-018-4590-8
Segura H, Espinoza JC, Junquas C, Lebel T, Vuille M, Garreaud R (2020) Recent changes in the precipitation-driving processes over the southern tropical Andes/western Amazon. Clim Dyn 54:2613–2631. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-020-05132-6
Shukla PR, Skea J, Slade R, van Diemen R, Haughey E, Malley J, Pathak M, Portugal Pereira J. (2019) Technical Summary. In Shukla PR, Skea J, Calvo Buendia E, Masson-Delmotte V, Pörtner HO, Roberts DC, Zhai P, Slade R, Connors S, van Diemen R, Ferrat M, Haughey E, Luz S, Neogi S, Pathak M, Petzold J, Portugal Pereira J, Vyas P, Huntley E, Kissick K, Belkacemi M, Malley J (eds) Climate change and land: an IPCC special report on climate change, desertification, land degradation, sustainable land management, food security, and greenhouse gas uxes in terrestrial ecosystems. (in press)
Stein AF, Draxler RR, Rolph GD, Stunder BJB, Cohen MD (2015) NOAA’s HYSPLIT Atmospheric Transport and Dispersion Modeling System. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 96:2059–2077. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-14-00110.1
Tan X, Gan TY, Chen YD (2018) Moisture sources and pathways associated with the spatial variability of seasonal extreme precipitation over Canada. Clim Dyn 50:629–640. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-3630-0
Valdés-Pineda R, Valdés JB, Diaz HF, Pizarro-Tapia R (2015) Analysis of spatio-temporal changes in annual and seasonal precipitation variability in South America-Chile and related ocean-atmosphere circulation patterns. Int J Climatol 36:2979–3001. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4532
Valdés-Pineda R, Cañón J, Valdés JB (2018) Multi-decadal 40-to 60-year cycles of precipitation variability in Chile (South America) and their relationship to the AMO and PDO signals. J Hydrol 556:1153–1170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.01.031
Vasconcellos FC, Deng Y, Zhang H, Martins G (2020) Austral summer precipitation biases over tropical South America in five CMIP5 earth system models. Int J Climatol. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.6595
Vincent LA, Zhang X, Bonsal BR, Hogg WD (2002) Homogenization of daily temperatures over Canada. J Clim 15:1322–1334. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2002)015%3c1322:HODTOC%3e2.0.CO;2
Williams CJR (2017) Climate change in Chile: an analysis of state-of-the-art observations, satellite-derived estimates and climate model simulations. J Earth Sci Clim Change 8:5. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7617.1000400
Zappalà DA, Barreiro M, Masoller C (2018) Quantifying changes in spatial patterns of surface air temperature dynamics over several decades. Earth Syst Dyn 9:383–391. https://doi.org/10.5194/esd-9-383-2018
Acknowledgements
The authors want to thank the FONDECYT Project 11160059 of the Chilean Government, the Climatology Group (2017SGR1362, Catalan Government) and the CLICES Project (CGL2017-83866-C3-2-R) for the institutional support. R.S.N. is funded by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (grant no. FJCI-2017-31595).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meseguer-Ruiz, O., Ponce-Philimon, P.I., Baltazar, A. et al. Synoptic attributions of extreme precipitation in the Atacama Desert (Chile). Clim Dyn 55, 3431–3444 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-020-05455-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-020-05455-4